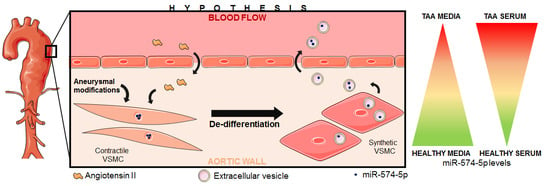
MiR-574-5p: A Circulating Marker of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Characteristics
2.3. MiRNA Expression Profiles in Human Aortic Media
2.4. Candidate MiRNA Selection
2.5. MiR-574-5p Expression in the Human Tissue Cohort
2.6. MiR-574-5p Expression in the Human Serum Cohort
2.7. MiR-574-5p in Fbn1C1041G/+ Aortic Tissues and EVs
2.8. MiR-574-5p Expression in Murine Organs
2.9. MiR-574-5p in EVs and VSMCs
2.10. Effects of Ang II on MiR-574-5p and EVs in Human VSMCs
2.11. MiR-574-5p Expression in Mice Plasma
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Aortic Tissue Samples–“Tissue Cohort”
4.2. Human Serum Samples–“Serum Cohort”
4.3. Mice
4.4. Isolation, Number and Size Distribution of Intact EVs
4.4.1. Isolation of Intact EVs
4.4.2. Number and Size Distribution of EVs
4.5. Primary VSMCs Isolation and Culture
4.6. RNA Extraction
4.7. Microarrays
4.8. Bioinformatics Analyses
4.9. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
4.10. Sequential FISH and Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| Fbn1 | Fibrillin 1 |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| MiRDB | microRNA Target Prediction Database |
| MiRNA | MicroRNA |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology information |
| TAA | Thoracic aortic aneurysm |
| VSMC | Vascular smooth muscle cell |
| Wt | Wild type |
References
- Elefteriades, J.A.; Sang, A.; Kuzmik, G.; Hornick, M. Guilt by association: Paradigm for detecting a silent killer (thoracic aortic aneurysm). Open Heart 2015, 2, e000169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbel, R.; Aboyans, V.; Boileau, C.; Bossone, E.; Bartolomeo, R.D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Falk, V.; Frank, H.; Gaemperli, O.; et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2873–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elefteriades, J.A.; Ziganshin, B.A. Paradigm for Detecting Silent Thoracic Aneurysm Disease. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 28, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vapnik, J.S.; Kim, J.B.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Cheng, Y.; Sundt, T.M., 3rd; MacGillivray, T.E.; Cambria, R.P.; Lindsay, M.E. Characteristics and Outcomes of Ascending Versus Descending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magenis, R.E.; Maslen, C.L.; Smith, L.; Allen, L.; Sakai, L.Y. Localization of the fibrillin (FBN) gene to chromosome 15, band q21.1. Genomics 1991, 11, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, H.I.; Della Corte, A.; Prakash, S.K.; Milewicz, D.M.; Evangelista, A.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. Bicuspid aortic valve aortopathy in adults: Incidence, etiology, and clinical significance. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 201, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo Borges, L.; Jaldin, R.G.; Dias, R.R.; Stolf, N.A.; Michel, J.B.; Gutierrez, P.S. Collagen is reduced and disrupted in human aneurysms and dissections of ascending aorta. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, J.B.; Jondeau, G.; Milewicz, D.M. From genetics to response to injury: Vascular smooth muscle cells in aneurysms and dissections of the ascending aorta. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzucidlo, E.M.; Martin, K.A.; Powell, R.J. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, A25–A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, N.; Gu, T.; Shi, E.; Zhang, G.; Yu, L.; Wang, C. Phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in animal model of rat thoracic aortic aneurysm. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milewicz, D.M.; Regalado, E. Heritable Thoracic Aortic Disease Overview. In GeneReviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Rateri, D.L.; Bruemmer, D.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Involvement of the renin-angiotensin system in abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms. Clin. Sci. 2012, 123, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Senapati, P.; Chen, Z.; Reddy, M.A.; Ganguly, R.; Lanting, L.; Mandi, V.; Bansal, A.; Leung, A.; Zhang, S.; et al. Regulation of angiotensin II actions by enhancers and super-enhancers in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, D.P.; Biery, N.J.; Keene, D.R.; Geubtner, J.; Myers, L.; Huso, D.L.; Sakai, L.Y.; Dietz, H.C. Evidence for a critical contribution of haploinsufficiency in the complex pathogenesis of Marfan syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, M.E.; Dietz, H.C. Lessons on the pathogenesis of aneurysm from heritable conditions. Nature 2011, 473, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goretti, E.; Wagner, D.R.; Devaux, Y. miRNAs as biomarkers of myocardial infarction: A step forward towards personalized medicine? Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beermann, J.; Piccoli, M.T.; Viereck, J.; Thum, T. Non-coding RNAs in Development and Disease: Background, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Approaches. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1297–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.A.; Stroud, R.E.; O’Quinn, E.C.; Black, L.E.; Barth, J.L.; Elefteriades, J.A.; Bavaria, J.E.; Gorman, J.H., 3rd; Gorman, R.C.; Spinale, F.G.; et al. Selective microRNA suppression in human thoracic aneurysms: Relationship of miR-29a to aortic size and proteolytic induction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, D.R.; Chin, J.T.; Dake, B.A.; Maegdefessel, L.; Miller, M.O.; Kimura, N.; Tsao, P.S.; Iosef, C.; Berry, G.J.; Mohr, F.W.; et al. miR-29b participates in early aneurysm development in Marfan syndrome. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, D.Z.; Lu, Q.; Deitch, E.A.; Huo, Y.; Delphin, E.S.; Zhang, C. MicroRNA-145, a novel smooth muscle cell phenotypic marker and modulator, controls vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Weber, J.; Baxter, D.; Galas, D.J. Export of microRNAs and microRNA-protective protein by mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7248–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Sheng, X.; Hou, D.; Chong, H.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, S.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Characterization of serum miRNAs as molecular biomarkers for acute Stanford type A aortic dissection diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Micaelo, N.; Beltran-Debon, R.; Baiges, I.; Faiges, M.; Alegret, J.M. Specific circulating microRNA signature of bicuspid aortic valve disease. J. Transl Med. 2017, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.R.; Goldstein, L.J.; Coady, M.A.; Tittle, S.L.; Rizzo, J.A.; Kopf, G.S.; Elefteriades, J.A. Yearly rupture or dissection rates for thoracic aortic aneurysms: Simple prediction based on size. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 73, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefteriades, J.A.; Ziganshin, B.A. Gratitude to the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection From the Aortic Community. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolenaar, J.L.; Froehlich, W.; Jonker, F.H.; Upchurch, G.R., Jr.; Rampoldi, V.; Tsai, T.T.; Bossone, E.; Evangelista, A.; O’Gara, P.; Pape, L.; et al. Predicting in-hospital mortality in acute type B aortic dissection: Evidence from International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. Circulation 2014, 130, S45–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, Y.; Vausort, M.; McCann, G.P.; Zangrando, J.; Kelly, D.; Razvi, N.; Zhang, L.; Ng, L.L.; Wagner, D.R.; Squire, I.B. MicroRNA-150: A novel marker of left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Lin, P.; Weng, X.; Su, J.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L. MicroRNA-574-5p promotes cell growth of vascular smooth muscle cells in the progression of coronary artery disease. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 97, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustin, A.N.; Chatrou, M.L.; Drozdov, I.; Zheng, Y.; Davidson, S.M.; Soong, D.; Furmanik, M.; Sanchis, P.; De Rosales, R.T.; Alvarez-Hernandez, D.; et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell calcification is mediated by regulated exosome secretion. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.A.; Karunakaran, D.; Geoffrion, M.; Cheng, H.S.; Tandoc, K.; Perisic Matic, L.; Hedin, U.; Maegdefessel, L.; Fish, J.E.; Rayner, K.J. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Atherogenic Macrophages Transfer MicroRNA to Inhibit Cell Migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Treguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, N.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C. Pathogenesis of aortic wall complications in Marfan syndrome. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2018, 33, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikesalingam, A.; Bahia, S.S.; Patterson, B.O.; Peach, G.; Vidal-Diez, A.; Ray, K.K.; Sharma, R.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Holt, P.J.; Thompson, M.M. The shortfall in long-term survival of patients with repaired thoracic or abdominal aortic aneurysms: Retrospective case-control analysis of hospital episode statistics. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2013, 46, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.D.; Barker, A.J.; Kansal, P.; Collins, J.D.; Carr, J.C.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Markl, M. Impact of aneurysm repair on thoracic aorta hemodynamics. Circulation 2013, 128, e341–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibender, S.; Wanga, S.; van der Made, I.; Vos, M.; Mulder, B.J.M.; Balm, R.; de Vries, C.J.M.; de Waard, V. Renal cystic disease in the Fbn1C1039G/+ Marfan mouse is associated with enhanced aortic aneurysm formation. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2019, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shao, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Peng, P.; Ba, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jehangir, T.; Bu, S.; et al. miRNA 206 and miRNA 574-5p are highly expression in coronary artery disease. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 36, e00295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocsai, A.; Jakus, Z.; Vantus, T.; Berton, G.; Lowell, C.A.; Ligeti, E. Kinase pathways in chemoattractant-induced degranulation of neutrophils: The role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activated by Src family kinases. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4321–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Kessinger, C.W.; Cheng, Y.; MacDonald, C.; MacGillivray, T.; Ghoshhajra, B.; Huleihel, L.; Nuri, S.; Yeri, A.S.; Jaffer, F.A.; et al. An HDAC9-MALAT1-BRG1 complex mediates smooth muscle dysfunction in thoracic aortic aneurysm. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Kessinger, C.W.; MacDonald, C.; Jassar, A.S.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Jaffer, F.A.; Lindsay, M.E. Inhibition of the methyltranferase EZH2 improves aortic performance in experimental thoracic aortic aneurysm. Jci Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Wong, D.K.; Hong, K.Y.; Raffai, R.L. Cushioned-Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation (C-DGUC): A Refined and High Performance Method for the Isolation, Characterization, and Use of Exosomes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1740, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoon, M.J.; Imoto, S.; Nolan, J.; Miyano, S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1453–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saldanha, A.J. Java Treeview--extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3246–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, D.M.; Baek, D.; Shin, C.; Bell, G.W.; Grimson, A.; Bartel, D.P. Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, N.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D146–D152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kostoulas, N.; Vlachos, I.S.; Vergoulis, T.; Reczko, M.; Filippidis, C.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-microT web server v5.0: Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W169–W173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, S.; Ammari, M.; Aranda, B.; Breuza, L.; Briganti, L.; Broackes-Carter, F.; Campbell, N.H.; Chavali, G.; Chen, C.; del-Toro, N.; et al. The MIntAct project--IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D358–D363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, J.P.; Graos, M.; Valente, A.X. POLAR MAPPER: A computational tool for integrated visualization of protein interaction networks and mRNA expression data. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boileau, A.; Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Courtois, A.; Zhang, L.; Rodosthenous, R.S.; Das, S.; Sakalihasan, N.; Michel, J.-B.; Lindsay, M.E.; Devaux, Y. MiR-574-5p: A Circulating Marker of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163924
Boileau A, Lino Cardenas CL, Courtois A, Zhang L, Rodosthenous RS, Das S, Sakalihasan N, Michel J-B, Lindsay ME, Devaux Y. MiR-574-5p: A Circulating Marker of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163924
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoileau, Adeline, Christian L. Lino Cardenas, Audrey Courtois, Lu Zhang, Rodosthenis S. Rodosthenous, Saumya Das, Natzi Sakalihasan, Jean-Baptiste Michel, Mark E. Lindsay, and Yvan Devaux. 2019. "MiR-574-5p: A Circulating Marker of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163924
APA StyleBoileau, A., Lino Cardenas, C. L., Courtois, A., Zhang, L., Rodosthenous, R. S., Das, S., Sakalihasan, N., Michel, J. -B., Lindsay, M. E., & Devaux, Y. (2019). MiR-574-5p: A Circulating Marker of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163924