Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer
Abstract
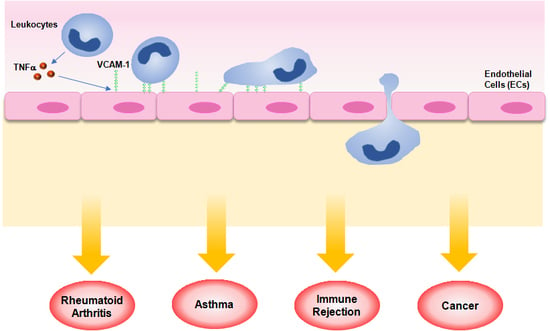
:1. Introduction
2. Role of VCAM-1 in Inflammation
3. Role of VCAM-1 in Immunological Disorders
3.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
3.2. Asthma
3.3. Transplant Rejection
4. Role of VCAM-1 in Cancer
4.1. VCAM-1 in Angiogenesis
4.2. VCAM-1 in Metastasis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatzantoni, K.; Mouzaki, A. Anti-TNF-α antibody therapies in autoimmune diseases. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Davis, M.; Faustman, D.L. The therapeutic potential of tumor necrosis factor for autoimmune disease: A mechanistically based hypothesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Harada, A.; Bluethmann, H.; Wang, J.B.; Nakao, S.; Mukaida, N.; Matsushima, K. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a physiologic regulator of hematopoietic progenitor cells: Increase of early hematopoietic progenitor cells in TNF receptor p55-deficient mice in vivo and potent inhibition of progenitor cell proliferation by TNFα in vitro. Blood 1995, 86, 2930–2937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carswell, E.A.; Old, L.J.; Kassel, R.L.; Green, S.; Fiore, N.; Williamson, B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, T.; Mitoma, H.; Harashima, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Shimoda, T. Transmembrane TNF-α: Structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Declercq, W.; Beyaert, R.; Fiers, W. Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: Structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 1995, 5, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.; Chun, H.J.; Zheng, L.; Siegel, R.M.; Bui, K.L.; Lenardo, M.J. A domain in TNF receptors that mediates ligand-independent receptor assembly and signaling. Science 2000, 288, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, D.W.; D’Arcy, A.; Janes, W.; Gentz, R.; Schoenfeld, H.J.; Broger, C.; Loetscher, H.; Lesslauer, W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNFβ complex: Implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell 1993, 73, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naude, P.J.; den Boer, J.A.; Luiten, P.G.; Eisel, U.L. Tumor necrosis factor receptor cross-talk. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider-Brachert, W.; Heigl, U.; Ehrenschwender, M. Membrane trafficking of death receptors: Implications on signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14475–14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajant, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, D.E. Potential role of TNF-α in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.M.; Combes, A.; Wagner, D.; Kadakomi, T.; Kubota, T.; Li, Y.Y.; McTiernan, C. The role of tumor necrosis factor in the pathophysiology of heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesten, L.S.; Zadelaar, A.S.; van Nieuwkoop, A.; Gijbels, M.J.; de Winther, M.P.; Havekes, L.M.; van Vlijmen, B.J. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes atherosclerotic lesion progression in APOE*3-Leiden transgenic mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 66, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Horssen, R.; Ten Hagen, T.L.; Eggermont, A.M. TNF-α in cancer treatment: Molecular insights, antitumor effects, and clinical utility. Oncologist 2006, 11, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, C.E.; Markowitz, N.P.; Saravolatz, L.D. The role of tumor necrosis factor in sepsis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 62, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.; Blaser, H.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S. Endothelial activation: Intracellular signaling pathways. Arthritis Res 2002, 4 (Suppl. S3), S109–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, G.E.; Bevilacqua, M.P. An inducible endothelial cell surface glycoprotein mediates melanoma adhesion. Science 1989, 246, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, L.; Hession, C.; Tizard, R.; Vassallo, C.; Luhowskyj, S.; Chi-Rosso, G.; Lobb, R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell 1989, 59, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook-Mills, J.M.; Marchese, M.E.; Abdala-Valencia, H. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: Regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1607–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Khaket, T.P.; Dutta, C.; Chakraborty, B.; Mukherjee, T.K. Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oosten, M.; van de Bilt, E.; de Vries, H.E.; van Berkel, T.J.; Kuiper, J. Vascular adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on rat liver cells after lipopolysaccharide administration in vivo. Hepatology 1995, 22, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, M.; Bendas, G. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)—An increasing insight into its role in tumorigenicity and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.N.; Bahaie, N.S.; Kang, B.N.; Hosseinkhani, M.R.; Ha, S.G.; Frenzel, E.M.; Liu, F.T.; Rao, S.P.; Sriramarao, P. Allergen-induced airway remodeling is impaired in galectin-3-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, R.; Kassner, P.D.; Carr, M.W.; Finger, E.B.; Hemler, M.E.; Springer, T.A. The integrin VLA-4 supports tethering and rolling in flow on VCAM-1. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 128, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, C.; Ridley, A.J. Endothelial cell-cell adhesion and signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, M.E.; Berdnikovs, S.; Cook-Mills, J.M. Distinct sites within the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) cytoplasmic domain regulate VCAM-1 activation of calcium fluxes versus Rac1 during leukocyte transendothelial migration. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 8235–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deem, T.L.; Cook-Mills, J.M. Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) activation of endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinases: Role of reactive oxygen species. Blood 2004, 104, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittchen, E.S. Endothelial signaling in paracellular and transcellular leukocyte transmigration. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2522–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deem, T.L.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; Cook-Mills, J.M. VCAM-1 activation of endothelial cell protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3865–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, H.F.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitroulis, I.; Alexaki, V.I.; Kourtzelis, I.; Ziogas, A.; Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte integrins: Role in leukocyte recruitment and as therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, A.S.; Munro, J.M.; Rice, G.E.; Bevilacqua, M.P.; Morimoto, C.; McIntyre, B.W.; Rhynhart, K.; Pober, J.S.; Nadler, L.M. Adhesion of human B cells to germinal centers in vitro involves VLA-4 and INCAM-110. Science 1990, 249, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.K.; Florey, O.; Weber, M.; Pillai, R.G.; Chan, C.; Tan, P.H.; Lechler, R.I.; McClure, M.O.; Haskard, D.O.; George, A.J. Knockdown of mouse VCAM-1 by vector-based siRNA. Transpl. Immunol. 2006, 16, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.; Salas, A.; Sans, M.; Gironella, M.; Elena, M.; Anderson, D.C.; Pique, J.M.; Panes, J. VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1 or MAdCAM-1, immunoblockade ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abonia, J.P.; Hallgren, J.; Jones, T.; Shi, T.; Xu, Y.; Koni, P.; Flavell, R.A.; Boyce, J.A.; Austen, K.F.; Gurish, M.F. α-4 integrins and VCAM-1, but not MAdCAM-1, are essential for recruitment of mast cell progenitors to the inflamed lung. Blood 2006, 108, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Hong, C.S.; Moon, K.D.; Park, J.W. A novel human anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody ameliorates airway inflammation and remodelling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, L.; Vassallo, C.; Benjamin, C.D. Activated endothelium binds lymphocytes through a novel binding site in the alternately spliced domain of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonderheide, R.H.; Tedder, T.F.; Springer, T.A.; Staunton, D.E. Residues within a conserved amino acid motif of domains 1 and 4 of VCAM-1 are required for binding to VLA-4. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, I.H.; Yoon, A.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Park, C.G.; Chung, J. An antibody to the sixth Ig-like domain of VCAM-1 inhibits leukocyte transendothelial migration without affecting adhesion. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4592–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Hoshi, D.; Kiire, A.; Yamanaka, H.; Kamatani, N. Molecular targets of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, N.; Takayanagi, H. Autoimmune arthritis: The interface between the immune system and joints. Adv. Immunol. 2012, 115, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.O.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9784–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, M.; Martinez-Munoz, L.; Cascio, G.; Lucas, P.; Pablos, J.L.; Rodriguez-Frade, J.M. T Cell Migration in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baert, F.J.; D’Haens, G.R.; Peeters, M.; Hiele, M.I.; Schaible, T.F.; Shealy, D.; Geboes, K.; Rutgeerts, P.J. Tumor necrosis factor α antibody (infliximab) therapy profoundly down-regulates the inflammation in Crohn’s ileocolitis. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnholt, J.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Kaltoft, K. The effect of etanercept and infliximab on the production of tumour necrosis factor α, interferon-gamma and GM-CSF in in vivo activated intestinal T lymphocyte cultures. Cytokine 2003, 23, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, B.; Brazil, M. Adalimumab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 693–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Q. Role and mechanism of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimiuk, P.A.; Sierakowski, S.; Latosiewicz, R.; Cylwik, J.P.; Cylwik, B.; Skowronski, J.; Chwiecko, J. Soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in patients with distinct variants of rheumatoid synovitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.D.; Slavotinek, J.; Au, V.; Weedon, H.; Parker, A.; Coleman, M.; Roberts-Thomson, P.J.; Ahern, M.J. Successful treatment of rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a reduction in synovial membrane cytokines and cell adhesion molecule expression. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, R.; Schuett, J.; Schuett, H.; Koch, A.K.; Luchtefeld, M.; Grote, K.; Schieffer, B. Targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor-α with Adalimumab: Effects on Endothelial Activation and Monocyte Adhesion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.A.; Campbell, I.K.; O’Donnel, K.L.; Wicks, I.P. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) blockade in collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint involvement and alters B cell trafficking. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Ducret, J.; Wayner, E.; Elices, M.J.; Alvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Firestein, G.S. α4/β1 integrin (VLA-4) ligands in arthritis. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in synovium and on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reparon-Schuijt, C.C.; van Esch, W.J.; van Kooten, C.; Rozier, B.C.; Levarht, E.W.; Breedveld, F.C.; Verweij, C.L. Regulation of synovial B cell survival in rheumatoid arthritis by vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD106) expressed on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Eguchi, K.; Ueki, Y.; Nakashima, M.; Yamashita, I.; Kawabe, Y.; Sakai, M.; Ida, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Nagataki, S. Interleukin 4 increases human synovial cell expression of VCAM-1 and T cell binding. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1994, 53, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, M.D.; Haas, C.S.; Rad, A.M.; Arbab, A.S.; Koch, A.E. The role of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1/very late activation antigen 4 in endothelial progenitor cell recruitment to rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochner, B.S.; Undem, B.J.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Immunological aspects of allergic asthma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 295–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Pathogenesis of airway inflammation in bronchial asthma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2011, 38, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, A.M.; Durham, S.R.; Robinson, D.S.; Menz, G.; Storz, C.; Cromwell, O.; Kay, A.B.; Wardlaw, A.J. Expression of endothelial and leukocyte adhesion molecules interacellular adhesion molecule-1, E-selectin, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in the bronchial mucosa in steady-state and allergen-induced asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 92, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, V.; Balkow, S.; Staats, R.; Matthys, H.; Luttmann, W.; Virchow, J.C., Jr. Increase in perforin-positive peripheral blood lymphocytes in extrinsic and intrinsic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, J.W.; Borish, L. Th2 cytokines and asthma. Interleukin-4: Its role in the pathogenesis of asthma, and targeting it for asthma treatment with interleukin-4 receptor antagonists. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Sano, H.; Nishimura, T.; Yoshida, S.; Iwamoto, I. Role of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1/very late activation antigen 4 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1/lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 interactions in antigen-induced eosinophil and T cell recruitment into the tissue. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminario, M.C.; Bochner, B.S. Expression and function of β1 integrins on human eosinophils. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1997, 92 (Suppl. S2), 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayson, M.H.; Van der Vieren, M.; Sterbinsky, S.A.; Michael Gallatin, W.; Hoffman, P.A.; Staunton, D.E.; Bochner, B.S. αdβ2 integrin is expressed on human eosinophils and functions as an alternative ligand for vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihara, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Kayaba, H.; Kakazu, T.; Kurachi, D.; Yamamoto, J.; Iwasa, S.; Iida, K.; Urayama, O.; Kobayashi, Y. Degranulation of eosinophils mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and its ligands is involved in adhesion molecule expression on endothelial cells-selective induction of VCAM-1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, S452–S456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Kita, H.; Busse, W.W. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 activation of eosinophil function. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 19, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petreccia, D.C.; Nauseef, W.M.; Clark, R.A. Respiratory burst of normal human eosinophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1987, 41, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawara, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Maruyama, N.; Hoshi, H.; Ohno, I.; Honma, M.; Tanno, Y.; Tamura, G.; Shirato, K.; Ohtani, H. In situ expression of the cell adhesion molecules in bronchial tissues from asthmatics with air flow limitation: In vivo evidence of VCAM-1/VLA-4 interaction in selective eosinophil infiltration. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1995, 12, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Numao, T.; Ando, N.; Arima, M.; Nakajima, H.; Sagara, H.; Adachi, T.; Motojima, S.; Makino, S. Role of interleukin-4 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in selective eosinophil migration into the airways in allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 14, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, L.; Bjornsson, E.; Janson, C.; Schmekel, B. Increased adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 of eosinophils from patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 96, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretolani, M.; Ruffie, C.; Lapa e Silva, J.R.; Joseph, D.; Lobb, R.R.; Vargaftig, B.B. Antibody to very late activation antigen 4 prevents antigen-induced bronchial hyperreactivity and cellular infiltration in the guinea pig airways. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, A.A.; Piper, P.J. Role of the VLA-4 integrin in leucocyte recruitment and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in the guinea-pig. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 282, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.E.; Hatfield, C.A.; Winterrowd, G.E.; Brashler, J.R.; Vonderfecht, S.L.; Fidler, S.F.; Griffin, R.L.; Kolbasa, K.P.; Krzesicki, R.F.; Sly, L.M.; et al. Airway recruitment of leukocytes in mice is dependent on α4-integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, L219–L229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreau, A.; Varey, E.; Anegon, I.; Cuturi, M.C. Effector mechanisms of rejection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingulli, E. Mechanism of cellular rejection in transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, M.D.; Davis, S.F.; Baum, M.A.; Melter, M.; Reinders, M.E.; Exeni, A.; Samsonov, D.V.; Fang, J.; Ganz, P.; Briscoe, D.M. The role of the graft endothelium in transplant rejection: Evidence that endothelial activation may serve as a clinical marker for the development of chronic rejection. Pediatr. Transpl. 2000, 4, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, F.; Schiopu, A.; Wood, K.J. Role of T cells in graft rejection and transplantation tolerance. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotti, G.; Palmisano, A.; Maggiore, U.; Buzio, C. Vascular endothelium as a target of immune response in renal transplant rejection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenschlager, I.; Hockerstedt, K.; Taskinen, E.; von Willebrand, E. Expression of adhesion molecules and their ligands in liver allografts during cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and acute rejection. Transpl. Int. 1996, 9 (Suppl. S1), S213–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, P.A.; Main, I.W.; Atkins, R.C. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in human renal allograft rejection. Kidney Int. 1995, 47, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, A.; Mann, D.; Behling, C.A.; McGraw, M.; Seslar, S.; Shiu, P.; Zhang, L.; Kriett, J.M. Increased expression of endoarterial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 mRNA in an experimental model of lung transplant rejection: Diagnosis by pulmonary arterial biopsy. Transplantation 2003, 75, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskowitz, A.; Mayne, A.E.; Willoughby, S.B.; Kanter, K.; Ansari, A.A. Patterns of myocardial cell adhesion molecule expression in human endomyocardial biopsies after cardiac transplantation. Induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 related to implantation and rejection. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, R.P.; Ohye, R.G.; Vanbuskirk, A.; Sedmak, D.D.; Kincade, P.; Ferguson, R.M.; Orosz, C.G. Importance of endothelial VCAM-1 for inflammatory leukocytic infiltration in vivo. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, D.M.; Yeung, A.C.; Schoen, F.J.; Allred, E.N.; Stavrakis, G.; Ganz, P.; Cotran, R.S.; Pober, J.S.; Schoen, E.L. Predictive value of inducible endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression for acute rejection of human cardiac allografts. Transplantation 1995, 59, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorcyznski, R.M.; Chung, S.; Fu, X.M.; Levy, G.; Sullivan, B.; Chen, Z. Manipulation of skin graft rejection in alloimmune mice by anti-VCAM-1:VLA-4 but not anti-ICAM-1:LFA-1 monoclonal antibodies. Transpl. Immunol. 1995, 3, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegall, M.D.; Dean, P.G.; Ninova, D.; Cohen, A.J.; Shepard, G.M.; Gup, C.; Gill, R.G. α4 integrin in islet allograft rejection. Transplantation 2001, 71, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.G.; Dai, X.Y.; Kozak, C.A.; Mims, M.P.; Gotto, A.M.; Ballantyne, C.M. Murine VCAM-1. Molecular cloning, mapping, and analysis of a truncated form. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 4088–4098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.W.; Cachianes, G.; Kuang, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 1989, 246, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battegay, E.J.; Rupp, J.; Iruela-Arispe, L.; Sage, E.H.; Pech, M. PDGF-BB modulates endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro via PDGF β-receptors. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, E.; Nagae, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Ohashi, Y.; Kinoshita, S.; Manabe, R. The effect of recombinant epidermal growth factor in corneal angiogenesis. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 1991, 95, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suri, C.; Jones, P.F.; Patan, S.; Bartunkova, S.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Davis, S.; Sato, T.N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996, 87, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.M.; Grant, D.S.; Kleinman, H.K.; Goldberg, I.D.; Bhargava, M.M.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Kinsella, J.L.; Polverini, P. Scatter factor (hepatocyte growth factor) is a potent angiogenesis factor in vivo. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1993, 47, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. APMIS 2004, 112, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J.; Browder, T.; Palmblad, J. Angiogenesis research: Guidelines for translation to clinical application. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 549–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheul, H.M.; Pinedo, H.M. Possible molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of angiogenesis inhibition. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriaga, Y.; Becerra, C.R. Adverse effects of bevacizumab and their management in solid tumors. Support. Cancer Ther. 2006, 3, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.S.; Cunningham, D. Managing patients treated with bevacizumab combination therapy. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. S3), 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, A.; Harter, P.N.; Cremer, S.; Yalcin, B.H.; Gurnik, S.; Yamaji, M.; Di Tacchio, M.; Sommer, K.; Baumgarten, P.; Bahr, O.; et al. Endothelial cell-derived angiopoietin-2 is a therapeutic target in treatment-naive and bevacizumab-resistant glioblastoma. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, S.; Pages, G. Mechanisms of resistance to anti-angiogenesis therapies. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.B.; Chen, G.Y.; Xia, J.G.; Zang, X.W.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, L. Association of VCAM-1 overexpression with oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis and metastasis of gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, G.J.; Ghellal, A.; Iddon, J.; Blann, A.D.; Venizelos, V.; Kumar, S.; Howell, A.; Bundred, N.J. Serum soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1: Role as a surrogate marker of angiogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearnley, G.W.; Odell, A.F.; Latham, A.M.; Mughal, N.A.; Bruns, A.F.; Burgoyne, N.J.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Zachary, I.C.; Hollstein, M.C.; Wheatcroft, S.B.; et al. VEGF-A isoforms differentially regulate ATF-2-dependent VCAM-1 gene expression and endothelial-leukocyte interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Moon, S.O.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Koh, Y.S.; Koh, G.Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and E-selectin through nuclear factor-kappa B activation in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmy-Susini, B.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sung, R.J.; Hwang, R.; Varner, J. Integrin α4β1-VCAM-1-mediated adhesion between endothelial and mural cells is required for blood vessel maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, J.; Ono, M.; Morikawa, W.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kuwano, M. The activity of soluble VCAM-1 in angiogenesis stimulated by IL-4 and IL-13. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Park, C.S.; Na, H.J.; Lee, K.; Yoon, A.; Chung, J.; Lee, S. Ig-like domain 6 of VCAM-1 is a potential therapeutic target in TNFα-induced angiogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.M.; Shiri, S.; Farsinejad, S. Metastasis review: From bench to bedside. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 8483–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minn, A.J.; Gupta, G.P.; Siegel, P.M.; Bos, P.D.; Shu, W.; Giri, D.D.; Viale, A.; Olshen, A.B.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005, 436, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Lin, H.Y.; Lai, S.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, B.R.; Chen, P.Y.; Wei, K.C.; Lu, D.Y. MiR-181b modulates EGFR-dependent VCAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion in glioblastoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5006–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalici, J.M.; Arapovic, S.; Saks, E.J.; Atkins, K.A.; Petroni, G.; Duska, L.R.; Slack-Davis, J.K. Mesothelium expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Cancer 2017, 123, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.R.; Jang, J.H.; Park, C.S.; Kim, T.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Chung, J.; Shim, H.; Nam, I.H.; Han, J.M.; Lee, S. A Human Antibody That Binds to the Sixth Ig-Like Domain of VCAM-1 Blocks Lung Cancer Cell Migration In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siyasi, M.; Mahjoubi, F.; Mahjoubi, B.; Shabani, S. Study of VCAM-1 Gene Expression in Normal and Tumoral Tissues in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Qiao, B.; Qin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-181a-5p Impedes IL-17-Induced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Migration through Targeting VCAM-1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Massague, J. Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, A.; Chirivi, R.G.; Foglieni, C.; Pigott, R.; Mortarini, R.; Martin-Padura, I.; Anichini, A.; Gearing, A.J.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Dejana, E.; et al. Involvement of the very late antigen 4 integrin on melanoma in interleukin 1-augmented experimental metastases. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okahara, H.; Yagita, H.; Miyake, K.; Okumura, K. Involvement of very late activation antigen 4 (VLA-4) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in tumor necrosis factor α enhancement of experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 3233–3236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Disease | Animal Model | Applied Antibody | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA | DBA/1 mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-2.7) | Reduction in overall clinical severity of disease | Carter et al., 2001 [55] |
| Chimeric SCID mouse/human synovial tissue model | Anti-VCAM-1 polyclonal antibody | Inhibition of marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell adhesion to RA synovial tissue | Silverman et al., 2007 [59] | |
| Asthma | BALB/c mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-1) | Prevention of eosinophil and lymphocyte infiltration into the trachea | Nakajima et al., 1994 [66] |
| C57BL/6 mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-2.7) | Inhibition of eosinophil and lymphocyte recruitment into the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid | Chin et al., 1997 [73] | |
| BALB/c mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (HD101) | Attenuation of macrophage, neutrophil, and eosinophil recruitment into bronchoalveolar lavage fluid | Lee et al., 2013 [40] | |
| Immune rejection | C3H/HEJ murine model of skin allograft | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (MK1.9) | Prolongation of skin allograft survival | Gorcyznski et al., 1995 [85] |
| CBA murine model of islet allograft | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (MK2.7) | Prolongation of islet allograft survival | Stegall et al., 2001 [86] | |
| C57BL/6 mouse model of cardiac allograft | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-2) | Prolongation of cardiac allograft survival | Pelletier et al., 1992 [83] | |
| C57BL/6 mouse model of islet allograft | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (MK2.7) | Prolongation of islet allograft survival | Lee et al., 2012 [43] | |
| Cancer | Matrigel plug nude mouse model | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-2) | Inhibition of neovascularization | Garmy-Susini et al., 2005 [107] |
| C57BL/6 mouse model of pulmonary metastasis | Anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibody (M/K-2) | Reduction of TNFα-enhanced pulmonary lung colonies | Okahara et al., 1994 [120] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, D.-H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, M.R.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, S. Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041057
Kong D-H, Kim YK, Kim MR, Jang JH, Lee S. Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Deok-Hoon, Young Kwan Kim, Mi Ra Kim, Ji Hye Jang, and Sukmook Lee. 2018. "Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041057
APA StyleKong, D. -H., Kim, Y. K., Kim, M. R., Jang, J. H., & Lee, S. (2018). Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041057