Rab38 Mutation and the Lung Phenotype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
2.1. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome and the Lung Phenotype
2.2. Animal Models of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
2.3. BLOC-3 Is a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor for Rab32/38
3. Expression of Rab38 in the Lung
3.1. Selective Expression of Rab38 in the Lower Respiratory Tract Epithelium
3.2. Intracellular Localization of Rab38 in Alveolar Type II Cells
4. Pulmonary Surfactant is Stored in Lamellar Bodies, i.e., Lysosome-Related Organelles, in Alveolar Type II Cells
4.1. Pulmonary Surfactant Is a Complex of Lipids and Apoproteins
4.2. Blocking of the Intracellular Transport Pathway via the Golgi Apparatus
4.3. Surfactant Phosphatidylcholine Transport Bypasses the Golgi-Dependent Pathway
4.4. Surfactant Protein-A Undergoes Constitutive Secretion and Reuptake
4.5. Surfactant Protein-B Is Transported to Lamellar Body via the Golgi-Dependent Pathway
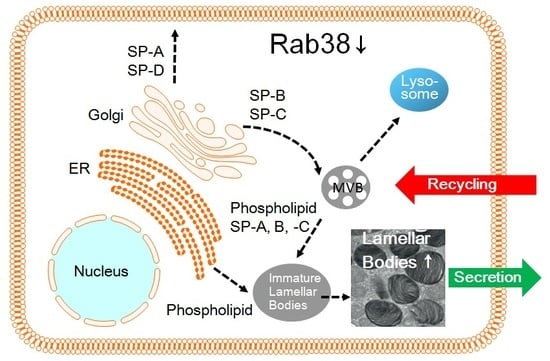
5. Rab38-Mutated Mice Show Abnormality in Homeostasis of Pulmonary Surfactant and Alveolar Architecture
5.1. Chocolate Is a Mouse Phenotype of a Rab38 Mutation
5.2. Aberrant Structure of Alveolar Tissues in Chocolate Mice
5.3. Abnormal Lung Surfactant Homeostasis in the Chocolate Mice
5.4. Characterization of the Rab38cht Protein
5.5. Chocolate Mutation and the Oculocutaneous Lung Disease
6. Rab38-Deficient Rats (Ruby) Are an Animal Model of Human Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
6.1. The Ruby Mutation Abolishes Translation of the Rab38 Gene in Rats
6.2. Altered Homeostasis of Lung Surfactant in Ruby Rats
6.3. Morphological Changes of Alveolar Type II Cells in Ruby Rats Share Similarity with those in Human HPS Lungs
6.4. Exogenous Gene Transfer of Rab38 Transgene into Ruby Rat Lungs
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPS | Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome |
| LRO | Lysosome-related organelle |
| BLOC | Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelle complex |
| SP | Surfactant protein |
| LEC | Long Evans Cinnamon |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar Lavage |
References
- Takai, Y.; Kaibuchi, K.; Kikuchi, A.; Kawata, M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 133, 187–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olkkonen, V.M.; Stenmark, H. Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1997, 176, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T. Molecular mechanisms for the regulation of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by small guanosine triphosphatases in skeletal muscle and adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18677–18692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goitre, L.; Trapani, E.; Trabalzini, L.; Retta, S.F. The Ras superfamily of small GTPases: The unlocked secrets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1120, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.H. Structural basis of membrane trafficking by Rab family small G protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8912–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, P.; Brennwald, P. Friends and family: The role of the Rab GTPases in vesicular traffic. Cell 1993, 75, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Matozaki, T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 153–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerial, M.; McBride, H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabra, M.C.; Wasmeier, C. Controlling the location and activation of Rab GTPases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, S.; Aivazian, D. Targeting Rab GTPases to distinct membrane compartments. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Iguchi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Nambu, Y.; Sakuma, T.; Toga, H.; Ohya, N.; Shimizu, H.; Fisher, J.H.; Voelker, D.R. Expression and localization of a novel Rab small G protein (Rab38) in the rat lung. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, D.; Stockert, E.; Jäger, E.; Güre, A.O.; Scanlan, M.J.; Knuth, A.; Old, L.J.; Chen, Y.T. Serological cloning of a melanocyte rab guanosine 5′-triphosphate-binding protein and a chromosome condensation protein from a melanoma complementary DNA library. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Takahashi, K.; Nakamura, K.; Takahashi, M.; Ishigaki, M.; Sakuma, T.; Toga, H.; Suzuki, T.; Voelker, D.R. Expression and characterization of Rab38, a new member of the Rab small G protein family. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, S.M.; Gerlinger, M.; de la Rosa, O.; Nuber, N.; Knights, A.; Gati, A.; Laumer, M.; Strauss, L.; Exner, C.; Schäfer, N.; et al. Spontaneous CD8 T cell responses against the melanocyte differentiation antigen RAB38/NY-MEL-1 in melanoma patients. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8212–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zippelius, A.; Gati, A.; Bartnick, T.; Walton, S.; Odermatt, B.; Jaeger, E.; Dummer, R.; Urosevic, M.; Filonenko, V.; Osanai, K.; et al. Melanocyte differentiation antigen RAB38/NY-MEL-1 induces frequent antibody responses exclusively in melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.; Hernandez, D.G.; Nalls, M.A.; Rohrer, J.D.; Ramasamy, A.; Kwok, J.B.; Dobson-Stone, C.; Brooks, W.S.; Schofield, P.R.; Halliday, G.M.; et al. Frontotemporal dementia and its subtypes: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimprich, A.; Biskup, S.; Leitner, P.; Lichtner, P.; Farrer, M.; Lincoln, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Uitti, R.J.; Calne, D.B.; et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 2004, 44, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waschbüsch, D.; Michels, H.; Strassheim, S.; Ossendorf, E.; Kessler, D.; Gloeckner, C.J.; Barnekow, A. LRRK2 transport is regulated by its novel interacting partner Rab32. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NCBI BLAST Graphics. Rab38 [Mus Musclus] GenBank: BAF02896.1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/BAF02896.1?report=graph (accessed on 26 July 2018).
- Huizing, M.; Anikster, Y.; Gahl, W.A. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome and related disorders of organelle formation. Traffic 2000, 1, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahl, W.A.; Brantly, M.; Kaiser-Kupfer, M.I.; Iwata, F.; Hazelwood, S.; Shotelersuk, V.; Duffy, L.F.; Kuehl, E.M.; Troendle, J.; Bernardini, I. Genetic defects and clinical characteristics of patients with a form of oculocutaneous albinism (Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome). N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, S.M.; Dell’Angelica, E.C. The cell biology of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Recent advances. Traffic 2005, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninkovic, I.; White, J.G.; Rangel-Filho, A.; Datta, Y.H. The role of Rab38 in platelet dense granule defects. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.L. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: A disease of protein trafficking and organelle function. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Sano, J.; Inayama, Y.; Kawano, N.; Yamanaka, S.; Miyagi, Y.; Nagashima, Y.; Ohbayashi, C.; Mizushima, M.; et al. Interstitial pneumonia in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Significance of florid foamy swelling/degeneration (giant lamellar body degeneration) of type-2 pneumocytes. Virchows Arch. 2000, 437, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Rusiniak, M.E.; Chintala, S.; Gautam, R.; Novak, E.K.; Swank, R.T. Murine Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome genes: Regulators of lysosome-related organelles. Bioessays 2004, 26, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Higuchi, J.; Oikawa, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsuchihara, K.; Iguchi, M.; Huang, J.; Voelker, D.R.; Toga, H. Altered lung surfactant system in a Rab38-deficient rat model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L243–L251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oiso, N.; Riddle, S.R.; Serikawa, T.; Kuramoto, T.; Spritz, R.A. The rat Ruby (R) locus is Rab38: Identical mutations in Fawn-hooded and Tester-Moriyama rats derived from an ancestral Long Evans rat sub-strain. Mamm. Genome 2004, 15, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieur, D.J.; Meyers, K.M. Genetics of the fawn-hooded rat strain. The coat color dilution and platelet storage pool deficiency are pleiotropic effects of the autosomal recessive red-eyed dilution gene. J. Hered. 1984, 75, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Novak, E.K.; Tan, J.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S.; Swank, R.T. Interaction of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome genes in the regulation of lysosome-related organelles. Traffic 2006, 7, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicary, G.W.; Vergne, Y.; Santiago-Cornier, A.; Young, L.R.; Roman, J. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, T.E.; Na, C.L.; Stahlman, M. Biogenesis of lamellar bodies, lysosome-related organelles involved in storage and secretion of pulmonary surfactant. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gochuico, B.R.; Huizing, M.; Golas, G.A.; Scher, C.D.; Tsokos, M.; Denver, S.D.; Frei-Jones, M.J.; Gahl, W.A. Interstitial lung disease and pulmonary fibrosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2, an adaptor protein-3 complex disease. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.D.; Huizing, M.; Claassen, D.A.; White, J.; Gahl, W.A. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 4 (HPS-4): Clinical and molecular characteristics. Hum. Genet. 2003, 113, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.H.; Li, W. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Pigmentary and non-pigmentary defects and their pathogenesis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerondopoulos, A.; Langemeyer, L.; Liang, J.R.; Linford, A.; Barr, F.A. BLOC-3 mutated in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is a Rab32/38 guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohbayashi, N.; Fukuda, M.; Kanaho, Y. Rab32 subfamily small GTPases: Pleiotropic Rabs in endosomal trafficking. J. Biochem. 2017, 162, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmeier, C.; Romao, M.; Plowright, L.; Bennett, D.C.; Raposo, G.; Seabra, M.C. Rab38 and Rab32 control post-Golgi trafficking of melanogenic enzymes. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bultema, J.J.; Di Pietro, S.M. Cell type-specific Rab32 and Rab38 cooperate with the ubiquitous lysosome biogenesis machinery to synthesize specialized lysosome-related organelles. Small GTPases 2013, 4, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bultema, J.J.; Ambrosio, A.L.; Burek, C.L.; Di Pietro, S.M. BLOC-2, AP-3, and AP-1 proteins function in concert with Rab38 and Rab32 proteins to mediate protein trafficking to lysosome-related organelles. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19550–19563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M. Multiple Roles of VARP in Endosomal Trafficking: Rabs, Retromer Components and R-SNARE VAMP7 Meet on VARP. Traffic 2016, 17, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, R.A.; Purushothaman, L.K.; Rani, S.; Bergam, P.; Setty, S.R. STX13 regulates cargo delivery from recycling endosomes during melanosome biogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 3263–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bultema, J.J.; Boyle, J.A.; Malenke, P.B.; Martin, F.E.; Dell’Angelica, E.C.; Cheney, R.E.; Di Pietro, S.M. Myosin VC interacts with Rab32 and Rab38 proteins and works in the biogenesis and secretion of melanosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33513–33528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.K.; Mantegazza, A.R.; Snir, O.L.; Tenza, D.; Acosta-Ruiz, A.; Delevoye, C.; Zorger, R.; Sitaram, A.; de Jesus-Rojas, W.; Ravichandran, K.; et al. BLOC-2 targets recycling endosomal tubules to melanosomes for cargo delivery. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marubashi, S.; Shimada, H.; Fukuda, M.; Ohbayashi, N. RUTBC1 Functions as a GTPase-activating Protein for Rab32/38 and regulates melanogenic enzyme trafficking in melanocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerial, M.; Parton, R.; Chavrier, P.; Frank, R. Localization of Rab family members in animal cells. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 219, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Oikawa, R.; Higuchi, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsuchihara, K.; Iguchi, M.; Jongsu, H.; Toga, H.; Voelker, D.R. A Mutation in Rab38 Small GTPase causes abnormal lung surfactant homeostasis and aberrant alveolar structure in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plopper, C.G.; Macklin, J.; Nishio, S.J.; Hyde, D.M.; Buckpitt, A.R. Relationship of cytochrome P-450 activity to Clara cell cytotoxicity. III. Morphometric comparison of changes in the epithelial populations of terminal bronchioles and lobar bronchi in mice, hamsters, and rats after parenteral administration of naphthalene. Lab. Investig. 1992, 67, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.R.; Williams, M.C.; Benson, B. Immunocytochemical localization of the major surfactant apoproteins in type II cells, Clara cells, and alveolar macrophages of rat lung. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1986, 34, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balis, J.U.; Paterson, J.F.; Paciga, J.E.; Haller, E.M.; Shelley, S.A. Distribution and subcellular localization of surfactant-associated glycoproteins in human lung. Lab. Investig. 1985, 52, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Massaro, G.D.; Singh, G.; Mason, R.; Plopper, C.G.; Malkinson, A.M.; Gail, D.B. Biology of the Clara cell. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, L101–L106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalina, M.; Mason, R.J.; Shannon, J.M. Surfactant protein C is expressed in alveolar type II cells but not in Clara cells of rat lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 6, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwabe, A.; Mason, R.J.; Voelker, D.R. Temporal segregation of surfactant secretion and lamellar body biogenesis in primary cultures of rat alveolar type II cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1991, 5, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Mason, R.J.; Voelker, D.R. Trafficking of newly synthesized surfactant protein A in isolated rat alveolar type II cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 19, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Mason, R.J.; Voelker, D.R. Pulmonary surfactant phosphatidylcholine transport bypasses the brefeldin A sensitive compartment of alveolar type II cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1531, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawgood, S. Pulmonary surfactant apoproteins: A review of protein and genomic structure. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, L13–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerke, J. Pulmonary surfactant: Functions and molecular composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1408, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobran, L.I.; Rooney, S.A. Regulation of SP-B and SP-C secretion in rat type II cells in primary culture. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L1413–L1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notter, R.H.; Finkelstein, J.N. Pulmonary surfactant: An interdisciplinary approach. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1984, 57, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagsman, H.P.; van Golde, L.M. Synthesis and assembly of lung surfactant. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1991, 53, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, M.; Lewis, J.F.; Tabor, B.; Rider, E.D.; Jobe, A.H. Surfactant protein A metabolism in preterm ventilated lambs. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, L765–L772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Yuan, L.C.; Bonifacino, J.S.; Klausner, R.D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: Evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell 1989, 56, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, L.; Tagaya, M.; Amherdt, M.; Perrelet, A.; Donaldson, J.G.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Klausner, R.D.; Rothman, J.E. Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non-clathrin-coated buds on Golgi cisternae. Cell 1991, 64, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Tsuchihara, C.; Hatta, R.; Oikawa, T.; Tsuchihara, K.; Iguchi, M.; Seki, T.; Takahashi, M.; Huang, J.; Toga, H. Pulmonary surfactant transport in alveolar type II cells. Respirology 2006, 11, S70–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeVine, A.M.; Bruno, M.D.; Huelsman, K.M.; Ross, G.F.; Whitsett, J.A.; Korfhagen, T.R. Surfactant protein A-deficient mice are susceptible to group B streptococcal infection. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 4336–4340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, M.; Korfhagen, T.R.; Bruno, M.D.; Whitsett, J.A.; Jobe, A.H. Surfactant metabolism in surfactant protein A-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, L479–L485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, A.; Kuroki, Y.; Akino, T. Pulmonary surfactant protein A-mediated uptake of phosphatidylcholine by alveolar type II cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, L193–L199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfhagen, T.R.; Bruno, M.D.; Ross, G.F.; Huelsman, K.M.; Ikegami, M.; Jobe, A.H.; Wert, S.E.; Stripp, B.R.; Morris, R.E.; Glasser, S.W.; et al. Altered surfactant function and structure in SP-A gene targeted mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9594–9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouch, E.; Hartshorn, K.; Ofek, I. Collectins and pulmonary innate immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 173, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botas, C.; Poulain, F.; Akiyama, J.; Brown, C.; Allen, L.; Goerke, J.; Clements, J.; Carlson, E.; Gillespie, A.M.; Epstein, C.; et al. Altered surfactant homeostasis and alveolar type II cell morphology in mice lacking surfactant protein D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11869–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foster, C.D.; Zhang, P.X.; Gonzales, L.W.; Guttentag, S.H. In vitro surfactant protein B deficiency inhibits lamellar body formation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogee, L.M.; Garnier, G.; Dietz, H.C.; Singer, L.; Murphy, A.M.; deMello, D.E.; Colten, H.R. A mutation in the surfactant protein B gene responsible for fatal neonatal respiratory disease in multiple kindreds. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1860–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokieda, K.; Whitsett, J.A.; Clark, J.C.; Weaver, T.E.; Ikeda, K.; McConnell, K.B.; Jobe, A.H.; Ikegami, M.; Iwamoto, H.S. Pulmonary dysfunction in neonatal SP-B-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, L875–L882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttentag, S.H.; Beers, M.F.; Bieler, B.M.; Ballard, P.L. Surfactant protein B processing in human fetal lung. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, L559–L566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, S.K.; Larson, D.M.; Baxter, L.L.; Antonellis, A.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Bittner, M.; Hammer, J.A.; Pavan, W.J. Mutation of melanosome protein RAB38 in chocolate mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, V.S.; Wasmeier, C.; Seabra, M.C.; Futter, C.E. Melanosome maturation defect in Rab38-deficient retinal pigment epithelium results in instability of immature melanosomes during transient melanogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3914–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, S.; Fukuchi, Y.; Uejima, Y.; Teramoto, K.; Oka, T.; Orimo, H. A novel model of senile lung: Senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Seyama, K.; Sato, Y.; Mori, H.; Souma, S.; Akiyoshi, T.; Kodama, Y.; Mori, T.; Goto, S.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Senescence marker protein-30 protects mice lungs from oxidative stress, aging, and smoking. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Voelker, D.R. Analysis and expression of Rab38 in oculocutaneous lung disease. In Small Gtpases in Disease, Part A; Balch, W.E., Der, C.J., Hall, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 438, pp. 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liang, Z. Phosphate-binding loop and Rab GTPase function: Mutations at Ser29 and Ala30 of Rab5 lead to loss-of-function as well as gain-of-function phenotype. Biochem. J. 2001, 355, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.F.; Magee, A.I.; Childs, J.E.; Marshall, C.J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell 1989, 57, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahl, W.A.; Brantly, M.; Troendle, J.; Avila, N.A.; Padua, A.; Montalvo, C.; Cardona, H.; Calis, K.A.; Gochuico, B. Effect of pirfenidone on the pulmonary fibrosis of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 76, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyerla, T.A.; Rusiniak, M.E.; Borchers, M.; Jahreis, G.; Tan, J.; Ohtake, P.; Novak, E.K.; Swank, R.T. Aberrant lung structure, composition, and function in a murine model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L643–L653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahavadi, P.; Korfei, M.; Henneke, I.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G.; Gochuico, B.R.; Markart, P.; Bellusci, S.; Seeger, W.; Ruppert, C.; et al. Epithelial stress and apoptosis underlie Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.R.; Pasula, R.; Gulleman, P.M.; Deutsch, G.H.; McCormack, F.X. Susceptibility of Hermansky-Pudlak mice to bleomycin-induced type II cell apoptosis and fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, A.V.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A. Regulation of surfactant secretion in alveolar type II cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L259–L271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Nakase, K.; Sakuma, T.; Nishiki, K.; Nojiri, M.; Kato, R.; Saito, M.; Fujimoto, Y.; Mizuno, S.; Toga, H. Exogenous gene transfer of Rab38 small GTPase ameliorates aberrant lung surfactant homeostasis in Ruby rats. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, K.; Robert, K.W.; DeBolt, K.M.; Hong, N.; Tao, J.Q.; Fukuda, M.; Fisher, A.B.; Huang, S. Rab38 targets to lamellar bodies and normalizes their sizes in lung alveolar type II epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L461–L477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene therapy comes of age. Science 2018, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Mouse HPS | Mouse HPS Gene | Protein (Complex) | Human HPS Gene | Lung Disease in Human HPS (Ref) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pale ear (ep) | HPS1 | BLOC-3 | HPS1 | + [22] |
| Pearl (pe) | AP3B1 | AP-3 | HPS2 | + [34] |
| Cocoa (coa) | HPS3 | BLOC-2 | HPS3 | − |
| Light ear (le) | HPS4 | BLOC-3 | HPS4 | + [35] |
| Ruby eye-2 (ru2) | HPS5 | BLOC-2 | HPS5 | − |
| Ruby eye (ru) | HPS6 | BLOC-2 | HPS6 | − |
| Sandy (sdy) | DTNBP1 | BLOC-1 | HPS7 | − |
| Reduced pigmentation (rp) | BLOC1S3 | BLOC-1 | HPS8 | − |
| Pallid (pa) | BLOC1S6 | BLOC-1 | HPS9 | +− |
| Mocha (mh) | AP3D1 | AP-3 | HPS10 | − |
| Muted (mu) | MUTED | BLOC-1 | − | |
| Cappuccino (cno) | CNO | BLOC-1 | − | |
| Gunmetal (gm) | RABGGTA | Rab GGTase | − | |
| Buff (bf) | Vps33A | Class C VPS | − | |
| KXD1-KO | KXD1 | BLOC1 | − | |
| Ashen | Rab27A | Rab27A | − | |
| Chocolate (cht), Ruby (R) * | Rab38 | Rab38 | − |
| LRO | Cells | Function | Affected Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamellar body | Alveolar type II cell | Storage of pulmonary surfactant | Interstitial pneumonia, Respiratory failure |
| Melanosome | Melanocyte | Melanin synthesis and transport | Albinism |
| Dense granule | Platelet, Megakaryocyte | Stopping bleeding | Bleeding diathesis |
| Lytic granule | Cytotoxic lymphocyte, Natural killer cell | Cell-mediated cytotoxicity | Immunodeficiency, Infectious susceptibility |
| Azurophil granule | Neutrophil, Eosinophil | Storage of proteases | Immunodeficiency, Infectious susceptibility |
| MHC class II compartment | B lymphocyte, Macrophage, Dendritic cell, Antigen-presenting cell | Intercellular recognition and communication | Immunodeficiency |
| Weibel-Palade body | Endothelial cell | Storage and secretion of hemostatic and proinflammatory substances | Bleeding diathesis |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osanai, K. Rab38 Mutation and the Lung Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082203
Osanai K. Rab38 Mutation and the Lung Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082203
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsanai, Kazuhiro. 2018. "Rab38 Mutation and the Lung Phenotype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082203
APA StyleOsanai, K. (2018). Rab38 Mutation and the Lung Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082203