Fabrication of Surfactant-Dispersed HiPco Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Alginate Hydrogel Composites as Cellular Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
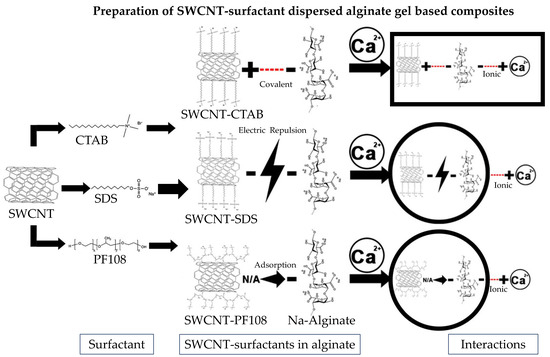
2.1. Fabrication of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.2. Raman Spectroscopic Characterization of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.3. Near-Infrared (NIR) Fluorescence Microscopy of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.4. Rheological Characterization of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.5. Electrical Characterization and Conductivity of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
2.7. Swelling and Degradation
2.8. Cell Culture and Live/Dead Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental
4.2. Fabrication of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.3. Raman Spectroscopic Characterization of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.4. Near-Infrared (NIR) fluorescence Microscopy of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.5. Rheological Characterization of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.6. Electrical Characterization and Conductivity of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy of SWCNT-Alginate Composites
4.8. Swelling and Degradation
4.9. Cell Culture and Live/Dead Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNT | Carbon Nanotubes |
| SWCNT | Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes |
| MWCNT | Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes |
| PF108 | Pluronic F108 |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide |
References
- Sun, J.; Tan, H.P. Alginate-based biomaterials for regenerative medicine applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.E.; Nuge, T.; Yeow, T.K.; Nordin, N.; Prasad, R.G.S.V. Gelatin based scaffolds for tissue engineering-a review. Polym. Res. J. 2015, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-based nanoparticles as drug and gene delivery systems: Reviewing three decades of research. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Chen, X.B.; Schreyer, D.J. Influence of calcium ions on cell survival and proliferation in the context of an alginate hydrogel. Isrn. Chem. Eng. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Gámez, M.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Low-cost advanced hydrogels of calcium alginate/carbon nanofibers with enhanced water diffusion and compression properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Aroca, A.; Iskandar, L.; Deb, S. Green synthetic routes to alginate-graphene oxide composite hydrogels with enhanced physical properties for bioengineering applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano-Aroca, A.; Ruiz-Pividal, J.F.; Llorens-Gámez, M. Enhancement of water diffusion and compression performance of crosslinked alginate films with a minuscule amount of graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joddar, B.; Garcia, E.; Casas, A.; Stewart, C.M. Development of functionalized multi-walled carbon-nanotube-based alginate hydrogels for enabling biomimetic technologies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronikowski, M.J.; Willis, P.A.; Colbert, D.T.; Smith, K.A.; Smalley, R.E. Gas-phase production of carbon single-walled nanotubes from carbon monoxide via the HiPco process: A parametric study. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2001, 19, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, V.C.; Strano, M.S.; Haroz, E.H.; Hauge, R.H.; Smalley, R.E.; Schmidt, J.; Talmon, Y. Individually suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes in various surfactants. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, E.; Dockery, P.; Greiser, U.; Murphy, M.; Barron, V. Carbon nanotubes and mesenchymal stem cells: Biocompatibility, proliferation and differentiation. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pok, S.; Vitale, F.; Eichmann, S.L.; Benavides, O.M.; Pasquali, M.; Jacot, J.G. Biocompatible carbon nanotube–chitosan scaffold matching the electrical conductivity of the heart. Acs. Nano 2014, 8, 9822–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaklamani, G.; Kazaryan, D.; Bowen, J.; Iacovella, F.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Deligeorgis, G. On the electrical conductivity of alginate hydrogels. Regen. Biomater. 2018, 5, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Iijima, S.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Carbon Nanotubes, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 1–198. [Google Scholar]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Jorio, A.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Saito, R. Raman spectroscopy on isolated single wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2002, 40, 2043–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Filho, A.G.; Chou, S.G.; Samsonidze, G.G.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; An, L.; Liu, J.; Swan, A.K.; Ünlü, M.S.; Goldberg, B.B.; et al. Stokes and anti-stokes raman spectra of small-diameter isolated carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 115428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennrich, F.; Krupke, R.; Lebedkin, S.; Arnold, K.; Fischer, R.; Resasco, D.E.; Kappes, M.M. Raman spectroscopy of individual single-walled carbon nanotubes from various sources. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 10567–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Laiho, P.; Kauppinen, E.I. Validity of measuring metallic and semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube fractions by quantitative Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudasaka, M.; Yomogida, Y.; Zhang, M.F.; Tanaka, T.; Nakahara, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Okamatsu-Ogura, Y.; Machida, K.; Ishihara, K.; Saeki, K.; et al. Near-infrared photoluminescent carbon nanotubes for imaging of brown fat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil Kumar, S.; Allen, A.C.; Tasnim, N.; Akter, T.; Park, S.; Kumar, A.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Ito, Y.; Suggs, L.J.; Joddar, B. The applicability of furfuryl-gelatin as a novel bioink for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Astrain, C.; Gandini, A.; Peña, C.; Algar, I.; Eceiza, A.; Corcuera, M.; Gabilondo, N. Diels–alder “click” chemistry for the cross-linking of furfuryl-gelatin-polyetheramine hydrogels. Rsc. Adv. 2014, 4, 35578–35587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Amirthalingam, S.; Jayakumar, R. Carrageenan based hydrogels for drug delivery, tissue engineering and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: III. Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, A.; Takano, Y.; Kamimura, Y.; Fujiwara, O. Effect of the averaging volume and algorithm on the in situ electric field for uniform electric-and magnetic-field exposures. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, N243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofani, G.; Raffa, V.; Pensabene, V.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. Dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous pluronic F127 solutions for biological applications. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2009, 17, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.A.; Lesser, A.J.; McCarthy, T.J. Preparation and characterization of microcellular polystyrene foams processed in supercritical carbon dioxide. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4614–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.C.; Wake, M.C.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Mikos, A.G. Biodegradable polymer scaffolds to regenerate organs. In Biopolymers Ii; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 245–274. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianova, G.P.; Pakhomov, S.I. Porous materials from crystallizable polyolefins produced by gel technology. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1997, 37, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Aroca, A.; Llorens-Gámez, M. Dynamic mechanical analysis and water vapour sorption of highly porous poly (methyl methacrylate). Polymer 2017, 125, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guvendiren, M.; Molde, J.; Soares, R.M.D.; Kohn, J. Designing biomaterials for 3D printing. Acs Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Aroca, A.; Vera-Donoso, C.; Moreno-Manzano, V. Bioengineering approaches for bladder regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursac, N.; Papadaki, M.; Cohen, R.J.; Schoen, F.J.; Eisenberg, S.R.; Carrier, R.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Freed, L.E. Cardiac muscle tissue engineering: Toward an in vitro model for electrophysiological studies. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1999, 277, H433–H444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; McMillin, J.B.; Lewis, A.; Moore, M.; Zhu, W.G.; Williams, R.S.; Kellems, R.E. Electrical stimulation of neonatal cardiac myocytes activates the NFAT3 and GATA4 pathways and up-regulates the adenylosuccinate synthetase 1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.; Castranova, V.; Kisin, E.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Murray, A.; Gandelsman, V.; Maynard, A.; Baron, P. Exposure to carbon nanotube material: Assessment of nanotube cytotoxicity using human keratinocyte cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2003, 66, 1909–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devre, R.D.; Budhlall, B.M.; Barry, C.F. Enhancing the colloidal stability and electrical conductivity of single-walled carbon nanotubes dispersed in water. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Gillispie, G.J.; Copus, J.S.; Seol, Y.J.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J.; Lee, S.J. Optimization of gelatin-alginate composite bioink printability using rheological parameters: A systematic approach. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 034106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, O.; Bouhadir, K.H.; Mansour, J.M.; Alsberg, E. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with tunable biodegradation rates and mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Richards, D.J.; Pollard, S.; Tan, Y.; Rodriguez, J.; Visconti, R.P.; Trusk, T.C.; Yost, M.J.; Yao, H.; Markwald, R.R.; et al. Engineering alginate as bioink for bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joddar, B.; Tasnim, N.; Thakur, V.; Kumar, A.; McCallum, R.; Chattopadhyay, M. Delivery of mesenchymal stem cells from gelatin-alginate hydrogels to stomach lumen for treatment of gastroparesis. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Choi, J.; Park, Y.D.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.J.; Ahn, C.B.; Choi, H.; Sun, K. Sodium alginate hydrogel-based bioprinting using a novel multinozzle bioprinting system. Artif. Organs. 2011, 35, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.H.; Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of high performance polyethersulfone UF hollow fiber membranes using amphiphilic Pluronic block copolymers as pore-forming additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 380, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H.; Fukumori, Y.; Peppas, N.A. Monodisperse nanoparticles of poly (ethylene glycol) macromers and N-isopropyl acrylamide for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Saha, A.; Maity, A.R.; Ray, S.C.; Jana, N.R. Carbon nanoparticle-based fluorescent bioimaging probes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Sadana, A.K.; Peera, A.; Chattopadhyay, J.; Gu, Z.N.; Hauge, R.H.; Billups, W.E. A convenient route to functionalized carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciubuc, J.; Manciu, M.; Maran, A.; Yaszemski, M.; Sundin, E.; Bennet, K.; Manciu, F. Raman spectroscopic and microscopic analysis for monitoring renal osteodystrophy signatures. Biosensors 2018, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowers, R.S.; Allen, S.C.; Suggs, L.J. Dynamic phototuning of 3D hydrogel stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 102, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolai, S.; Leu, H.Y.; Magda, J.; Tabib-Azar, M. Metal-Oxide-Hydrogel Field-Effect Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 28–31 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]







| Sample Description | Raman Spectra for SWCNT | NIR Spectra for SWCNT | Elastic Moduli & Complex Viscosity | Electrical Conductivity | Pore Size | Swelling and Degradation | Biocompatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWCNT-PF108-alginate | Highest Signal Intensity | Highest Signal Intensity | Not statistically different compared to baseline | A significant increase compared to baseline p = 0.02 (*1); p = 0.02(*2) | Not statistically different compared to baseline | A significant decrease compared to baseline p = 0.03 | Similar to the baseline |
| SWCNT-CTAB-alginate | Less compared to PF108 | Less compared to PF108 | Significant increase; p = 0.02 and p = 0.03, respectively | Not statistically different compared to baseline | Not statistically different compared to baseline | Not statistically different compared to baseline | NA |
| SWCNT-SDS-alginate | Less compared to PF108 | Less compared to PF108 | Not statistically different compared to baseline | Not statistically different compared to baseline | Not statistically different compared to baseline | Not statistically different compared to baseline | NA |
| Alginate | NA | NA | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline | Baseline |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez-Primo, F.; Anil Kumar, S.; Manciu, F.S.; Joddar, B. Fabrication of Surfactant-Dispersed HiPco Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Alginate Hydrogel Composites as Cellular Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194802
Alvarez-Primo F, Anil Kumar S, Manciu FS, Joddar B. Fabrication of Surfactant-Dispersed HiPco Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Alginate Hydrogel Composites as Cellular Products. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194802
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez-Primo, Fabian, Shweta Anil Kumar, Felicia S. Manciu, and Binata Joddar. 2019. "Fabrication of Surfactant-Dispersed HiPco Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Alginate Hydrogel Composites as Cellular Products" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194802
APA StyleAlvarez-Primo, F., Anil Kumar, S., Manciu, F. S., & Joddar, B. (2019). Fabrication of Surfactant-Dispersed HiPco Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Alginate Hydrogel Composites as Cellular Products. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194802