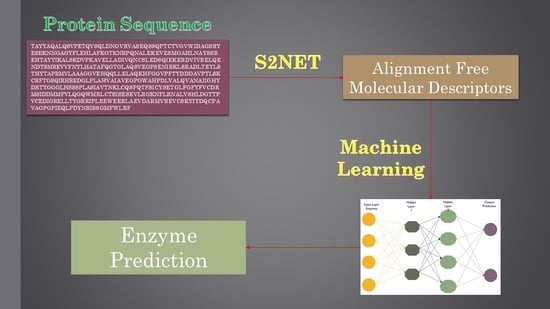
Alignment-Free Method to Predict Enzyme Classes and Subclasses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LDA Model
2.2. ANN models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Molecular Descriptor Calculation
4.3. Multi-Target Linear model
4.4. Non-Linear Models
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nomenclature, E. Enzyme nomenclature: Recommendations (1972) of the international union of pure and applied chemistry and the international union of biochemistry: Supplement i: Corrections & additions (1975). Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Enzymol. 1976, 429, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, P.W.; Prlić, A.; Altunkaya, A.; Bi, C.; Bradley, A.R.; Christie, C.H.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. The RCSB protein data bank: Integrative view of protein, gene and 3D structural information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D271–D281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.J.; Gupta, R.; Blom, N.S.; Devos, D.; Tamames, J.; Kesmir, C.; Nielsen, H.; Stærfeldt, H.; Rapacki, K.; Workman, C.; et al. Prediction of Human Protein Function from Post-translational Modifications and Localization Features. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, N.J.; Wang, X. Non-Alignment Features based Enzyme/Non-Enzyme Classification Using an Ensemble Method. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Washington, DC, USA, 12–14 December 2010; pp. 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, X.B.; Yang, Z.X.; Deng, N.Y. Prediction of enzyme subfamily class via pseudo amino acid composition by incorporating the conjoint triad feature. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concu, R.; Dias Soeiro Cordeiro, M.; Munteanu, C.R.; Gonzalez-Diaz, H. Ptml model of enzyme subclasses for mining the proteome of bio-fuel producing microorganisms. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, P.D.; Doig, A.J. Distinguishing enzyme structures from non-enzymes without alignments. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Ju, Y.; Xuan, P.; Long, R.; Xing, F. Identification of Multi-Functional Enzyme with Multi-Label Classifier. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, A.; Amidi, S.; Vlachakis, D.; Megalooikonomou, V.; Paragios, N.; Zacharaki, E.I. EnzyNet: Enzyme classification using 3D convolutional neural networks on spatial representation. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.N.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Z.; Yang, X.; Deng, Z. Assignment of EC Numbers to Enzymatic Reactions with Reaction Difference Fingerprints. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Chilton, J.M.; Grüning, B.; Johnson, J.E.; Soranzo, N. Ncbi blast integrated into galaxy. Gigascience 2015, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.E.; Orengo, C.A.; Thornton, J.M. Evolution of function in protein superfamilies, from a structural perspective. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1113–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Skolnick, J. How Well is Enzyme Function Conserved as a Function of Pairwise Sequence Identity? J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 863–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rost, B.; Liu, J.; Nair, R.; Wrzeszczynski, K.O.; Ofran, Y. Automatic prediction of protein function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2003, 60, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagao, C.; Nagano, N.; Mizuguchi, K. Prediction of Detailed Enzyme Functions and Identification of Specificity Determining Residues by Random Forests. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 84623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quester, S.; Schomburg, D. EnzymeDetector: An integrated enzyme function prediction tool and database. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt, C. Ongoing and future developments at the universal protein resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D214–D219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. From genomics to chemical genomics: New developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D354–D357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frishman, D.; Mokrejs, M.; Kosykh, D.; Kastenmüller, G.; Kolesov, G.; Zubrzycki, I.; Gruber, C.; Geier, B.; Kaps, A.; Albermann, K.; et al. The pedant genome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Umarov, R.; Xie, B.; Fan, M.; Li, L.; Gao, X. Deepre: Sequence-based enzyme ec number prediction by deep learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkiran, A.; Rifaioglu, A.S.; Martin, M.J.; Cetin-Atalay, R.; Atalay, V.; Doğan, T. ECPred: A tool for the prediction of the enzymatic functions of protein sequences based on the EC nomenclature. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.B.; Chou, K.C. EzyPred: A top–down approach for predicting enzyme functional classes and subclasses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bairoch, A. The enzyme data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 3155–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.; Choudhary, A. A top-down approach to classify enzyme functional classes and sub-classes using random forest. EURASIP J. Bioinform. Syst. Biol. 2012, 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuta, Y.; Ito, M.; Tohsato, Y. Ecoh: An enzyme commission number predictor using mutual information and a support vector machine. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüero-Chapin, G.; González-Díaz, H.; Molina, R.; Varona-Santos, J.; Uriarte, E.; González-Díaz, Y. Novel 2D maps and coupling numbers for protein sequences. The first QSAR study of polygalacturonases; isolation and prediction of a novel sequence fromPsidium guajavaL. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concu, R.; Dea-Ayuela, M.; Pérez-Montoto, L.G.; Prado-Prado, F.J.; Uriarte, E.; Fernandez, F.B.; Podda, G.; Pazos, A.; Munteanu, C.-R.; Ubeira, F.; et al. 3D entropy and moments prediction of enzyme classes and experimental-theoretic study of peptide fingerprints in Leishmania parasites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concu, R.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Pérez-Montoto, L.G.; Bolas-Fernández, F.; Prado-Prado, F.J.; Podda, G.; Uriarte, E.; Ubeira, F.M.; González-Díaz, H. Prediction of Enzyme Classes from 3D Structure: A General Model and Examples of Experimental-Theoretic Scoring of Peptide Mass Fingerprints ofLeishmaniaProteins. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes, J.S.; E Pedreira, C. A review of protein function prediction under machine learning perspective. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2013, 7, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barigye, S.J.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Pérez-Giménez, F.; Bonchev, D. Trends in information theory-based chemical structure codification. Mol. Divers. 2014, 18, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.J.; Malarkey, C.; Schulmerich, M.V. Information Content in Organic Molecules: Quantification and Statistical Structure via Brownian Processing. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 35, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, D.J.; Schacht, D. Base information content in organic molecular formulae. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 40, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.J. Information content and organic molecules: Aggregation states and solvent effects. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2005, 45, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.J. Information Content in Organic Molecules: Brownian Processing at Low Levels. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2007, 38, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Díaz, H.; Molina, R.; Uriarte, E. Markov entropy backbone electrostatic descriptors for predicting proteins biological activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4691–4695. [Google Scholar]
- González-Díaz, H.; Saíz-Urra, L.; Molina, R.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. A Model for the Recognition of Protein Kinases Based on the Entropy of 3D van der Waals Interactions. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Fernandez, P.; Munteanu, C.-R.; Escobar, M.; Prado-Prado, F.J.; Martín-Romalde, R.; Pereira, D.; Villalba, K.; Duardo-Sánchez, A.; González-Díaz, H. New Markov–Shannon Entropy models to assess connectivity quality in complex networks: From molecular to cellular pathway, Parasite–Host, Neural, Industry, and Legal–Social networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 293, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkasov, A.; Muratov, E.N.; Fourches, D.; Varnek, A.; Baskin, I.I.; Cronin, M.; Dearden, J.; Gramatica, P.; Martin, Y.C.; Todeschini, R.; et al. QSAR Modeling: Where Have You Been? Where Are You Going To? J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4977–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.C.; Natarajan, R.; Mills, D.; Hawkins, D.M.; Kraker, J.J. Quantitative Structure—Activity Relationship Modeling of Juvenile Hormone Mimetic Compounds for Culex pipiens Larvae, with a Discussion of Descriptor-Thinning Methods. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2006, 37, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.; Lewicki, P. Statistics Methods and Applications. In A Comprehensive Reference for Science, Industry and Data Mining; StatSoft: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2006; Volume 1, p. 813. [Google Scholar]
- Shahsavari, S.; Bagheri, G.; Mahjub, R.; Bagheri, R.; Radmehr, M.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Application of artificial neural networks for optimization of preparation of insulin nanoparticles composed of quaternized aromatic derivatives of chitosan. Drug Res. 2014, 64, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Borroto, E.; Rivas, C.G.P.; Chagoyán, J.C.V.; Castañedo, N.; Prado-Prado, F.J.; Garcia-Mera, X.; González-Díaz, H. ANN multiplexing model of drugs effect on macrophages; theoretical and flow cytometry study on the cytotoxicity of the anti-microbial drug G1 in spleen. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6181–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honório, K.M.; De Lima, E.F.; Quiles, M.G.; Romero, R.A.F.; Molfetta, F.A.; Da Silva, A.B.F.; Da Silva, A.B.F. Artificial Neural Networks and the Study of the Psychoactivity of Cannabinoid Compounds. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 75, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, N.K.; Kang, S.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, J.M.; Choi, K.; Jung, D.H. Machine learning study for the prediction of transdermal peptide. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erol, R.; Ogulata, S.N.; Sahin, C.; Alparslan, Z.N.; Erol, R. A Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN) Approach for Structural Classification of Thyroid Diseases. J. Med Syst. 2008, 32, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerianos, A.; Papadimitriou, S.; Alexopoulos, D. Radial basis function neural networks for the characterization of heart rate variability dynamics. Artif. Intell. Med. 1999, 15, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.-R.; Magalhaes, A.; Duardo-Sánchez, A.; Pazos, A.; González-Díaz, H. S2SNet: A Tool for Transforming Characters and Numeric Sequences into Star Network Topological Indices in Chemoinformatics, Bioinformatics, Biomedical, and Social-Legal Sciences. Curr. Bioinform. 2013, 8, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, J.; Aguiar, V.; Seoane, J.A.; Freire, A.; Serantes, J.; Dorado, J.; Pazos, A.; Munteanu, C.-R. Star Graphs of Protein Sequences and Proteome Mass Spectra in Cancer Prediction. Curr. Proteom. 2009, 6, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randić, M.; Zupan, J.; Vikic-Topic, D. On representation of proteins by star-like graphs. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2007, 26, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Blanco, E.; Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Munteanu, C.R.; Dorado, J. Random Forest classification based on star graph topological indices for antioxidant proteins. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 317, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Lozano, C.; Cuiñas, R.F.; Seoane, J.A.; Fernández-Blanco, E.; Dorado, J.; Munteanu, C.-R. Classification of signaling proteins based on molecular star graph descriptors using Machine Learning models. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 384, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munteanu, C.R.; González-Díaz, H.; Magalhães, A.L. Enzymes/non-enzymes classification model complexity based on composition, sequence, 3D and topological indices. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 254, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Huang, H.; Ding, C. From Protein Sequence to Protein Function via Multi-Label Linear Discriminant Analysis. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2017, 14, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendryli, J.; Fanany, M.I. Classifying Abnormal Activities in Exam using Multi-Class Markov Chain LDA Based on MODEC Features. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT), Bandung, Indonesia, 25–27 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Safo, S.E.; Ahn, J. General sparse multi-class linear discriminant analysis. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2016, 99, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleites, C.; Salzer, R. Assessing and improving the stability of chemometric models in small sample size situations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ion-Mărgineanu, A.; Kocevar, G.; Stamile, C.; Sima, D.M.; Durand-Dubief, F.; Van Huffel, S.; Sappey-Marinier, D. Machine Learning Approach for Classifying Multiple Sclerosis Courses by Combining Clinical Data with Lesion Loads and Magnetic Resonance Metabolic Features. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughorbel, S.; Jarray, F.; El-Anbari, M. Optimal classifier for imbalanced data using Matthews Correlation Coefficient metric. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0177678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Training | Validation | Overall | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | All | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | All | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | |
| −1 | 98.13 | 40,781 | 778 | 98.27 | 13,613 | 240 | 98.16 | 54,394 | 1018 |
| 1 | 99.7 | 57 | 19,498 | 99.71 | 19 | 6498 | 99.71 | 76 | 25,996 |
| Total | 98.63 | 40,838 | 20,276 | 98.73 | 13,632 | 6738 | 98.66 | 54,470 | 27,014 |
| Eigenvalue | CanonicalR | Wilk’sLambda | Chi-Sqr. | df | p-value | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.241879 | 0.744275 | 0.446054 | 49334.99 | 4.000000 | 0.00 | 0.97 |
| Obs. Sets a | Stat. Param. a | Pred. Stat. a | Predicted sets | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | nj | |||
| Training Series | |||||
| 1 | Sp a | 100 | 17,500 | 0 | 57,039 |
| −1 | Sn a | 100 | 0 | 39,539 | 0 |
| total | Ac a | 100 | 17,500 | 39,539 | 57,039 |
| Validation Series | |||||
| 1 | Sp a | 100 | 8572 | 0 | 24,445 |
| −1 | Sn a | 100 | 0 | 15,873 | 0 |
| total | Ac a | 100 | 8572 | 15,873 | 24,445 |
| Overall | |||||
| 1 | Sp a | 100 | 26,072 | 0 | 81,484 |
| −1 | Sn a | 100 | 0 | 55,412 | 0 |
| total | Ac a | 100 | 26,072 | 55,412 | 81,484 |
| Training | Validation | Overall | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | All | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | All | −1 = Sn | 1 = Sp | All | |
| BEST MLP: 4-9-2 | Total | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 | |
| Incorrect | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.MLP 4-7-2 | Total | 39,448 | 17,591 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,448 | 17,567 | 57,015 | 15,873 | 8562 | 24,435 | 55,412 | 26,034 | 81,446 | |
| Incorrect | 0 | 24 | 24 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 38 | 38 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 99.86 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.88 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.85 | 99.95 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.05 | |
| 2.MLP 4-8-2 | Total | 39,448 | 17,591 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,448 | 17,565 | 57,013 | 15,873 | 8563 | 24,436 | 55,412 | 26,037 | 81,449 | |
| Incorrect | 0 | 26 | 26 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 35 | 35 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 99.85 | 99.95 | 100.00 | 99.90 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.87 | 99.96 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| 3.MLP 4-10-2 | Total | 39,448 | 17,591 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,448 | 17,565 | 57,013 | 15,873 | 8563 | 24,436 | 55,412 | 26,037 | 81,449 | |
| Incorrect | 0 | 26 | 26 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 35 | 35 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 99.85 | 99.95 | 100.00 | 99.90 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.87 | 99.96 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| 4.MLP 4-11-2 | Total | 39,448 | 17,591 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,448 | 17,566 | 57,014 | 15,873 | 8563 | 24,436 | 55,412 | 26,037 | 81,449 | |
| Incorrect | 0 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 35 | 35 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 99.86 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.90 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 99.87 | 99.96 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| 5.MLP 4-16-2 | Total | 39,448 | 17,591 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,321 | 26,163 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,448 | 17,567 | 57,015 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,321 | 26,139 | 81,460 | |
| Incorrect | 0 | 24 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Correct (%) | 100 | 99.86 | 99.96 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.91 | 99.97 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.03 | |
| 6.RBF 4-21-2 | Total | 39,539 | 17,500 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,520 | 16,426 | 55,946 | 15,855 | 8059 | 23,914 | 55,375 | 24,485 | 79,860 | |
| Incorrect | 19 | 1074 | 1093 | 18 | 513 | 531 | 37 | 1587 | 1624 | |
| Correct (%) | 99.95 | 93.86 | 98.08 | 99.89 | 94.02 | 97.83 | 99.93 | 93.91 | 98.01 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0.05 | 6.14 | 1.92 | 0.11 | 5.98 | 2.17 | 0.07 | 6.09 | 1.99 | |
| 7.RBF 4-29-2 | Total | 39,539 | 17,500 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,165 | 17,475 | 56,640 | 15,714 | 8561 | 24,275 | 54,879 | 26,036 | 80,915 | |
| Incorrect | 374 | 25 | 399 | 159 | 11 | 170 | 533 | 36 | 569 | |
| Correct (%) | 99.05 | 99.86 | 99.3 | 99.00 | 99.87 | 99.30 | 99.04 | 99.86 | 99.30 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0.7 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.14 | 0.70 | |
| 8.RBF 4-21-2 | Total | 39,539 | 17,500 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,526 | 16,138 | 55,664 | 15,868 | 7873 | 23,741 | 55,394 | 24,011 | 79,405 | |
| Incorrect | 13 | 1362 | 1375 | 5 | 699 | 704 | 18 | 2061 | 2079 | |
| Correct (%) | 99.97 | 92.22 | 97.59 | 99.97 | 91.85 | 97.12 | 99.97 | 92.09 | 97.45 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0.03 | 7.78 | 2.41 | 0.03 | 8.15 | 2.88 | 0.03 | 7.91 | 2.55 | |
| 9.RBF 4-28-2 | Total | 39,539 | 17,500 | 57,039 | 15,197 | 8571 | 23,768 | 53,008 | 26,060 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 39,489 | 16,000 | 23,489 | 15,197 | 8448 | 23,645 | 53,008 | 25,674 | 78,682 | |
| Incorrect | 50 | 1500 | 1,450 | 0 | 123 | 123 | 0 | 386 | 386 | |
| Correct (%) | 99.87 | 91.43 | 95.65 | 100.00 | 98.56 | 99.48 | 100.00 | 98.52 | 99.51 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 0.03 | 7.78 | 4.35 | 0.00 | 1.44 | 0.52 | 0.00 | 1.48 | 0.49 | |
| 10.RBF 4-26-2 | Total | 39,539 | 17,500 | 57,039 | 15,873 | 8572 | 24,445 | 55,412 | 26,072 | 81,484 |
| Correct | 11,880 | 6629 | 18,509 | 4748 | 3170 | 7918 | 16,628 | 9799 | 26,427 | |
| Incorrect | 27659 | 10871 | 38530 | 11125 | 5402 | 16527 | 38784 | 16273 | 55057 | |
| Correct (%) | 30.05 | 37.88 | 32.45 | 29.91 | 36.98 | 32.39 | 30.01 | 37.58 | 32.43 | |
| Incorrect (%) | 69.95 | 62.12 | 67.55 | 70.09 | 63.02 | 67.61 | 69.99 | 62.42 | 67.57 | |
| Model | Class | Fail | Total Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. MLP 4-7-2 | 6.4 | 1 | 104 |
| 6.5 | 34 | 36 | |
| 2. MLP 4-8-2 | 1.6 | 3 | 4 |
| 6.4 | 1 | 104 | |
| 6.5 | 34 | 36 | |
| 3. MLP 4-10-2 | 1.6 | 3 | 4 |
| 6.4 | 1 | 104 | |
| 6.5 | 33 | 36 | |
| 4. MLP 4-11-2 | 1.6 | 3 | 4 |
| 6.4 | 1 | 104 | |
| 6.5 | 32 | 36 | |
| 5. MLP 4-16-2 | 6.4 | 1 | 104 |
| 6.5 | 33 | infer 36 |
| Input Variable | Variable Sensitivity | Variable Name/Details |
|---|---|---|
| <Tr5(srn)> | 15,896,991 | Expected value of Trace of order 5 of the srn for the sequence |
| D Tr5(srn) | 1,288,626 | Deviation of Trace of order 5 of the srn with respect to the mean value of the class |
| <Tr3(srn)> | 591,331.9 | Expected value of Trace of order 3 of the srn for the sequence |
| D Tr3(srn) | 108.7591 | Deviation of Trace of order 3 of the srn with respect to the mean value of the class |
| EC Subclass | Number of Sequences | EC Subclass | Number of Sequences | EC Subclass | Number of Sequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 555 | 2.3 | 722 | 4.6 | 120 |
| 1.2 | 250 | 2.4 | 424 | 4.99 | 95 |
| 1.3 | 172 | 2.5 | 291 | 5.1 | 176 |
| 1.4 | 108 | 2.6 | 19 | 5.2 | 74 |
| 1.5 | 5 | 2.7 | 3112 | 5.3 | 247 |
| 1.6 | 4 | 2.8 | 71 | 5.4 | 160 |
| 1.7 | 91 | 2.9 | 10 | 5.5 | 115 |
| 1.8 | 165 | 3.1 | 1559 | 5.6 | 159 |
| 1.9 | 73 | 3.11 | 7 | 5.99 | 3 |
| 1.10 | 555 | 3.13 | 3 | 6.1 | 277 |
| 1.11 | 136 | 3.2 | 700 | 6.2 | 38 |
| 1.12 | 32 | 3.3 | 164 | 6.3 | 291 |
| 1.13 | 123 | 3.4 | 1481 | 6.4 | 104 |
| 1.14 | 244 | 3.5 | 561 | 6.5 | 36 |
| 1.15 | 162 | 3.6 | 417 | 7.1 | 8827 |
| 1.16 | 173 | 3.7 | 69 | 7.2 | 927 |
| 1.17 | 121 | 3.8 | 77 | 7.4 | 189 |
| 1.18 | 45 | 3.9 | 3 | 7.5 | 187 |
| 1.20 | 250 | 4.1 | 486 | 7.6 | 197 |
| 1.21 | 28 | 4.2 | 460 | ||
| 1.23 | 3 | 4.3 | 97 | ||
| 2.1 | 522 | 4.4 | 39 | ||
| 2.2 | 107 | 4.5 | 25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Concu, R.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Alignment-Free Method to Predict Enzyme Classes and Subclasses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215389
Concu R, Cordeiro MNDS. Alignment-Free Method to Predict Enzyme Classes and Subclasses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(21):5389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215389
Chicago/Turabian StyleConcu, Riccardo, and M. Natália D. S. Cordeiro. 2019. "Alignment-Free Method to Predict Enzyme Classes and Subclasses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 21: 5389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215389
APA StyleConcu, R., & Cordeiro, M. N. D. S. (2019). Alignment-Free Method to Predict Enzyme Classes and Subclasses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), 5389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215389