DK1 Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
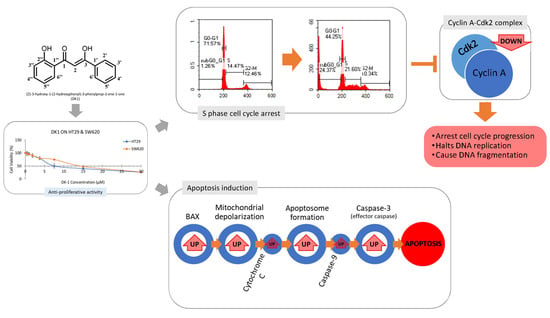
2.1. DK1 Decreases Cell Viability of HT29 and SW620
2.2. Treatment of DK1 Alters Morphological Appearance and Induces Apoptosis in HT29 and SW620
2.3. Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase in HT29 and SW620 Cells
2.4. Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway Induced by DK1 Treatment
2.5. DK1 Regulates Several Apoptotic Genes and Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Curcumin Analogue, DK1
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide(MTT) Assay
4.4. Cell Treatment
4.5. Acridine Orange/PropidiumIodide (AO/PI) Double-Staining Assay
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Annexin-V/FITC Assay
4.8. JC-1 (Mitoscreen) Assay
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
4.10. Proteome Profiling
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, B.W.K.P.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-92-832-0432-9. [Google Scholar]
- Amos-Landgraf, J.M.; Heijmans, J.; Wielenga, M.C.B.; Dunkin, E.; Krentz, K.J.; Clipson, L.; Ederveen, A.G.; Groothuis, P.G.; Mosselman, S.; Muncan, V.; et al. Sex disparity in colonic adenomagenesis involves promotion by male hormones, not protection by female hormones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16514–16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolligs, F.T. Diagnostics and epidemiology of colorectal cancer. Visc. Med. 2016, 32, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Li, Z.; Ni, J.; Song, Z. Curcumin inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation by regulating the metabotropic glutamate receptor-4 expression on dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 46, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaghinejad, M.; Motevalian, M.; Fatima, S.; Hashemi, H.; Gholami, M. Curcumin confers neuroprotection against alcohol-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration via CREB-BDNF pathway in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, S.; Khan, S.I.; Kandi, S.K.; Raj, K.; Sun, G.; Yang, X.; Molina, A.; Ni, N.; Wang, B.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity and cytotoxic potential of new monocarbonyl analogues of curcumin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamori, T.; Lubet, R.; Steele, V.; Kelloff, G.; Kaskey, R.; Rao, C.; Reddy, B. Chemopreventive Effect of Curcumin, a Naturally Occurring Anti-Inflammatory Agent, during the Promotion/Progression Stages of Colon Cancer Chemopreventive Effect of Curcumin, a Naturally Occurring Anti-Inflammatory Agent, during the Promotion/Progression. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; He, Z.-M.; Wang, F.-L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Liu, X.-Z.; Zhai, D.-D.; Chen, W.-D. Curcumin and its promise as an anticancer drug: An Analysis of its anticancer and antifungal effects in cancer and associated complication from invasive fungal infections. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 772, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedzadeh, M.H.; Safari, Z.; Zare, A.; Navashenaw, J.G.; Razavi, S.A.; Kardar, G.A.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Study of curcumin immunomodulatory effects on reactive astrocyte cell function. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Correa, H.A.; Paula, J.T.; Kayano, A.C.A.V.; Queiroga, C.L.; Magalhães, P.M.; Costa, F.T.M.; Cabral, F.A. Composition and antimalarial activity of extracts of Curcuma longa L. obtained by a combination of extraction processes using supercritical CO2, ethanol and water as solvents. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 119, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Thomas, S.G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sundaram, C.; Harikumar, K.B.; Sung, B.; Tharakan, S.; Misra, K.; Priyadarsini, I.; Rajasekharan, K.; et al. Biological activities of curcumin and its analogues (Congeners) made by man and Mother Nature. Biochemical Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1590–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sufi, S.A.; Adigopula, L.N.; Syed, S.B.; Mukherjee, V.; Coumar, M.S.; Rao, H.S.P.; Rajagopalan, R. In-silico and in vitro anti-cancer potential of a curcumin analogue (1E, 6E)-1, 7-di (1H-indol-3-yl) hepta-1, 6-diene-3, 5-dione. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Zuo, Y.; Ke, H.; Luo, J.; Lou, L.; Qin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Sun, H.; et al. Identification of 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as novel proteasome inhibitors for potential anticancer agents targeting 19S regulatory particle associated deubiquitinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 137, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zuo, Y.; Huang, L.; Wen, G.; Shang, N.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; et al. MC37, a new mono-carbonyl curcumin analog, induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Yeap, S.K.; Abu, N.; Lim, K.L.; Ky, H.; Pauzi, A.Z.M.; Ho, W.Y.; Tan, S.W.; Alan-Ong, H.K.; Zareen, S.; et al. Synthetic curcumin derivative DK1 possessed G2/M arrest and induced apoptosis through accumulation of intracellular ROS in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2017, 23, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.N.M.; Hussin, Y.; Che Rahim, N.F.; Nordin, N.; Mohamad, N.E.; Yeap, S.K.; Yong, C.Y.; Masarudin, M.J.; Cheah, Y.K.; Abu, N.; et al. Curcumin Analog DK1 Induces Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro through Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.-M.; Chen, P.-J.; Sung, P.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Wu, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L. The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozada-García, M.; Enríquez, R.; Ramírez-Apán, T.; Nieto-Camacho, A.; Palacios-Espinosa, J.; Custodio-Galván, Z.; Arteche, O.; Pérez-Villanueva, J. Synthesis of Curcuminoids and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhaidaat, N.M.; Bouklihacene, M.; Thorne, R.F. 5-Fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells is caspase-9-dependent and mediated by activation of protein kinase C-δ. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Mao, Y.B.; Cai, Q.F.; Yao, L.M.; Ouyang, G.L.; Bao, S.D. Curcumin induces human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell apoptosis by activating p53 and regulating apoptosis-related protein expression. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohori, H.; Yamakoshi, H.; Tomizawa, M.; Shibuya, M.; Kakudo, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Takahashi, S.; Kato, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ishioka, C.; et al. Synthesis and biological analysis of new curcumin analogues bearing an enhanced potential for the medicinal treatment of cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2563–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Abu, N.; Yeap, S.; Ho, W.; Omar, A.; Ismail, N.; Ahmad, S.; Pirozyan, M.; Akhtar, N.; Alitheen, N. Combinatorial Cytotoxic Effects of Damnacanthal and Doxorubicin against Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells in Vitro. Molecules 2016, 21, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymański, J.; Janikiewicz, J.; Michalska, B.; Patalas-Krawczyk, P.; Perrone, M.; Ziółkowski, W.; Duszyński, J.; Pinton, P.; Dobrzyń, A.; Więckowski, M. Interaction of Mitochondria with the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Plasma Membrane in Calcium Homeostasis, Lipid Trafficking and Mitochondrial Structure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puccinelli, M.; Stan, S. Dietary Bioactive Diallyl Trisulfide in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, F.; Li, X.; Dan Tao, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, S. Polyphyllin I induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in U251 human glioma cells via mitochondrial dysfunction and the JNK signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; De Guevara, R.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Liu, H. Cloning and transcriptional activity of the mouse Omi/HtrA2 gene promoter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2016, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.; Tome, M.; Briehl, M. Mitochondrial adaptations to oxidative stress confer resistance to apoptosis in lymphoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10212–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cell Lines | Inhibitory Concentrations of DK1 (µM) | Inhibitory Concentrations (IC50) of Curcumin (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC25 | IC50 | IC75 | ||
| HT29 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 7.5 ± 1.6 | 28.0 ± 2.0 | 20.2 ± 0.6 |
| SW620 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 14.5 ± 1.2 | 27.8 ± 1.4 | >50 |
| Cells | Proteins | Relative Intensity (Fold Change) | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| HT29 | Pro-caspase-3 | 2.10 * ± 0.06 | Up |
| Cleaved caspase-3 | 1.98 ± 0.11 | Up | |
| Bax | 2.41 * ± 0.18 | Up | |
| Cytochrome C | 1.78 * ± 0.07 | Up | |
| HTRA2/Omi | 2.21 * ± 0.13 | Up | |
| SMAC/Diablo | 1.14 ± 0.01 | Up | |
| SW620 | Pro-caspase-3 | −0.98 ± 0.06 | Down |
| Cleaved caspase-3 | −0.70 ± 0.05 | Down | |
| Bax | −0.75 ± 0.04 | Down | |
| Cytochrome c | −0.55 ± 0.02 | Down | |
| HTRA2/Omi | 1.25* ± 0.01 | Up | |
| SMAC/Diablo | −0.96 ± 0.01 | Down |
| Gene | Accession No. | Forward Sequence(5′3′) | Reverse Sequence(5′3′) | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caspase-3 | NM_004346 | AGAACTGGACTGTGGCATTGAG | GCTTGTCGGCATACTGTTTCAG | 191 |
| Caspase-8 | NM_001228 | CATCCAGTCACTTTGCCAGA | GCATCTGTTTCCCCATGTTT | 128 |
| Caspase-9 | NM_001229 | TGTCCTACTCTACTTTCCCAGGTTTT | GTGAGCCCACTGCTCAAAGAT | 101 |
| Bax | BC014175.2 | TTCTGACGGCAACTTCAACT | CAGCCCATGATGGTTCTGAT | 153 |
| Cytochrome c | NM_018947.5 | GGGCCAAATCTCCATGGTCT | GGCAGTGGCCAATTATTACTC | 246 |
| Cyclin A | M25753.1 | GGTGTCACTGCCATGTTTATTG | TCTGTCTGATTTGGTGCTTAGT | 160 |
| CDK 2 | NG_029877.1 | CCACAGCTACTCACCTGTTATC | ATGTCAACCCACCTTAATCTCTC | 173 |
| ACTB | NM_001101.3 | AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC | AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG | 184 |
| 18srRNA | X03205 | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | 151 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussin, Y.; Aziz, M.N.M.; Che Rahim, N.F.; Yeap, S.K.; Mohamad, N.E.; Masarudin, M.J.; Nordin, N.; Abd Rahman, N.M.A.-N.; Yong, C.Y.; Akhtar, M.N.; et al. DK1 Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041151
Hussin Y, Aziz MNM, Che Rahim NF, Yeap SK, Mohamad NE, Masarudin MJ, Nordin N, Abd Rahman NMA-N, Yong CY, Akhtar MN, et al. DK1 Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041151
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussin, Yazmin, Muhammad Nazirul Mubin Aziz, Nurul Fattin Che Rahim, Swee Keong Yeap, Nurul Elyani Mohamad, Mas Jaffri Masarudin, Noraini Nordin, Nik Mohd Afizan-Nik Abd Rahman, Chean Yeah Yong, Muhammad Nadeem Akhtar, and et al. 2018. "DK1 Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041151
APA StyleHussin, Y., Aziz, M. N. M., Che Rahim, N. F., Yeap, S. K., Mohamad, N. E., Masarudin, M. J., Nordin, N., Abd Rahman, N. M. A. -N., Yong, C. Y., Akhtar, M. N., Zamrus, S. N. H., & Alitheen, N. B. (2018). DK1 Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041151