The Cooperative Induction of CCL4 in Human Monocytic Cells by TNF-α and Palmitate Requires MyD88 and Involves MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TNF-α/Palmitate Cooperativity Triggers the CCL4 Expression in Human Monocytic Cells and Primary Human Macrophages
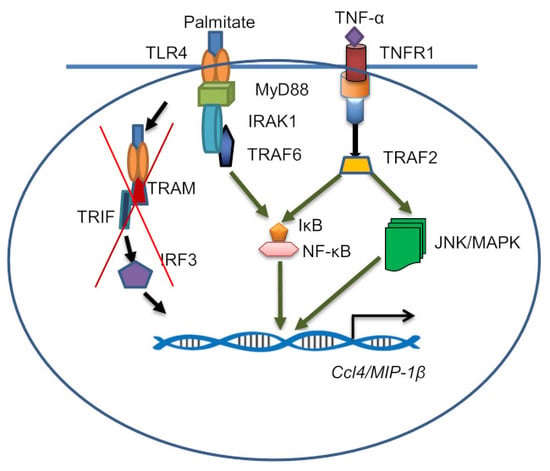
2.2. CCL4 Co-Induction by TNF-α/Palmitate Requires TLR4 Signaling and Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis
2.3. CCL4 Co-Induced by TNF-α/Palmitate is MyD88 Dependent
2.4. CCL4 Expression by TNF-α/Palmitate Co-Stimulation Involves the MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Stimulation
4.2. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs), Primary Macrophage Differentiation and Stimulation
4.3. TLR4 Neutralization or Chemical Inhibition
4.4. Trafficking Inhibition
4.5. Measurement of Cell Viability by MTT Assay
4.6. Measurement of NF-κB/AP-1 Activity
4.7. siRNA-Mediated Genetic Suppression
4.8. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.9. ELISA
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, M.; Guo, Q.; Guo, L.; Lenz, M.; Qian, F.; Koenen, R.R.; Xu, H.; Schilling, A.B.; Weber, C.; Ye, R.D.; Dinner, A.R.; Tang, W.J. Polymerization of MIP-1 chemokine (CCL3 and CCL4) and clearance of MIP-1 by insulin-degrading enzyme. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3952–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bystry, R.S.; Aluvihare, V.; Welch, K.A.; Kallikourdis, M.; Betz, A.G. B cells and professional APCs recruit regulatory T cells via CCL4. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Stebut, E.; Metz, M.; Milon, G.; Knop, J.; Maurer, M. Early macrophage influx to sites of cutaneous granuloma formation is dependent on MIP-1alpha /beta released from neutrophils recruited by mast cell-derived TNFalpha. Blood 2003, 101, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, M.D.; Lundquist, P.G. Labyrinthine morphology and temperature in cryosurgery (guinea pig). Acta Otolaryngol. 1974, 77, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; von Stebut, E. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2004, 36, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, L.M.; Molina, M.J.; Mayor, A.M.; Cruz, J.J.; Rios-Olivares, E.; Rios, Z. Association of serum MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES with clinical manifestations, disease activity, and damage accrual in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczucinski, A.; Losy, J. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in multiple sclerosis. Potential targets for new therapies. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 115, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Hiura, K.; Wilde, J.; Moriyama, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Ozaki, S.; Wakatsuki, S.; Kosaka, M.; Kido, S.; Inoue, D.; Matsumoto, T. Role for macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. Blood 2002, 100, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrosa, E.; Carretero-Iglesia, L.; Boada, A.; Colobran, R.; Faner, R.; Pujol-Autonell, I.; Palou, E.; Esteve, A.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; Ferrandiz, C.; et al. CCL4L polymorphisms and CCL4/CCL4L serum levels are associated with psoriasis severity. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrugacz, M. CCL4/MIP-1beta levels in tear fluid and serum of patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyk, A.; Pierzchala, E.; Caramori, G.; Sozanska, E. Increased expression of CCL4/MIP-1beta in CD8+ cells and CD4+ cells in sarcoidosis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2014, 27, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, D.; Jones, P.L.; Boss, J.M. TNF regulates the in vivo occupancy of both distal and proximal regulatory regions of the MCP-1/JE gene. Immunity 1996, 4, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.C.; Martin, T.; Felts, K.A.; Cobb, R.R. IL-1beta-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in endothelial cells is blocked by proteasome inhibitors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, A.; Wong, F.; Ayala, J.M.; Struthers, M.; Ujjainwalla, F.; Wright, S.D.; Springer, M.S.; Evans, J.; Cui, J. Leukotriene B4 strongly increases monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human monocytes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czermak, B.J.; Lentsch, A.B.; Bless, N.M.; Schmal, H.; Friedl, H.P.; Ward, P.A. Synergistic enhancement of chemokine generation and lung injury by C5a or the membrane attack complex of complement. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchjorsen, J.; Sorensen, L.N.; Paludan, S.R. Expression and function of chemokines during viral infections: from molecular mechanisms to in vivo function. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2003, 74, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yang, S.; Kim, S.O.; Reid, G.; Challis, J.R.; Bocking, A.D. Lipopolysaccharide-induced profiles of cytokine, chemokine, and growth factors produced by human decidual cells are altered by lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 supernatant. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullberg, K.B.; Larsen, J.O.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Effects of LPS and dietary free fatty acids on MCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and macrophages in vitro. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, P.; Chen, Q.; Shah, S.; Du, J.; Tao, B.; Tzameli, I.; Yan, W.; Xu, H. Obesity-related upregulation of monocyte chemotactic factors in adipocytes: involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways. Diabetes 2009, 58, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A.; Wurmbrand, A.P.; Ribeiro, L.; Neto, F.L.; Shore, S.A. Induction of IL-17A precedes development of airway hyperresponsiveness during diet-Induced obesity and correlates with complement factor D. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G. Obesity and free fatty acids. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North. Am. 2008, 37, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P.; Ryden, M. Fatty acids, obesity and insulin resistance. Obesity Facts 2015, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasu, M.R.; Jialal, I. Free fatty acids in the presence of high glucose amplify monocyte inflammation via Toll-like receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E145–E154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.C.; Young, D.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Christ, W.J.; Gusovsky, F. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10689–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic Stojanov, S.; Martinovic, V.; Bogojevic, D.; Poznanovic, G.; Petrovic, A.; Ivanovic-Matic, S.; Grigorov, I. Modulation of diabetes-related liver injury by the HMGB1/TLR4 inflammatory pathway. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, C.L.; Kennedy, E.B.; Roche, H.M. Metabolic inflammation-differential modulation by dietary constituents. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochumon, S.; Wilson, A.; Chandy, B.; Shenouda, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R. Palmitate activates CCL4 expression in human monocytic cells via TLR4/MyD88 dependent activation of NF-kappaB/MAPK/ PI3K signaling systems. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernandez-Veledo, S.; Kramer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin resistance associated to obesity: the link TNF-alpha. Arch Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cildir, G.; Akincilar, S.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation: all immune cells on the stage. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmi, B.K.; Hasty, A.H. The role of chemokines in recruitment of immune cells to the artery wall and adipose tissue. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2010, 52, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzanavari, T.; Giannogonas, P.; Karalis, K.P. TNF-alpha and obesity. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Roub, A.; Kochumon, S.; Akther, N.; Thomas, R.; Kumari, M.; Koshy, M.S.; Tiss, A.; Hannun, Y.A.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. The synergy between palmitate and TNF-alpha for CCL2 production is dependent on the TRIF/IRF3 pathway: Implications for metabolic inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3599–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jialal, I.; Kaur, H.; Devaraj, S. Toll-like receptor status in obesity and metabolic syndrome: a translational perspective. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Atizado, V.; Sindhu, S. Increased adipose tissue expression of TLR8 in obese individuals with or without type-2 diabetes: significance in metabolic inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Mass, A.; Atizado, V.; Al-Hubail, A.; Al-Ghimlas, F.; Al-Arouj, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Dermime, S.; Behbehani, K. Elevated expression of the toll like receptors 2 and 4 in obese individuals: its significance for obesity-induced inflammation. J. Inflam. 2012, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Akhter, N.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Wilson, A.; Shenouda, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Increased expression of the innate immune receptor TLR10 in obesity and type-2 diabetes: Association with ROS-mediated oxidative stress. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Maratha, A.; Siednienko, J.; Natarajan, A.; Gajanayake, T.; Hoashi, S.; Miggin, S. Analysis of inflammatory cytokine and TLR expression levels in type 2 diabetes with complications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatematsu, M.; Yoshida, R.; Morioka, Y.; Ishii, N.; Funami, K.; Watanabe, A.; Saeki, K.; Seya, T.; Matsumoto, M. Raftlin controls lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR4 internalization and TICAM-1 signaling in a cell type-specific manner. J. Inflam. 2016, 196, 3865–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, N.; Hasan, A.; Shenouda, S.; Wilson, A.; Kochumon, S.; Ali, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R. TLR4/MyD88 -mediated CCL2 production by lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin): Implications for metabolic inflammation. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2018, 17, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Al-Roub, A.; Koshy, M.; Thomas, R.; Ahmad, R. Palmitate-induced MMP-9 expression in the human monocytic cells is mediated through the TLR4-MyD88 dependent mechanism. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Manabe, I.; Oishi-Tanaka, Y.; Ohsugi, M.; Kono, N.; Ogata, F.; Yagi, N.; Ohto, U.; Kimoto, M.; Miyake, K.; et al. Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link beta cell dysfunction and islet inflammation. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro-Munoz, I.; Compte, M.; Alvarez-Cienfuegos, A.; Alvarez-Vallina, L.; Sanz, L. Lipopolysaccharide activates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated NF-kappaB signaling pathway and proinflammatory response in human pericytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, J.; Jenner, R.G.; Murray, H.L.; Gerber, G.K.; Gifford, D.K.; Young, R.A. Coordinated binding of NF-kappaB family members in the response of human cells to lipopolysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5899–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bryan, J.L.; DeLassus, E.; Chang, L.W.; Liao, W.; Sandell, L.J. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta and NF-kappaB mediate high level expression of chemokine genes CCL3 and CCL4 by human chondrocytes in response to IL-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33092–33103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.J.; Douglas, S.D.; Lai, J.P.; Pleasure, D.E.; Li, Y.; Williams, M.; Bannerman, P.; Song, L.; Ho, W.Z. Interleukin-1beta stimulates macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha and -1beta expression in human neuronal cells (NT2-N). J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.T.; Ahmad, R.; Morisset, R.; Ahmad, A.; Menezes, J. Peripheral blood cytotoxic gammadelta T lymphocytes from patients with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and AIDS lyse uninfected CD4+ T cells, and their cytocidal potential correlates with viral load. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sindhu, S.; Kochumon, S.; Shenouda, S.; Wilson, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. The Cooperative Induction of CCL4 in Human Monocytic Cells by TNF-α and Palmitate Requires MyD88 and Involves MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184658
Sindhu S, Kochumon S, Shenouda S, Wilson A, Al-Mulla F, Ahmad R. The Cooperative Induction of CCL4 in Human Monocytic Cells by TNF-α and Palmitate Requires MyD88 and Involves MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184658
Chicago/Turabian StyleSindhu, Sardar, Shihab Kochumon, Steve Shenouda, Ajit Wilson, Fahd Al-Mulla, and Rasheed Ahmad. 2019. "The Cooperative Induction of CCL4 in Human Monocytic Cells by TNF-α and Palmitate Requires MyD88 and Involves MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184658
APA StyleSindhu, S., Kochumon, S., Shenouda, S., Wilson, A., Al-Mulla, F., & Ahmad, R. (2019). The Cooperative Induction of CCL4 in Human Monocytic Cells by TNF-α and Palmitate Requires MyD88 and Involves MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184658