Integrins in T Cell Physiology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Integrins in Thymocyte Differentiation
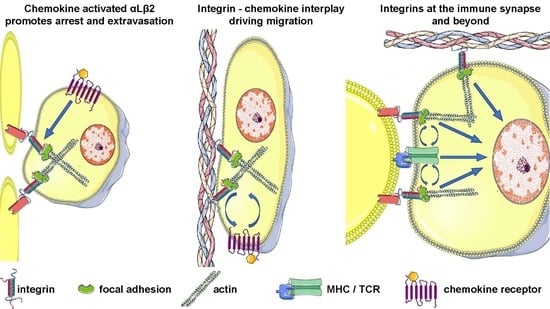
3. Integrins before Antigen Encounter: From Lymphocyte Migration to T Cell Homing
4. Role of Integrins as Costimulatory Molecules: At the Immune Synapse and Beyond
5. Matrix Adhesion as a Costimulation
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogg, N.; Patzak, I.; Willenbrock, F. The insider’s guide to leukocyte integrin signalling and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, M.E.; Berdnikovs, S.; Cook-Mills, J.M. Distinct sites within the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) cytoplasmic domain regulate VCAM-1 activation of calcium fluxes versus Rac1 during leukocyte transendothelial migration. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 8235–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.; Amos, C.L.; Walters, C.E.; Couraud, P.O.; Lyck, R.; Engelhardt, B.; Adamson, P. Intracellular domain of brain endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is essential for T lymphocyte-mediated signaling and migration. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J. Integrin ligands at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, T.; Kang, J. Immunological Genome Project and systems immunology. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Chen, X. Why integrin as a primary target for imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2011, 1, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailaie, S.; Robert, P.A.; Toker, A.; Huehn, J.; Meyer-Hermann, M. A signal integration model of thymic selection and natural regulatory T cell commitment. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5983–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, W.; Mendes-Da-Cruz, D.A.; Smaniotto, S.; Silva-Monteiro, E.; Villa-Verde, D.M. Molecular mechanisms governing thymocyte migration: Combined role of chemokines and extracellular matrix. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.I.; Duke-Cohan, J.S.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Rossy, J.; Tabarin, T.; Ju, L.; Gui, J.; Gaus, K.; Zhu, C.; et al. Dynamic control of β1 integrin adhesion by the plexinD1-sema3E axis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, M.; Nagamine, J.; Takeda, K.; Utsumi, K.; Kosugi, A.; Tatsumi, Y.; Hamaoka, T.; Miyake, K.; Nakajima, K.; Watanabe, T. Expression of VLA-4 on thymocytes. Maturation stage-associated transition and its correlation with their capacity to adhere to thymic stromal cells. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bose, T.O.; Colpitts, S.L.; Pham, Q.M.; Puddington, L.; Lefrançois, L. CD11a is essential for normal development of hematopoietic intermediates. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, K.; Sawada, M.; Narumiya, S.; Nagamine, J.; Sakata, T.; Iwagami, S.; Kita, Y.; Teraoka, H.; Hirano, H.; Ogata, M. Adhesion of immature thymocytes to thymic stromal cells through fibronectin molecules and its significance for the induction of thymocyte differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5685–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.R.; Crisa, L.; Mojcik, C.F.; Ishii, J.K.; Klier, G.; Shevach, E.M. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is expressed by cortical thymic epithelial cells and mediates thymocyte adhesion. Implications for the function of alpha4beta1 (VLA4) integrin in T-cell development. Blood 1997, 89, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linhares-Lacerda, L.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Nogueira, A.C.; Mendes-da-Cruz, D.A.; Magalhães, D.A.; Dardenne, M.; Passos, G.A.; Savino, W. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of CD49e (α5 integrin chain) in human thymic epithelial cells modulates the expression of multiple genes and decreases thymocyte adhesion. BMC Genom. 2010, 11 (Suppl. 5), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottrand, G.; Courau, T.; Thomas-Vaslin, V.; Prevel, N.; Vazquez, T.; Ruocco, M.G.; Lambrecht, B.; Bellier, B.; Colombo, B.M.; Klatzmann, D. Regulatory T-cell development and function are impaired in mice lacking membrane expression of full length intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Immunology 2015, 146, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paessens, L.C.; Singh, S.K.; Fernandes, R.J.; van Kooyk, Y. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) provide co-stimulation in positive selection along with survival of selected thymocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, E.; Kina, T.; Katsura, Y.; Tadakuma, T. Enhancement of activation-induced cell death by fibronectin in murine CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes. Immunology 1998, 95, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivinus-Nebot, M.; Ticchioni, M.; Mary, F.; Hofman, P.; Quaranta, V.; Rousselle, P.; Bernard, A. Laminin 5 in the human thymus: Control of T cell proliferation via alpha6beta4 integrins. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.G.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.K.; Lolkema, M.; Yim, J.; Hong, S.H.; Schwartz, R.H. Epithelial cell-specific laminin 5 is required for survival of early thymocytes. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prockop, S.E.; Palencia, S.; Ryan, C.M.; Gordon, K.; Gray, D.; Petrie, H.T. Stromal cells provide the matrix for migration of early lymphoid progenitors through the thymic cortex. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4354–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Katagiri, K.; Tomiyama, T.; Yasuda, K.; Habiro, K.; Katakai, T.; Ikehara, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Kinashi, T. Mst1 regulates integrin-dependent thymocyte trafficking and antigen recognition in the thymus. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, M.A.; Sánchez-Mateos, P.; Nieto, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Chemokines regulate cellular polarization and adhesion receptor redistribution during lymphocyte interaction with endothelium and extracellular matrix. Involvement of cAMP signaling pathway. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, M.A.; Cabañas, C.; Montoya, M.C.; Ager, A.; Sánchez-Mateos, P.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. ICAMs redistributed by chemokines to cellular uropods as a mechanism for recruitment of T lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 137, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlino, G.; Barreiro, O.; Baixauli, F.; Robles-Valero, J.; González-Granado, J.M.; Villa-Bellosta, R.; Cuenca, J.; Sánchez-Sorzano, C.O.; Veiga, E.; Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; et al. Miro-1 links mitochondria and microtubule Dynein motors to control lymphocyte migration and polarity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, Z.; Shinder, V.; Klein, E.; Grabovsky, V.; Yeger, O.; Geron, E.; Montresor, A.; Bolomini-Vittori, M.; Feigelson, S.W.; Kirchhausen, T.; et al. Lymphocyte crawling and transendothelial migration require chemokine triggering of high-affinity LFA-1 integrin. Immunity 2009, 30, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordenfelt, P.; Elliott, H.L.; Springer, T.A. Coordinated integrin activation by actin-dependent force during T-cell migration. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoudjit, F.; Potworowski, E.F.; St-Pierre, Y. Bi-directional induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 during T lymphoma/endothelial cell contact: Implication of ICAM-1. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Peixoto, A.; Imai, Y.; Goodarzi, A.; Cheng, G.; Carman, C.V.; von Andrian, U.H.; Shimaoka, M. Distinct roles for LFA-1 affinity regulation during T-cell adhesion, diapedesis, and interstitial migration in lymph nodes. Blood 2010, 115, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, P.; Smith, A.; McDowall, A.; Nicol, A.; Zicha, D.; Hogg, N. Intermediate-affinity LFA-1 binds alpha-actinin-1 to control migration at the leading edge of the T cell. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Carrasco, Y.R.; Stanley, P.; Kieffer, N.; Batista, F.D.; Hogg, N. A talin-dependent LFA-1 focal zone is formed by rapidly migrating T lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Stanley, P.; Willenbrock, F.; Hogg, N. The Gαq/11 proteins contribute to T lymphocyte migration by promoting turnover of integrin LFA-1 through recycling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, P.; Tooze, S.; Hogg, N. A role for Rap2 in recycling the extended conformation of LFA-1 during T cell migration. Biol. Open 2012, 1, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Rodríguez, C.; Nueda, A.; Grospierre, B.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Fischer, A.; Springer, T.A.; Corbí, A.L. Characterization of two new CD18 alleles causing severe leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, T.A.; Thompson, W.S.; Miller, L.J.; Schmalstieg, F.C.; Anderson, D.C. Inherited deficiency of the Mac-1, LFA-1, p150,95 glycoprotein family and its molecular basis. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 1901–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Howarth, K.; McDowall, A.; Patzak, I.; Evans, R.; Ussar, S.; Moser, M.; Metin, A.; Fried, M.; Tomlinson, I.; et al. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-III is caused by mutations in KINDLIN3 affecting integrin activation. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kooyk, Y.; van de Wiel-van Kemenade, E.; Weder, P.; Huijbens, R.J.; Figdor, C.G. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 dominates very late antigen 4 in binding of activated T cells to endothelium. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issekutz, A.C.; Issekutz, T.B. The role of E-selectin, P-selectin, and very late activation antigen-4 in T lymphocyte migration to dermal inflammation. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Costa, A.; Isern de Val, S.; Sevilla-Movilla, S.; Borgman, K.J.; Manzo, C.; Teixidó, J.; Garcia-Parajo, M.F. Lateral Mobility and Nanoscale Spatial Arrangement of Chemokine-activated α4β1 Integrins on T Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21053–21062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.M.; Chung, H.L.; McGrath, J.L.; Waugh, R.E.; Kim, M. Activated integrin VLA-4 localizes to the lamellipodia and mediates T cell migration on VCAM-1. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakubenko, V.P.; Lobb, R.R.; Plow, E.F.; Ugarova, T.P. Differential induction of gelatinase B (MMP-9) and gelatinase A (MMP-2) in T lymphocytes upon alpha(4)beta(1)-mediated adhesion to VCAM-1 and the CS-1 peptide of fibronectin. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 260, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarra, M.; Vilardell, C.; Matsumoto, K.; Esparza, J.; Lozano, E.; Serra-Pages, C.; Urbano-Márquez, A.; Yamada, K.M.; Cid, M.C. Dual function of focal adhesion kinase in regulating integrin-induced MMP-2 and MMP-9 release by human T lymphoid cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1875–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.J.; Butcher, E.C. Rapid acquisition of tissue-specific homing phenotypes by CD4(+) T cells activated in cutaneous or mucosal lymphoid tissues. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, A.R.; Engelhard, V.H. CD8 T cells activated in distinct lymphoid organs differentially express adhesion proteins and coexpress multiple chemokine receptors. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4079–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewert, C.; Menning, A.; Dudda, J.; Siegmund, K.; Lauer, U.; Floess, S.; Campbell, D.J.; Hamann, A.; Huehn, J. Induction of organ-selective CD4+ regulatory T cell homing. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, T.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. P-, E-, and L-selectin mediate migration of activated CD8+ T lymphocytes into inflamed skin. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4307–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, W.; Allemand, Y.; Borges, E.; von Laer, D.; Hallmann, R.; Vestweber, D.; Hamann, A. CD4+ T cells migrate into inflamed skin only if they express ligands for E- and P-selectin. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woyciechowski, S.; Hofmann, M.; Pircher, H. α4 β1 integrin promotes accumulation of tissue-resident memory CD8(+) T cells in salivary glands. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koni, P.A.; Joshi, S.K.; Temann, U.A.; Olson, D.; Burkly, L.; Flavell, R.A. Conditional vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 deletion in mice: Impaired lymphocyte migration to bone marrow. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briskin, M.; Winsor-Hines, D.; Shyjan, A.; Cochran, N.; Bloom, S.; Wilson, J.; McEvoy, L.M.; Butcher, E.C.; Kassam, N.; Mackay, C.R.; et al. Human mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 is preferentially expressed in intestinal tract and associated lymphoid tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin-Blondel, G.; Pignolet, B.; Tietz, S.; Yshii, L.; Gebauer, C.; Perinat, T.; Van Weddingen, I.; Blatti, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Liblau, R. Migration of encephalitogenic CD8 T cells into the central nervous system is dependent on the α4β1-integrin. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 3302–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolber, F.M.; Curtis, J.L.; Mály, P.; Kelly, R.J.; Smith, P.; Yednock, T.A.; Lowe, J.B.; Stoolman, L.M. Endothelial selectins and alpha4 integrins regulate independent pathways of T lymphocyte recruitment in the pulmonary immune response. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4396–4403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Brakebusch, C.; Coisne, C.; Sixt, M.; Wekerle, H.; Engelhardt, B.; Fässler, R. Beta1 integrins differentially control extravasation of inflammatory cell subsets into the CNS during autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, J.R.; Bono, M.R.; Manjunath, N.; Weninger, W.; Cavanagh, L.L.; Rosemblatt, M.; Von Andrian, U.H. Selective imprinting of gut-homing T cells by Peyer’s patch dendritic cells. Nature 2003, 424, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, A.; Liaskou, E.; Eksteen, B.; Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. CCL25 and CCL28 promote alpha4 beta7-integrin-dependent adhesion of lymphocytes to MAdCAM-1 under shear flow. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G1257–G1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepek, K.L.; Shaw, S.K.; Parker, C.M.; Russell, G.J.; Morrow, J.S.; Rimm, D.L.; Brenner, M.B. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature 1994, 372, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Bevan, M.J. Transforming growth factor-β signaling controls the formation and maintenance of gut-resident memory T cells by regulating migration and retention. Immunity 2013, 39, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminara, N.M.; Gelfand, J.M. Assessing long-term drug safety: Lessons (re) learned from raptiva. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2010, 29, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerer, J.M.; Horne, P.H.; Fiessinger, L.A.; Fisher, M.G.; Jayashankar, K.; Garcia, S.F.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; van Rooijen, N.; Bumgardner, G.L. Inhibition of recall responses through complementary therapies targeting CD8+ T-cell- and alloantibody-dependent allocytotoxicity in sensitized transplant recipients. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredget, E.B.; Arefanian, H.; Gill, R.G.; Rajotte, R.V.; Rayat, G.R. Monotherapy with anti-LFA-1 monoclonal antibody promotes long-term survival of rat islet xenografts. Cell Transplant. 2008, 17, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R. Rovelizumab (ICOS Corp). IDrugs 2000, 3, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qualls, J.E.; Murray, P.J. A double agent in cancer: Stopping macrophages wounds tumors. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viglietta, V.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Weiner, H.L.; Hafler, D.A. Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elices, M.J.; Osborn, L.; Takada, Y.; Crouse, C.; Luhowskyj, S.; Hemler, M.E.; Lobb, R.R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell 1990, 60, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makker, J.; Hommes, D.W. Etrolizumab for ulcerative colitis: The new kid on the block? Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léger, O.J.; Yednock, T.A.; Tanner, L.; Horner, H.C.; Hines, D.K.; Keen, S.; Saldanha, J.; Jones, S.T.; Fritz, L.C.; Bendig, M.M. Humanization of a mouse antibody against human alpha-4 integrin: A potential therapeutic for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Hum. Antib. 1997, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, S.J.; Karlik, S.J.; Cannon, C.; Hines, D.K.; Yednock, T.A.; Fritz, L.C.; Horner, H.C. A monoclonal antibody to alpha 4 integrin suppresses and reverses active experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1995, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.H.; Khan, O.A.; Sheremata, W.A.; Blumhardt, L.D.; Rice, G.P.; Libonati, M.A.; Willmer-Hulme, A.J.; Dalton, C.M.; Miszkiel, K.A.; O’Connor, P.W.; et al. A controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; O’Connor, P.W.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; Miller, D.H.; Phillips, J.T.; Lublin, F.D.; Giovannoni, G.; Wajgt, A.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer-Gould, A.; Atlas, S.W.; Green, A.J.; Bollen, A.W.; Pelletier, D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with natalizumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, M.L.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Shaw, A.S. Understanding the structure and function of the immunological synapse. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Molina, A.; Escribese, M.M.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Escudero, E.; Ursa, A.; Tejedor, R.; Mampaso, F.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. VLA-4 integrin concentrates at the peripheral supramolecular activation complex of the immune synapse and drives T helper 1 responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11058–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, M.L. The immunological synapse. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Wu, X.S.; Crites, T.; Hammer, J.A. Actin retrograde flow and actomyosin II arc contraction drive receptor cluster dynamics at the immunological synapse in Jurkat T cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaizuka, Y.; Douglass, A.D.; Varma, R.; Dustin, M.L.; Vale, R.D. Mechanisms for segregating T cell receptor and adhesion molecules during immunological synapse formation in Jurkat T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20296–20301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, S.; Hong, J.; Yi, J.; Li, D.; Beach, J.R.; Shao, L.; Meinhardt, J.; Madison, G.; Wu, X.; Betzig, E.; et al. Formin-generated actomyosin arcs propel T cell receptor microcluster movement at the immune synapse. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comrie, W.A.; Babich, A.; Burkhardt, J.K. F-actin flow drives affinity maturation and spatial organization of LFA-1 at the immunological synapse. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comrie, W.A.; Li, S.; Boyle, S.; Burkhardt, J.K. The dendritic cell cytoskeleton promotes T cell adhesion and activation by constraining ICAM-1 mobility. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto-Tane, A.; Sakuma, M.; Ike, H.; Yokosuka, T.; Kimura, Y.; Ohara, O.; Saito, T. Micro-adhesion rings surrounding TCR microclusters are essential for T cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, B.; Bushnell, T.; Miller, J. LFA-1-mediated T cell costimulation through increased localization of TCR/class II complexes to the central supramolecular activation cluster and exclusion of CD45 from the immunological synapse. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabdanov, E.; Gondarenko, S.; Kumari, S.; Liapis, A.; Dustin, M.L.; Sheetz, M.P.; Kam, L.C.; Iskratsch, T. Micropatterning of TCR and LFA-1 ligands reveals complementary effects on cytoskeleton mechanics in T cells. Integr. Biol. 2015, 7, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitakis, M.; Dogniaux, S.; Goudot, C.; Bufi, N.; Asnacios, S.; Maurin, M.; Randriamampita, C.; Asnacios, A.; Hivroz, C. Different TCR-induced T lymphocyte responses are potentiated by stiffness with variable sensitivity. eLife 2017, 6, e23190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husson, J.; Chemin, K.; Bohineust, A.; Hivroz, C.; Henry, N. Force generation upon T cell receptor engagement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholer, A.; Hugues, S.; Boissonnas, A.; Fetler, L.; Amigorena, S. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1-dependent stable interactions between T cells and dendritic cells determine CD8+ T cell memory. Immunity 2008, 28, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.F.; McKall-Faienza, K.; Schmits, R.; Bouchard, D.; Beach, J.; Speiser, D.E.; Mak, T.W.; Ohashi, P.S. Distinct roles for LFA-1 and CD28 during activation of naive T cells: Adhesion versus costimulation. Immunity 1997, 7, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, N.K.; Klussman, K.; Aruffo, A. Intercellular adhesion molecule-2, a second counter-receptor for CD11a/CD18 (leukocyte function-associated antigen-1), provides a costimulatory signal for T-cell receptor-initiated activation of human T cells. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beemiller, P.; Jacobelli, J.; Krummel, M.F. Integration of the movement of signaling microclusters with cellular motility in immunological synapses. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, T.N.; Soos, T.J.; Xenias, H.S.; Dubin-Thaler, B.; Hofman, J.M.; Waite, J.C.; Cameron, T.O.; Thomas, V.K.; Varma, R.; Wiggins, C.H.; et al. Opposing effects of PKCtheta and WASp on symmetry breaking and relocation of the immunological synapse. Cell 2007, 129, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capece, T.; Walling, B.L.; Lim, K.; Kim, K.D.; Bae, S.; Chung, H.L.; Topham, D.J.; Kim, M. A novel intracellular pool of LFA-1 is critical for asymmetric CD8(+) T cell activation and differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3817–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, M.L.; Springer, T.A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature 1989, 341, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolz, J.C.; Medeiros, R.B.; Mitchell, J.S.; Zhu, P.; Freedman, B.D.; Shimizu, Y.; Billadeau, D.D. WAVE2 regulates high-affinity integrin binding by recruiting vinculin and talin to the immunological synapse. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 5986–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Van Seventer, G.A.; Horgan, K.J.; Shaw, S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature 1990, 345, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Seventer, G.A.; Shimizu, Y.; Horgan, K.J.; Luce, G.E.; Webb, D.; Shaw, S. Remote T cell co-stimulation via LFA-1/ICAM-1 and CD2/LFA-3: Demonstration with immobilized ligand/mAb and implication in monocyte-mediated co-stimulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedwick, C.E.; Morgan, M.M.; Jusino, L.; Cannon, J.L.; Miller, J.; Burkhardt, J.K. TCR, LFA-1, and CD28 play unique and complementary roles in signaling T cell cytoskeletal reorganization. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Dai, H.; Yatim, K.M.; Abou-Daya, K.; Williams, A.L.; Oberbarnscheidt, M.H.; Camirand, G.; Rudd, C.E.; Lakkis, F.G. CD8+ Effector T Cell Migration to Pancreatic Islet Grafts Is Dependent on Cognate Antigen Presentation by Donor Graft Cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.M.; Londrigan, S.L.; Brady, J.L.; Carrington, E.M.; Marchingo, J.M.; Heinzel, S.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Graham, K.L.; Kay, T.W.; Zhan, Y.; et al. Cognate antigen engagement on parenchymal cells stimulates CD8(+) T cell proliferation in situ. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.T.; Deeths, M.J.; Li, W.; Mueller, D.L.; Mescher, M.F. Signaling pathways activated by leukocyte function-associated Ag-1-dependent costimulation. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5183–5189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanner, S.B.; Grosmaire, L.S.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Damle, N.K. Beta 2-integrin LFA-1 signaling through phospholipase C-gamma 1 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7099–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Seventer, G.A.; Bonvini, E.; Yamada, H.; Conti, A.; Stringfellow, S.; June, C.H.; Shaw, S. Costimulation of T cell receptor/CD3-mediated activation of resting human CD4+ T cells by leukocyte function-associated antigen-1 ligand intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 involves prolonged inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and sustained increase of intracellular Ca2+ levels. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 3872–3880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.T.; Deeths, M.J.; Mescher, M.F. LFA-1-mediated costimulation of CD8+ T cell proliferation requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6523–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, N.; Suresh, R.; Bal, V.; Rath, S.; George, A. Lack of ICAM-1 on APCs during T cell priming leads to poor generation of central memory cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, N.K.; Klussman, K.; Leytze, G.; Aruffo, A.; Linsley, P.S.; Ledbetter, J.A. Costimulation with integrin ligands intercellular adhesion molecule-1 or vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 augments activation-induced death of antigen-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kandula, S.; Abraham, C. LFA-1 on CD4+ T cells is required for optimal antigen-dependent activation in vivo. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeths, M.J.; Mescher, M.F. ICAM-1 and B7-1 provide similar but distinct costimulation for CD8+ T cells, while CD4+ T cells are poorly costimulated by ICAM-1. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Goldstein, J.S.; O’Boyle, K.; Whitman, M.C.; Brunswick, M.; Kozlowski, S. ICAM-1 co-stimulation has differential effects on the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shier, P.; Ngo, K.; Fung-Leung, W.P. Defective CD8+ T cell activation and cytolytic function in the absence of LFA-1 cannot be restored by increased TCR signaling. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 4826–4832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makgoba, M.W.; Sanders, M.E.; Ginther Luce, G.E.; Gugel, E.A.; Dustin, M.L.; Springer, T.A.; Shaw, S. Functional evidence that intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for LFA-1-dependent adhesion in T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, N.K.; Aruffo, A. Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 induces T-cell antigen receptor-dependent activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6403–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, A.L.; Pandiyan, P.; Zheng, L.; Krummey, S.M.; Lenardo, M.J. The power and the promise of restimulation-induced cell death in human immune diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, N.K.; Leytze, G.; Klussman, K.; Ledbetter, J.A. Activation with superantigens induces programmed death in antigen-primed CD4+ class II+ major histocompatibility complex T lymphocytes via a CD11a/CD18-dependent mechanism. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarovinsky, T.O.; Monick, M.M.; Hunninghake, G.W. Integrin receptors are crucial for the restimulation of activated T lymphocytes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoudjit, F.; Vuori, K. Engagement of the alpha2beta1 integrin inhibits Fas ligand expression and activation-induced cell death in T cells in a focal adhesion kinase-dependent manner. Blood 2000, 95, 2044–2051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stallmach, A.; Giese, T.; Pfister, K.; Wittig, B.M.; Künne, S.; Humphries, M.; Zeitz, M.; Meuer, S.C. Activation of beta(1) integrins mediates proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of intestinal CD4-positive lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggio, E.; Dianzani, C.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Soluri, M.F.; Clemente, N.; Cappellano, G.; Toth, E.; Raineri, D.; Ferrara, B.; Comi, C.; et al. Thrombin Cleavage of Osteopontin Modulates Its Activities in Human Cells In Vitro and Mouse Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis In Vivo. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 9345495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, W.H.; Hales, J.M.; Camp, R.D. Potent costimulation of effector T lymphocytes by human collagen type I. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 4935–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, N.H.; Torimoto, Y.; Schlossman, S.F.; Morimoto, C. Human CD4 helper T cell activation: Functional involvement of two distinct collagen receptors, 1F7 and VLA integrin family. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Yamada, A.; Kay, J.; Yamada, K.M.; Akiyama, S.K.; Schlossman, S.F.; Morimoto, C. Activation of CD4 cells by fibronectin and anti-CD3 antibody. A synergistic effect mediated by the VLA-5 fibronectin receptor complex. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, Y.; Humphries, M.J.; Mould, A.P.; Komoriya, A.; Yamada, K.M.; Schlossman, S.F.; Morimoto, C. VLA-4 mediates CD3-dependent CD4+ T cell activation via the CS1 alternatively spliced domain of fibronectin. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; van Seventer, G.A.; Horgan, K.J.; Shaw, S. Costimulation of proliferative responses of resting CD4+ T cells by the interaction of VLA-4 and VLA-5 with fibronectin or VLA-6 with laminin. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ybarrondo, B.; O’Rourke, A.M.; McCarthy, J.B.; Mescher, M.F. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte interaction with fibronectin and vitronectin: Activated adhesion and cosignalling. Immunology 1997, 91, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.; Bürger, A.; Radsak, M.; Blum, S.; Hug, F.; Hänsch, G.M. Fibronectin synthesis by activated T lymphocytes: Up-regulation of a surface-associated isoform with signalling function. Immunology 2000, 99, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.; Hug, F.; Hänsch, G.M.; Wagner, C. Fibronectin on activated T lymphocytes is bound to gangliosides and is present in detergent insoluble microdomains. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2005, 83, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B.; Ashkar, S.; Cantor, H.; Weber, G.F. Costimulation by extracellular matrix proteins determines the response to TCR ligation. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 210, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, S.; Kato, K.; Kudoh, S.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Tenascin suppresses CD3-mediated T cell activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 250, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, S.E.; Uzunel, M.; Talme, T.; Bergdahl, E.; Sundqvist, K.G. Antigen-induced regulation of T-cell motility, interaction with antigen-presenting cells and activation through endogenous thrombospondin-1 and its receptors. Immunology 2015, 144, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.W.; Kaur, S.; Ivins-O’Keefe, K.; Roberts, D.D. Thrombospondin-1 is a CD47-dependent endogenous inhibitor of hydrogen sulfide signaling in T cell activation. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Calzada, M.J.; Sipes, J.M.; Cashel, J.A.; Krutzsch, H.C.; Annis, D.S.; Mosher, D.F.; Roberts, D.D. Interactions of thrombospondins with alpha4beta1 integrin and CD47 differentially modulate T cell behavior. J. Cell. Biol. 2002, 157, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkar, S.; Weber, G.F.; Panoutsakopoulou, V.; Sanchirico, M.E.; Jansson, M.; Zawaideh, S.; Rittling, S.R.; Denhardt, D.T.; Glimcher, M.J.; Cantor, H. Eta-1 (osteopontin): An early component of type-1 (cell-mediated) immunity. Science 2000, 287, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siokis, A.; Robert, P.A.; Meyer-Hermann, M. Mathematical Modeling of Synaptic Patterns. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1584, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zaman, M.H. Modeling, signaling and cytoskeleton dynamics: Integrated modeling-experimental frameworks in cell migration. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| β Subunit | α Subunit | Alternative Names | Ligand/Counterreceptors | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagens | Laminin | Fibronectin | Vitronectin | Tenascin | Fibrinogen | VCAM-1 | MadCAM-1 | ICAM-s | E-cadherin | Thrombospondin | Osteopontin | vWf | Factor X | iC3b | LAP-TGF-β | MFG-E8, DEL-1, BSP | Fibrillin, PECAM-1 | |||
| β1 (ITGB1, CD29) | α1 (ITGA1, CD49a) | VLA-1 | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| α2 (ITGA2, CD49b) | VLA-2 | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| α3 (ITGA3, CD49c) | VLA-3 | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| α4 (ITGA4, CD49d) | VLA-4 | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||
| α5 (ITGA5, CD49e) | VLA-5 | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| α6 (ITGA6, CD49f) | VLA-6 | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| α7 (ITGA7, CD49g) | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| α8 (ITGA8, CD49h) | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| α9 (ITGA9) | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| α10 (ITGA10) | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| α11 (ITGA11) | x | |||||||||||||||||||
| αv (ITGAV, CD51) | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| β2 (ITGB2, CD18) | αD (ITGAD) | x | x | |||||||||||||||||
| αL (ITGAL, CD11a p180) | LFA-1 | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| αM (ITGAM, CD11b) | Mac-1 | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| αx (ITGAX, CD11c) | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| β3 (ITGB3, CD61) | αIIb (ITGA2B, CD41) | gpIIb/IIIa | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||
| αv (ITGAV, CD51) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| β4 (ITGB4) | α6 (ITGA6, CD49f) | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| αε (ITGAE, CD107) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| β5 (ITGB5) | αv (ITGAV, CD51) | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| β6 (ITGB6) | αv (ITGAV, CD51) | x | x | x | ||||||||||||||||
| β7 (ITGB7) | α4 (ITGA4, CD49d) | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||
| αε (ITGAE, CD103) | HML-1 | x | ||||||||||||||||||
| β8 (ITGB8) | αv (ITGAV, CD51) | x | ||||||||||||||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertoni, A.; Alabiso, O.; Galetto, A.S.; Baldanzi, G. Integrins in T Cell Physiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020485
Bertoni A, Alabiso O, Galetto AS, Baldanzi G. Integrins in T Cell Physiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020485
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertoni, Alessandra, Oscar Alabiso, Alessandra Silvia Galetto, and Gianluca Baldanzi. 2018. "Integrins in T Cell Physiology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020485
APA StyleBertoni, A., Alabiso, O., Galetto, A. S., & Baldanzi, G. (2018). Integrins in T Cell Physiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020485