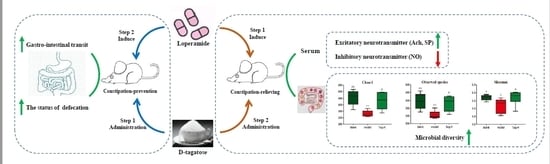
The Constipation-Relieving Property of d-Tagatose by Modulating the Composition of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of d-Tagatose on the Gastrointestinal Transit Rate
2.2. Effects of d-Tagatose on the Defecation Status
2.3. Effects of d-Tagatose on Serum Neurotransmitter
2.4. Effect of d-Tagatose on the Composition of Rectum Microbiota
2.5. The Relative Abundance of Rectum Microbiota
2.6. Correlation between Intestinal Microflora and Biological Indexes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2.1. The Gastrointestinal Transit Experiment
4.2.2. The Experiment of Defecation
4.2.3. The Slow Transit Constipation Experiment
4.3. Determination of Ach, NO, SP, and VIP Levels in Serum
4.4. DNA Extraction, PCR, and 16S rDNA Sequencing
4.5. Analysis of Sequences and Relative Abundance of Microbiota Community Members
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ach | acetylcholine |
| SP | substance P |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| VIP | vasoactive intestinal peptide |
| ENS | enteric nervous system |
| FDA | USA Food and Drug Administration |
| CFDA | China Food and Drug Administration |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| SPF | specific pathogen free |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| RDP | ribosomal database project |
| PCoA | principal co-ordinates analysis |
| SRA | sequence read archive |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units |
References
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Yin, B.; Fang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium adolescentis Exerts Strain-Specific Effects on Constipation Induced by Loperamide in BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Pemberton, J.H.; Locke, G.R. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on constipation. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.G.; Wen, P.; Fu, H.Z.; Lin, G.Y.; Liao, S.T.; Zou, Y.X. Protective effect of mulberry (Morus atropurpurea) fruit against diphenoxylate-induced constipation in mice through the modulation of gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.B. Intestinal microbiota and chronic constipation. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkusa, T.; Koido, S.; Nishikawa, Y.; Sato, N. Gut Microbiota and Chronic Constipation: A Review and Update. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppi, G.; Cinquetti, M.; Luciano, A.; Benini, A.; Muner, A.; Bertazzoni Minelli, E. The intestinal ecosystem in chronic functional constipation. Acta Paediatr. 1998, 87, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; DiBaise, J.K.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Crowell, M.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Rittmann, B.E.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Gut microbial and short-chain fatty acid profiles in adults with chronic constipation before and after treatment with lubiprostone. Anaerobe 2015, 33, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhao, W.; Ding, C.; Tian, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Ni, L.; Jiang, J.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; et al. Potential role of fecal microbiota from patients with slow transit constipation in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.D.; Camilleri, M.; Chirapongsathorn, S.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Valentin, N.; Shin, A.; Erwin, P.J.; Wang, Z.; Murad, M.H. Comparison of efficacy of pharmacological treatments for chronic idiopathic constipation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2017, 66, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.; Quigley, E.M.M. An update on prucalopride in the treatment of chronic constipation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.W.; Stanghellini, V.; Geraint, M.; Halphen, M. Randomized clinical trial: Macrogol/PEG 3350 plus electrolytes for treatment of patients with constipation associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B. Pathologic changes in the colon produced by anthraquinone purgatives. Dis. Colon Rectum 1973, 16, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, M.R.; Park, J.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Song, B.R.; Son, H.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, K.M.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Quercetin promotes gastrointestinal motility and mucin secretion in loperamide-induced constipation of SD rats through regulation of the mAChRs downstream signal. Pharm. Biol 2018, 56, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Yin, H.; Wu, D.; Su, Q. Naringenin induces laxative effects by upregulating the expression levels of c-Kit and SCF, as well as those of aquaporin 3 in mice with loperamide-induced constipation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Yan, S.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effects of different oligosaccharides at various dosages on the composition of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in mice with constipation. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chikkerur, J.; Roy, S.C.; Dhali, A.; Kolte, A.P.; Sridhar, M.; Samanta, A.K. Tagatose as a Potential Nutraceutical: Production, Properties, Biological Roles, and Applications. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, G.V. Tagatose, the new GRAS sweetener and health product. J. Med. Food 2002, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laerke, H.N.; Jensen, B.B. d-tagatose has low small intestinal digestibility but high large intestinal fermentability in pigs. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, H.; Andersen, H.; Tvede, M. Fermentation of d-Tagatose by Human Intestinal Bacteria and Dairy Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microb. Ecol. Health 2001, 13, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, H. d-tagatose a novel low-calorie bulk sweetener with prebiotic properties. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1999, 85, 98–109. [Google Scholar]
- Son, S.J.; Koh, J.H.; Park, M.R.; Ryu, S.; Lee, W.J.; Yun, B.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y. Effect of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG and tagatose as a synbiotic combination in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis murine model. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.D.S.; Tahan, S.; Weber, T.K.; Araujo-Filho, H.B.; de Morais, M.B. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Parallel Clinical Trial Assessing the Effect of Fructooligosaccharides in Infants with Constipation. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Zheng, Y.P.; Tan, J.C.; Xiong, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L. Effects of Prebiotics and Synbiotics on Functional Constipation. Am. J. Med Sci. 2017, 353, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Lin, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Bacterial Cellulose Relieves Diphenoxylate-Induced Constipation in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasibul, K.; Nakayama-Imaohji, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamasaki, H.; Ogawa, T.; Waki, J.; Tada, A.; Yoneda, S.; Tokuda, M.; Miyake, M.; et al. d-Tagatose inhibits the growth and biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacteria exert species-specific effects on constipation in BALB/c mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3587–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Mou, H. Study on the ability of partially hydrolyzed guar gum to modulate the gut microbiota and relieve constipation. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Röcken, C.; Mawrin, C.; Weise, W.; Höllt, V.; Schulz, S. Immunocytochemical identification of VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptors in normal and neoplastic human tissues with subtype-specific antibodies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8235–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, G.; Yi, R.; Park, K.Y.; Song, J.L. Lactobacillus plantarum YS2 (yak yogurt Lactobacillus) exhibited an activity to attenuate activated carbon-induced constipation in male Kunming mice. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassano, S.; Tesoriere, L.; Rotondo, A. Inhibition of the Mechanical Activity of Mouse Ileum by Cactus Pear (Opuntia Ficus Indica, L, Mill.) Fruit Extract and Its Pigment Indicaxanthin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7565–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Chia, N.; O’Connor, H.M.; Wolf, P.G.; Gaskins, H.R.; Bharucha, A.E. Relationship Between Microbiota of the Colonic Mucosa vs Feces and Symptoms, Colonic Transit, and Methane Production in Female Patients With Chronic Constipation. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, C.C.; Kien, C.L.; Bouthillier, L.; Levy, E. Short-chain fatty acids: Ready for prime time? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2006, 21, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Nakao, M.; Hoshi, S.; Yamada, K.; Inagaki, K.; Nishida, M.; Nabeshima, T. Effect of dietary fiber on morphine-induced constipation in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelmann, S.; Seedorf, H.; Walters, W.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I.; Janssen, P.H. Simultaneous amplicon sequencing to explore co-occurrence patterns of bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic microorganisms in rumen microbial communities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e47879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosalbes, M.J.; Durbán, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Abellan, J.J.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. Metatranscriptomic approach to analyze the functional human gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, C.J.; Beiko, R.G. A phylogenomic view of ecological specialization in the Lachnospiraceae, a family of digestive tract-associated bacteria. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, P.; Young, P.; Holtrop, G.; Flint, H.J. Diversity of human colonic butyrate-producing bacteria revealed by analysis of the butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase gene. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Pither, J.; Baumeister, P.; Little, J.P.; Gill, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi-Vand, Z.; Marsden, K.R.; Gibson, D.L. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kverka, M.; Zakostelska, Z.; Klimesova, K.; Sokol, D.; Hudcovic, T.; Hrncir, T.; Rossmann, P.; Mrazek, J.; Kopecny, J.; Verdu, E.F.; et al. Oral administration of Parabacteroides distasonis antigens attenuates experimental murine colitis through modulation of immunity and microbiota composition. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 163, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Liu, L.; Gamallat, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xin, Y. Enteromorpha and polysaccharides from enteromorpha ameliorate loperamide-induced constipation in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gordon, J.I. Honor thy symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10452–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNulty, N.P.; Wu, M.; Erickson, A.R.; Pan, C.; Erickson, B.K.; Martens, E.C.; Pudlo, N.A.; Muegge, B.D.; Henrissat, B.; Hettich, R.L.; et al. Effects of diet on resource utilization by a model human gut microbiota containing Bacteroides cellulosilyticus WH2, a symbiont with an extensive glycobiome. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, E.C.; Chiang, H.C.; Gordon, J.I. Mucosal glycan foraging enhances fitness and transmission of a saccharolytic human gut bacterial symbiont. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Investigations of Bacteroides spp. towards next-generation probiotics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barcenilla, A.; Pryde, S.E.; Martin, J.C.; Duncan, S.H.; Stewart, C.S.; Henderson, C.; Flint, H.J. Phylogenetic relationships of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pryde, S.E.; Duncan, S.H.; Hold, G.L.; Stewart, C.S.; Flint, H.J. The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 217, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal function: Evidence from animal models. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2009, 2, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Yi, R.; Qian, Y.; Park, K.Y. Lactobacillus plantarum YS-3 Prevents Activated Carbon-Induced Constipation in Mice. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-J.; Tang, X.-D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, X.-R. Gut microbiota alterations from different Lactobacillus probiotic-fermented yoghurt treatments in slow-transit constipation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Ji, J.; Xie, G. Total Glucosides of Paeony Promote Intestinal Motility in Slow Transit Constipation Rats through Amelioration of Interstitial Cells of Cajal. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faith, D.P.; Baker, A.M. Phylogenetic diversity (PD) and biodiversity conservation: Some bioinformatics challenges. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2007, 2, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerfield, P.J. Identification of the Bray-Curtis similarity index: Comment on Yoshioka (2008). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 372, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Group | Ach (pg/L) | NO (μmol/L) | VIP (pg/L) | SP (pg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| blank | 38.17 ± 10.17 # | 30.71 ± 3.81 | 18.19 ± 3.75 ## | 31.97 ± 12.81 |
| model | 27.82 ± 7.28 * | 26.99 ± 4.77 | 26.19 ± 4.53 ** | 24.76 ± 6.23 |
| Tag-H | 37.98 ± 11.58 # | 15.60 ± 2.76 *,## | 24.07 ± 2.50 | 49.11 ± 11.25 ## |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.-X.; Wen, P.; Wang, Y.; OuYang, D.-M.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Song, Y.; Deng, J.; Sun, Y.-M.; Wang, H. The Constipation-Relieving Property of d-Tagatose by Modulating the Composition of Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225721
Liang Y-X, Wen P, Wang Y, OuYang D-M, Wang D, Chen Y-Z, Song Y, Deng J, Sun Y-M, Wang H. The Constipation-Relieving Property of d-Tagatose by Modulating the Composition of Gut Microbiota. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225721
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yu-Xuan, Peng Wen, Yu Wang, Dong-Mei OuYang, Da Wang, Yu-Zhong Chen, Ya Song, Jie Deng, Yuan-Ming Sun, and Hong Wang. 2019. "The Constipation-Relieving Property of d-Tagatose by Modulating the Composition of Gut Microbiota" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225721
APA StyleLiang, Y. -X., Wen, P., Wang, Y., OuYang, D. -M., Wang, D., Chen, Y. -Z., Song, Y., Deng, J., Sun, Y. -M., & Wang, H. (2019). The Constipation-Relieving Property of d-Tagatose by Modulating the Composition of Gut Microbiota. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225721