Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
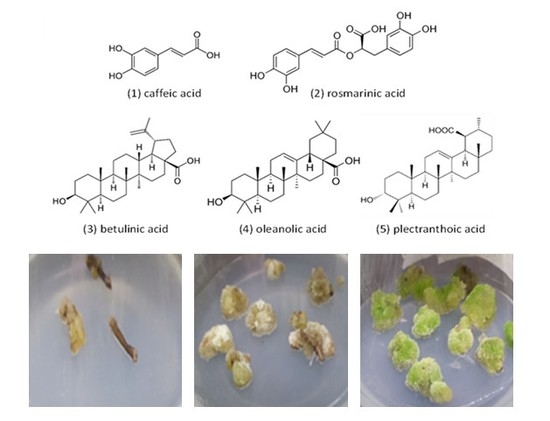
2.1. Optimization of Callogenesis from Different Initial Explants
2.2. Evaluation of Secondary Metabolites Production
2.3. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Potential of I. rugosus Callus Extracts
2.4. Correlations Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Callogenic Frequency
3.4. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds Content
3.5. Quantification and Identification by HPLC
3.6. Antioxidant DPPH Assay
3.7. Antioxidant ORAC Assay
3.8. Antioxidant ABTS Assay
3.9. Antioxidant FRAP Assay
3.10. Antioxidant CUPRAC Assay
3.11. Metal Chelating Activity Assay
3.12. Collagenase Assay
3.13. Elastase Assay
3.14. Hyaluronidase Assay
3.15. Tyrosinase Assay
3.16. Anti-AGE Formation Activity
3.17. SIRT-1 Assay
3.18. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAA | α-Naphthalene acetic acid |
| BAP | 6-Benzyl adenine |
| TDZ | Thidiazuron |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| CE | Callus Extract |
| WPE | Whole plant extract |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| TPC | Total Phenolic Content |
| TFC | Total Flavonoid Content |
| DW | Dry Weight |
| FW | Fresh Weight |
| PGRs | Plant Growth Regulators |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| CUPRAC | Cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity |
| ORAC | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
| ABTS | 2,2-Azinobis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| AGE | Advanced glycation end products |
References
- Abbasi, A.M.; Dastagir, G.; Hussain, F.; Sanaullah, P. Ethnobotany and marketing of crude drug plants in district Haripur. Pak. J. Plant Sci. 2005, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.H.; Huang, S.X.; Han, Q.B. Diterpenoids from Isodon species and their biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 673–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Rashid, A.; Murad, W.; Bergmeier, E. Diversity and use of ethnomedicinal plants in the region of Swat. North Pak. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2013, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, A.; Uddin, N.; Atif, M. Antibacterial and phytotoxic profile of selected Pakistani medicinal plants. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 20, 540–544. [Google Scholar]
- Janbaz, K.H.; Arif, J.; Saqib, F.; Imran, I.; Ashraf, M.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; De Feo, V. In-vitro and in-vivo validation of ethnopharmacological uses of methanol extract of Isodon rugosus Wall. ex Benth. (Lamiaceae). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.W.; Khatoon, S. Ethnobotanical studies on useful trees and shrubs of Haramosh and Bugrote valleys, in Gilgit northern areas of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2007, 39, 699–710. [Google Scholar]
- Habtemariam, S. Molecular pharmacology of rosmarinic and salvianolic acids: Potential seeds for Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothana, R.A.; Al-Said, M.S.; Al-Yahya, M.A.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Khaled, J.M. GC and GC/MS analysis of essential oil composition of the endemic Soqotraen Leucas virgata Balf. f. and its antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 23129–23139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Ahmad, S.; Ayaz, M. Phytochemical and toxicological investigations of crude methanolic extracts, subsequent fractions and crude saponins of Isodon rugosus. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Ahmad, S.; Ayaz, M. Investigations of anticholinestrase and antioxidant potentials of methanolic extract, subsequent fractions, crude saponins and flavonoids isolated from Isodon rugosus. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, M.; Ahmad, S.; Sadiq, A. Demonstration of biological activities of extracts from Isodon rugosus Wall. Ex Benth: Separation and identification of bioactive phytoconstituents by GC-MS analysis in the ethyl acetate extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, A.; Zeb, A.; Ullah, F.; Ahmad, S.; Ayaz, M.; Rashid, U.; Muhammad, N. Chemical characterization, analgesic, antioxidant, and anticholinesterase potentials of essential oils from Isodon rugosus Wall. ex. Benth. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Xu, J.G. Assessment of the bioactive compounds, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Isodon rubescens as affected by drying methods. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mogib, M.; Albar, H.A.; Batterjee, S.M. Chemistry of genus Plectranthus. Molecules 2002, 7, 271–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, O.; Simoes, M.F.; Duarte, A.; Valderia, M.L.; Torre, M.C.; Rodriguez, B. An antimicrobial abietane from the roots of Plectranthus hereroensis. Phytochemistry 1994, 38, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.; Wahlqvist, M.L. A model for the role of the proline-linked pentose-phosphate pathway in phenolic phytochemical bio-synthesis and mechanism of action for human health and environmental applications. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S. Plants: A rich source of herbal medicine. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Q.L.; Rinehart, A.R.; Simon, S.R.; Cheronis, J.C. Inhibition of human leucocyte elastase by ursolic acid. Evidence for a binding site for pentacyclic triterpenes. Biochem. J. 1991, 277, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coricovac, D.O.; Soica, C.O.; Muntean, D.A.; Popovici, R.A.; Dehelean, C.A.; Hogea, E.L. Assessment of the effects induced by two triterpenoids on liver mitochondria respiratory function isolated from aged rats. Rev. Chim. 2015, 66, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Howitz, K.T.; Bitterman, K.J.; Cohen, H.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Lavu, S.; Wood, J.G.; Zipkin, R.E.; Chung, P.; Kisielewski, A.; Zhang, L.L.; et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, K.N.; Sharma, N.C.; Tiwari, V.; Singh, B.D. Micropropagation of Centella asiatica (L.), a valuable medicinal herb. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2000, 63, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renouard, S.; Corbin, C.; Drouet, S.; Medvedec, B.; Doussot, J.; Colas, C.; Maunit, B.; Bhambra, A.S.; Gontier, E.; Jullian, N.; et al. Investigation of Linum flavum (L.) hairy root cultures for the production of anticancer aryltetralin lignans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaniarasu, R.; Kumar, T.S.; Rao, M.V. Mass propagation of Plectranthus bourneae Gamble through indirect organogenesis from leaf and internode explants. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2016, 22, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotoarison, D.A.; Greesier, B.; Trotin, F.; Brunet, C.; Luyckx, M.; Vasseur, J.; Cazin, M.; Cazin, J.C.; Pinkas, M. Antioxidant activities of polyphenolic extracts from flowers, in vitro cultures and cell suspension cultures of Crataegus monogyna. Pharmazie 1997, 52, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pietta, P.G. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xian, J.; Xiao, S.; Xu, H. In vitro culture and rapid propagation of Isodon serra. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs 2001, 32, 255–256. [Google Scholar]
- Thirugnanasampandan, R.; Mahendran, G.; Bai, V.N. High frequency in vitro propagation of Isodon wightii (Bentham) H. Hara. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Su, Y.; Chao, E.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, F.; Xue, T.; Sheng, W.; Teng, J.; Xue, J. Callus-mediated plant regeneration in Isodon amethystoides using young seedling leaves as starting materials. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquah, A.; Hashmi, S.S.; Mushtaq, S.; Renouard, S.; Blondeau, J.P.; Abbasi, R.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Exploiting in vitro potential and characterization of surface modified Zinc oxide nanoparticles of Isodon rugosus extract: Their clinical potential towards HepG2 cell line and human pathogenic bacteria. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sreedevi, E.; Anuradha, M.; Pullaiah, T. Plant regeneration from leaf-derived callus in Plectranthus barbatus Andr. [Syn.: Coleus forskohlii (Wild.) Briq.]. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, S.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C. Trends in accumulation of pharmacologically important antioxidant-secondary metabolites in callus cultures of Linum usitatissimum L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 129, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Shekhawat, G.S. Establishment and characterization of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) cell suspension culture: An in-vitro approach for production of stevioside. Acta Physiol. Plant 2013, 35, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yu, L.J.; Hu, Q.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Sun, Y.P. Establishment of callus and cell suspension cultures of Corydalis saxicola Bunting, a rare medicinal plant. Z. Naturforsch. C 2006, 61, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijaya, T.; Reddy, N.V.; Ghosh, S.B.; Chandramouli, K.; Pushpalatha, B.; Anitha, D.; Pragathi, D. Optimization of biomass yield and asiaticoside accumulation in the callus cultures from the leaves of Centella asiatica. URBAN. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 2, 5966–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, B.N.S.; Victor, J.; Singh, R.P.S.; Fletcher, R.A.; Saxena, P.K. In vitro regeneration of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Stimulation of direct organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis by thidiazuron. Plant Growth Regul. 1996, 19, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoo, A.; Babalar, M.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Fattahi Moghaddam, M.R.; Nejad Ebrahimi, S.S.N. In-vitro callus induction and rosmarinic acid quantification in callus culture of Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad (Lamiaceae). Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.T. Cytokinin-controlled indoleacetic acid oxidase isoenzymes in tobacco callus cultures. Plant Physiol. 1971, 47, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Abbasi, B.H.; Zeb, A.; Xu, L.L.; Wei, Y.H. Thidiazuron: A multi-dimensional plant growth regulator. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 8984–9000. [Google Scholar]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, H. Production of biologically active phenolic acids in Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott in vitro cultures cultivated on different variants of the Murashige and Skoog medium. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 72, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, A.; Fadzliana, N.; Sekeli Rogayah, S.; Shaharuddin Azmi, N.; Abdulla Janna, O.A. Addition of l-tyrosine to improve betalain production in red pitaya callus. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2017, 40, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, U.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Morphogenic and biochemical variations under different spectral lights in callus cultures of Artemisia absinthium L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 130, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, M.; Drouet, S.; Nadeem, M.; Giglioli-Guivarc’h, N.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Differential accumulation of silymarin induced by exposure of Silybum marianum L. callus cultures to several spectres of monochromatic lights. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 184, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.O.; Chun, O.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Moon, H.-Y.; Lee, C.Y. Quantification of polyphenolics and their antioxidant capacity in fresh plums. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6509–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djeridane, A.; Yousfi, M.; Nadjemi, B.; Boutassouna, D.; Stocker, P.; Vidal, N. Antioxidant activity of some Algerian medicinal plants extracts containing phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, M.M.; Boyce, A.N.; Osman, N.; Hossain, A.S. Physiochemical and phytochemical properties of wax apple (Syzygium samarangense [Blume] Merrill & L. M. Perry var. Jambu Madu) as affected by growth regulator application. Sci. World J. 2012, 13, 728613. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta, A.; Kamiya, K.; Satake, T.; Saiki, Y. Triterpenoids from callus tissue cultures of Paeonia Species. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudone, L.; Zymone, K.; Raudonis, R.; Vainoriene, R.; Motiekaityte, V.; Janulis, V. Phenological changes in triterpenic and phenolic composition of Thymus L. species. Ind. Crop Prod. 2017, 15, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A. Anti-nociceptive Activity of Ethnomedicinally Important Analgesic Plant Isodon rugosus Wall. ex Benth: Mechanistic Study and Identifications of Bioactive Compounds. Front Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.S.; Pandey, V.; Chauhan, A.; Tiwari, R. Characterization of the essential oil composition of Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd. from garhwal region of western himalaya. Med. Aromat. Plants 2015, S3, 002. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Khan, A.U.; Ullah, R.; SAlsaid, M.; Salman, S.; Iftikhar, S.; Marwat, G.A.; Sadique, M.; Jan, S.; Adnan, M.; et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-bacterialpotential of essential oil of medicinal plant Isodon rugosus. J. Essent Oil Bear. Plants 2017, 20, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, H.; Pandey, P.; Singh, S.; Gupta, R.; Suchitra Banerjee, S. Production of anti-cancer triterpene (betulinic acid) from callus cultures of different Ocimum species and its elicitation. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 64–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Chaturvedi, R. Simultaneous determination and quantification of three pentacyclic triterpenoids—Betulinic acid, oleanolic acid, and ursolic acid in cell cultures of Lantana camara L. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2010, 46, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiar, Z.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Sonboli, A.; Farimani, M.M.; Ayyar, M. In vitro propagation, genetic and phytochemical assessment of Thymus persicus a medicinally important source of pentacyclic triterpenoid. Biologia 2014, 69, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoreyev, S.A.; Inyushkina, Y.V.; Bulgakov, V.P.; Veselova, M.V.; Tchernoded, G.K.; Gerasimenko, A.V.; Zhuravlev, Y.N. Production of allantoin, rabdosiin and rosmarinic acid in callus cultures of the seacoastal plant Mertensia maritima (Boraginaceae). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2012, 110, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagina, Y.V.; Kiselev, K.V.; Bulgakov, V. Biotechnological analysis of caffeic acid metabolites possessing potent antinephritic activity. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2140–2141. [Google Scholar]
- Khojasteh, A.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Hidalgo, D.; Corchete, P.; Palazon, J. New trends in biotechnological production of rosmarinic acid. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 2393–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Cao, G.; Matin, A.; Sofic, E.; McEwen, J.; O’Brien, C.; Lischner, N.; Ehlenfeldt, M.; Kalt, W.; Krewer, G.; et al. Antioxidant capacity as influenced by total phenolic and anthocyanin content, maturity, and variety of Vaccinium species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanaarachchi, G.D.; Samarasekera, J.K.; Mahanama, K.R.; Hemalal, K.D. Tyrosinase, elastase, hyaluronidase, inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Sri Lankan medicinal plants for novel cosmeceuticals. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 31, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, R. Investigations of anti-aging potential of Hypericum origanifolium Willd. for skincare formulations. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 31, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkogkolou, P.; Böhm, M. Advanced glycation end products: Key players in skin aging? Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, Y.S.; Kuno, A.; Hosoda, R.; Horio, Y. Regulation of FOXOs and p53 by SIRT1 modulators under oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, H.S. The anti-aging, metabolism potential of SIRT1. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 9, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, M.; Kim, S.K.; Berdichevsky, A.; Guarente, L. A role for SIR-2.1 regulation of ER stress response genes in determining C. elegans life span. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.H.; Poon, P.C.; Glatt-Deeley, H.; Abrams, J.M.; Helfand, S.L. Neuronal expression of p53 dominant-negative proteins in adult Drosophila melanogaster extends lifespan. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.; Guarente, L. Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan by sir-2.1 transgenes. Nature 2011, 477, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Cho, J.J.; Park, E.J.; Choi, J.D. Anti-elastase and anti-hyaluronidase of phenolic substance from Areca catechu as a new anti-ageing agent. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2001, 23, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Production of commercially important secondary metabolites and antioxidant activity in cell suspension cultures of Artemisia absinthium L. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 49, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velioglu, Y.S.; Mazza, G.; Gao, L.; Oomah, B.D. Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected fruits, vegetables, and grain products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4113–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Güçlü, K.; Özyürek, M.; Karademir, S.E. Novel total antioxidant capacity index for dietary polyphenols and vitamins C and E, using their cupric ion reducing capability in the presence of neocuproine: CUPRAC method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.; Chauhan, A.S.; Sharma, B. Isolation and characterization of some phytochemicals from Indian traditional plants. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 549850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenauer, J.; Mäckle, S.; Sußmann, D.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Carle, R. Inhibitory effects of polyphenols from grape pomace extract on collagenase and elastase activity. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakul, P.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Phytochemicals and anti-aging potentials of the extracts from Lagerstroemia speciosa and Lagerstroemia floribunda. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.M.; Huang, Q.; Lin, M.Z.; Ou-Yang, C.; Huang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, K.L.; Feng, H.L. Condensed tannins from longan bark as inhibitor of tyrosinase: Structure, activity, and mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewseejan, N.; Siriamornpun, S. Bioactive components and properties of ethanolic extract and its fractions from Gynura procumbens leaves. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| S. No. | Treatment (mg/L) | Callus Initiation (day) | Callus Induction Frequency (%) | Callus Color | Callus Texture | Degree of Callus Formation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem | Leaf | Stem | Leaf | |||||
| 0 | Control (MS0) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1 | MS + TDZ 1.0 | 10 | 14 | 80–100 | DG | F | C | +++ |
| 2 | MS + TDZ 2.0 | 10 | 14 | 80–100 | DG | F | C | +++ |
| 3 | MS + TDZ 3.0 | 10 | 14 | 80–100 | DG | F | C | +++ |
| 4 | MS + TDZ 4.0 | 10 | 14 | 80–100 | DG | F | C | +++ |
| 5 | MS + TDZ 5.0 | 10 | 14 | 80–100 | DG | F | C | +++ |
| 6 | MS + NAA 1.0 | 12 | 12 | 40–60 | SG | F | C | ++ |
| 7 | MS + NAA 2.0 | 12 | 12 | 40–60 | SG | F | C | ++ |
| 8 | MS + NAA 3.0 | 12 | 12 | 40–60 | SG | F | C | ++ |
| 9 | MS + NAA 4.0 | 12 | 12 | 40–60 | SG | F | C | ++ |
| 10 | MS + NAA 5.0 | 12 | 12 | 40–60 | SG | F | C | ++ |
| 11 | MS + BAP 1.0 | 20 | 20 | 20–30 | SLG | F | C | + |
| 12 | MS + BAP 2.0 | 20 | 20 | 20–30 | SLG | F | C | + |
| 13 | MS + BAP 3.0 | 20 | 20 | 20–30 | SLG | F | C | + |
| 14 | MS + BAP 4.0 | 20 | 20 | 20–30 | SLG | F | C | + |
| 15 | MS + BAP 5.0 | 20 | 20 | 20–30 | SLG | F | C | + |
| 16 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + NAA 1.0 | 8 | 8 | 90–100 | FG | F | C | +++ |
| 17 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + NAA 2.0 | 8 | 8 | 90–100 | FG | F | C | +++ |
| 18 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + NAA 3.0 | 8 | 8 | 90–100 | FG | F | C | +++ |
| 19 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + NAA 4.0 | 8 | 8 | 90–100 | FG | F | C | +++ |
| 20 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + NAA 5.0 | 8 | 8 | 90–100 | FG | F | C | +++ |
| 21 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + BAP 1.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + BAP 2.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + BAP 3.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + BAP 4.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | MS + TDZ 1.0 + BAP 5.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sample | CA (µg/g DW) | RA (µg/g DW) | BA (µg/g DW) | OA (µg/g DW) | PA (µg/g DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ir#1 | 614.8 ± 20.2 | 1074.7 ± 18.9 | 98.0 ± 14.3 | 536.2 ± 18.8 | 454.8 ± 39.1 |
| Ir#2 | 488.4 ± 24.6 | 751.6 ± 24.1 | 91.8 ± 19.5 | 201.7 ± 5.3 | 113.7 ± 33.9 |
| Ir#3 | 784.0 ± 14.8 | 1519.5 ± 17.8 | 104.3 ± 18.8 | 348.4 ± 16.3 | 304.6 ± 33.0 |
| Ir#4 | 735.6 ± 26.9 | 1158.3 ± 27.1 | 141.8 ± 16.3 | 317.1 ± 19.5 | 207.6 ± 28.2 |
| Ir#5 | 728.2 ± 7.6 | 1685.2 ± 44.7 | 132.5 ± 24.8 | 631.0 ± 24.8 | 379.7 ± 14.2 |
| Ir#6 | 979.5 ± 12.1 | 1259.0 ± 27.5 | 66.7 ± 9.4 | 198.2 ± 9.4 | 116.8 ± 23.6 |
| Ir#7 | 575.6 ± 20.7 | 1279.0 ± 9.0 | 54.2 ± 5.4 | 389.0 ± 19.6 | 132.5 ± 18.8 |
| Ir#8 | 901.6 ± 10.3 | 1708.9 ± 57.1 | 85.7 ± 9.1 | 386.0 ± 24.8 | 207.6 ± 8.8 |
| Ir#9 | 647.2 ± 19.8 | 936.7 ± 13.1 | 22.9 ± 5.8 | 204.4 ± 23.6 | 69.9 ± 14.3 |
| Ir#10 | 779.3 ± 18.0 | 797.1 ± 37.0 | 91.8 ± 10.8 | 248.3 ± 14.3 | 145.0 ± 23.6 |
| Ir#11 | 886.8 ± 24.2 | 2013.5 ± 18.7 | 171.2 ± 9.2 | 331.2 ± 16.4 | 313.8 ± 14.1 |
| Ir#12 | 835.8 ± 9.9 | 1335.9 ± 67.2 | 145.4 ± 5.1 | 429.8 ± 23.9 | 429.8 ± 14.3 |
| Sample | DPPH (TEAC) | ABTS (TEAC) | ORAC (TEAC) | FRAP (AEAC) | CUPRAC (AEAC) | Chelation (µmol Fe2+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ir#1 | 674.4 ± 4.7 | 585.5 ± 9.0 | 421.8 ± 23.1 | 285.4 ± 6.3 | 260.3 ± 4.7 | 31.6 ± 0.9 |
| Ir#2 | 474.4 ± 13.5 | 434.5 ± 15.4 | 306.7 ± 18.5 | 211.9 ± 3.2 | 193.3 ± 8.4 | 23.0 ± 1.4 |
| Ir#3 | 911.7 ± 14.2 | 798.8 ± 15.1 | 529.4 ± 18.3 | 393.4 ± 6.9 | 354.2 ± 8.7 | 41.6 ± 1.0 |
| Ir#4 | 721.2 ± 5.9 | 659.6 ± 25.1 | 453.2 ± 22.3 | 318.1 ± 6.4 | 273.5 ± 7.1 | 33.8 ± 1.7 |
| Ir#5 | 1005.5 ± 13.8 | 879.5 ± 60.1 | 624.8 ± 9.0 | 456.8 ± 2.6 | 401.3 ± 2.7 | 45.2 ± 2.7 |
| Ir#6 | 779.4 ± 5.4 | 708.1 ± 9.3 | 470.9 ± 14.5 | 354.8 ± 13.6 | 312.5 ± 8.8 | 34.3 ± 2.5 |
| Ir#7 | 780.8 ± 6.2 | 688.2 ± 8.2 | 466.8 ± 9.6 | 349.3 ± 12.3 | 277.8 ± 8.4 | 34.9 ± 3.3 |
| Ir#8 | 1043.2 ± 15.9 | 945.8 ± 6.4 | 641.0 ± 11.5 | 475.3 ± 10.0 | 410.8 ± 7.8 | 47.3 ± 1.5 |
| Ir#9 | 563.1 ± 15.3 | 522.4 ± 5.2 | 350.1 ± 5.5 | 251.3 ± 9.0 | 235.7 ± 10.7 | 26.6 ± 2.8 |
| Ir#10 | 516.3 ± 9.2 | 444.7 ± 18.2 | 318.1 ± 13.0 | 231.0 ± 8.8 | 186.1 ± 13.4 | 27.0 ± 2.8 |
| Ir#11 | 1203.7 ± 53.2 | 944.7 ± 37.1 | 733.53 ± 7.3 | 535.8 ± 9.9 | 460.2 ± 5.5 | 54.8 ± 2.2 |
| Ir#12 | 823.1 ± 25.6 | 727.1 ± 13.4 | 581.3 ± 173.5 | 353.8 ± 8.9 | 317.0 ± 4.8 | 35.9 ± 4.1 |
| Sample | Elastase | Collagenase | Hyaluronidase | Tyrosinase | AGEs | SIRT1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ir#1 | 77.8 ± 2.9 | 64.3 ± 3.0 | 85.8 ± 1.7 | 62.9 ± 2.3 | 78.5 ± 0.7 | 140.8 ± 5.0 |
| Ir#2 | 90.7 ± 0.8 | 86.2 ± 2.2 | 88.4 ± 1.4 | 85.4 ± 1.7 | 79.8 ± 1.4 | 88.9 ± 3.3 |
| Ir#3 | 79.8 ± 1.2 | 77.7 ± 3.0 | 88.6 ± 0.9 | 27.8 ± 12.1 | 84.4 ± 0.8 | 162.0 ± 7.0 |
| Ir#4 | 83.0 ± 2.2 | 75.0 ± 3.3 | 87.7 ± 2.0 | 75.6 ± 2.6 | 77.6 ± 2.7 | 134.3 ± 10.3 |
| Ir#5 | 76.8 ± 4.6 | 63.5 ± 4.3 | 80.1 ± 1.4 | 52.1 ± 4.4 | 73.8 ± 1.9 | 194.1 ± 6.4 |
| Ir#6 | 87.9 ± 2.2 | 84.8 ± 0.3 | 85.6 ± 1.5 | 87.6 ± 1.9 | 76.1 ± 2.2 | 124.3 ± 11.0 |
| Ir#7 | 85.8 ± 1.7 | 77.1 ± 1.9 | 86.6 ± 2.8 | 79.3 ± 1.4 | 76.9 ± 2.6 | 137.8 ± 5.8 |
| Ir#8 | 85.9 ± 2.7 | 78.5 ± 0.9 | 89.2 ± 0.9 | 82.8 ± 1.7 | 83.2 ± 1.9 | 185.4 ± 11.0 |
| Ir#9 | 90.2 ± 1.2 | 85.8 ± 1.6 | 88.7 ± 1.2 | 87.2 ± 1.5 | 83.7 ± 1.7 | 94.8 ± 4.2 |
| Ir#10 | 86.2 ± 1.3 | 79.7 ± 1.3 | 91.5 ± 0.9 | 85.2 ± 1.1 | 85.1 ± 1.3 | 92.6 ± 3.2 |
| Ir#11 | 79.2 ± 1.9 | 68.8 ± 2.1 | 78.7 ± 0.9 | 74.5 ± 2.7 | 70.8 ± 1.8 | 203.3 ± 6.2 |
| Ir#12 | 74.7 ± 1.1 | 65.8 ± 2.2 | 77.8 ± 0.9 | 63.9 ± 2.5 | 65.9 ± 2.7 | 154.4 ± 7.9 |
| CA | RA | BA | OA | PA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH | 0.546 | 0.997 *** | 0.471 | 0.477 | 0.537 |
| ABTS | 0.575 | 0.982 *** | 0.484 | 0.447 | 0.466 |
| ORAC | 0.562 | 0.975 *** | 0.511 | 0.550 | 0.604 * |
| FRAP | 0.555 | 0.997 *** | 0.447 | 0.423 | 0.510 |
| CUPRAC | 0.566 | 0.992 *** | 0.454 | 0.466 | 0.513 |
| Chelation | 0.534 | 0.992 *** | 0.456 | 0.465 | 0.559 |
| Elastase | 0.126 | 0.525 | 0.827 ** | 0.902 *** | 0.748 * |
| Collagenase | 0.097 | 0.571 | 0.900 *** | 0.936 *** | 0.720 ** |
| Hyaluronidase | 0.467 | 0.897 *** | 0.572 | 0.602 * | 0.538 |
| Tyrosinase | -0.221 | 0.072 | 0.440 | 0.603 * | 0.622 * |
| AGEs | 0.608 * | 0.943 *** | 0.527 | 0.522 | 0.447 |
| SIRT1 | 0.435 | 0.970 *** | 0.665 * | 0.646 * | 0.625 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasi, B.H.; Siddiquah, A.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Bose, S.; Younas, M.; Garros, L.; Drouet, S.; Giglioli-Guivarc’h, N.; Hano, C. Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020452
Abbasi BH, Siddiquah A, Tungmunnithum D, Bose S, Younas M, Garros L, Drouet S, Giglioli-Guivarc’h N, Hano C. Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020452
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasi, Bilal Haider, Aisha Siddiquah, Duangjai Tungmunnithum, Shankhamala Bose, Muhammad Younas, Laurine Garros, Samantha Drouet, Nathalie Giglioli-Guivarc’h, and Christophe Hano. 2019. "Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020452
APA StyleAbbasi, B. H., Siddiquah, A., Tungmunnithum, D., Bose, S., Younas, M., Garros, L., Drouet, S., Giglioli-Guivarc’h, N., & Hano, C. (2019). Isodon rugosus (Wall. ex Benth.) Codd In Vitro Cultures: Establishment, Phytochemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020452