Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Structural Identification of Compounds
2.2. Neuroprotective Activity Screening of the Isolated Compounds Using a Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Hyperoside Inhibits 6-OHDA-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
2.4. Hyperoside Prevents 6-OHDA-Induced Intracellular ROS Accumulation and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Dysfunction in SH-SY5Y Cells
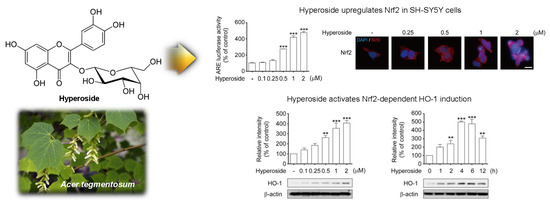
2.5. Hyperoside-Mediated Activation of Nrf2 Occurred in a Time- and Concentration-Dependent Manner in SH-SY5Y Cells
2.6. Hyperoside Induced the Expression of HO-1 in a Time and Concentration-Dependent Manner in SH-SY5Y Cells
2.7. Nrf2 Gene Knockdown Eliminated the Neuroprotective Effects of Hyperoside on Nrf2-Mediated HO-1 Transcriptional Induction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.3. Measurement of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release
4.4. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.5. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Accumulation
4.6. Measurement of Intracellular Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
4.7. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Transient Transfection with siRNA
4.9. Cytosolic and Nuclear Lysate Preparation
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Transient Transfection and Dual-Luciferase Assay
4.12. Immunocytochemistry
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Kuan, W.L. Parkinson′s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson′s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon publication: Brisbane, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.S.; Geng, W.S.; Jia, J.J. Neurotoxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson Disease: Pathogenic Mechanism and Assessment. ASN Neuro 2018, 10, 1759091418777438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer′s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, S.C.; Shaw, P.J. Oxidative stress in ALS: Key role in motor neuron injury and therapeutic target. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puspita, L.; Chung, S.Y.; Shim, J.W. Oxidative stress and cellular pathologies in Parkinson′s disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filograna, R.; Beltramini, M.; Bubacco, L.; Bisaglia, M. Anti-Oxidants in Parkinson′s Disease Therapy: A Critical Point of View. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.M.; Eom, H.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, I.K.; Baek, K.-H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.H. Bioactivity evaluations of betulin identified from the bark of Betula platyphylla var. japonica for cancer therapy. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Roh, H.-S.; Baek, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; So, H.M.; Moon, E.; Pang, C.; Jang, T.S.; Kim, K.H. Bioactivity-guided isolation of ginsenosides from Korean Red Ginseng with cytotoxic activity against human lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Choi, E.; Eom, H.J.; Jo, M.S.; Kim, S.; So, H.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, K.H. LC/MS-based analysis of bioactive compounds from the bark of Betula platyphylla var. japonica and their effects on regulation of adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Roh, H.-S.; Song, S.-S.; Ryoo, R.; Pang, C.; Baek, K.-H.; Kim, K.H. Cytotoxic Constituents from the Sclerotia of Poria cocos against Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Inducing Mitochondrial Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Song, J.H.; Song, J.-H.; Ko, H.-J.; Baek, J.Y.; Trinh, T.A.; Beemelmanns, C.; Yamabe, N.; Kim, K.H. Chemical Identification of Isoflavonoids from a Termite-Associated Streptomyces sp. RB1 and Their Neuroprotective Effects in Murine Hippocampal HT22 Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, J.M.; Yang, E.J.; Choi, S.H.; Song, K.S. Isolation of phenolic glucosides from the Stems of Acer tegmentosum Max. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2006, 49, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, N.H.; Ding, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Bae, K.H.; Kim, Y.H. Total peroxyl radical-scavenging capacity of the chemical components from the stems of Acer tegmentosum maxim. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10510–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.M.; Yang, M.C.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.R.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. Cytotoxic phenolic constituents of Acer tegmentosum maxim. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Park, Y.J.; Han, Y.B.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.H. Isoamericanoic Acid B from Acer tegmentosum as a Potential Phytoestrogen. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.Y.; Jung, Y.S.; Yoon, C.S.; Oh, J.S.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.Y. Fraxin Prevents Chemically Induced Hepatotoxicity by Reducing Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2017, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parga, J.A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Garcia-Garrote, M.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Angiotensin II induces oxidative stress and upregulates neuroprotective signaling from the NRF2 and KLF9 pathway in dopaminergic cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Patil, J.; D′Angelo, B.; Weber, S.G.; Mallard, C. NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: Implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakel, R.J.; Townsend, J.A.; Kraft, A.D.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2-mediated protection against 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res. 2007, 1144, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, F. Icariin attenuates neuroinflammation and exerts dopamine neuroprotection via an Nrf2-dependent manner. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, O.; Mandel, S.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Amit, T. Targeting dysregulation of brain iron homeostasis in Parkinson′s disease by iron chelators. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Song, N.; Wang, R.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Preferential Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Striatal Astrocytes Antagonizes Dopaminergic Neuron Degeneration in MPTP-Intoxicated Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5056–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in sulfuretin-induced protection against amyloid beta25-35 neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 2015, 304, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, H. Naringenin Inhibit the Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells Injury Through Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 36, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Amin, F.U.; Khan, M.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer′s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, K. Tricetin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in Parkinson′s disease model by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and preventing mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 378, 114617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, V.B.; Rosa, P.B.; Moretti, M.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Involvement of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2283–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, M.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Townsend, J.A.; Vargas, M.R.; Dowell, J.A.; Williamson, T.P.; Kraft, A.D.; Lee, J.; Li, J.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2--a therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Park, H.B.; Kim, K.H. Highly Sensitive, Simple, and Cost- and Time-Effective Method to Determine the Absolute Configuration of a Secondary Alcohol Using Competing Enantioselective Acylation Coupled with LC/MS. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13212–13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.X.; Ren, J.; Qin, J.J.; Cheng, X.R.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yan, S.K.; Jin, H.Z.; Zhang, W.D. Phenylpropanoids and lignanoids from Euonymus acanthocarpus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, G.; Nishimura, H.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and Related Compounds. IV. Seven New Phenol Glucoside Gallates from Quercus stenophylla MAKINO (1). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1982, 30, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.W.; Cui, C.B. One New and Nine Known Flavonoids from Choerospondias axillaries and Their in Vitro Antitumor, Anti-Hypoxia and Antibacterial Activities. Molecules 2014, 19, 21363–21377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guvenalp, Z.; Demirezer, L.O. Flavonol Glycosides from Asperula arvensis L. Turk. J. Chem. 2005, 29, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ek, S.; Kartimo, H.; Mattila, S.; Tolonen, A. Characterization of phenolic compounds from lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 9834–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Thuong, P.T.; Jin, W.Y.; Su, N.D.; Sok, D.E.; Bae, K.; Kang, S.S. Antioxidant activity of anthraquinones and flavonoids from flower of Reynoutria sachalinensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of flavonoids as vasorelaxant agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 3949–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, H.; Germer, S.; Elsaber, J.; Ritter, T. Benzopyranones and Their Sulfate Esters from Pelargonium sidoides. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerezano, A.; Jimenez, F.; Carmen Cruz, M.; Montiel, L.E.; Delgado, F.; Tamariz, J. New Approach for the Construction of the Coumarin Frame and Application in the Total Synthesis of Natural Products. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, S.; Suphapong, S.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Lawung, R.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Bioactive Metabolites from Spilanthes acmella Murr. Molecules 2009, 14, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaya, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Miura, S.; Akutagawa, T.; Hotta, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Niwa, M. Antioxidant Constituents in Distillation Residue of Awamori Spirits. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Kawabata, J. Effects of electron-withdrawing substituents on DPPH radical scavenging reactions of protocatechuic acid and its analogues in alcoholic solvents. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8101–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Reddy, M.L.P.; Cowley, A.H.; Vasudevan, K.V. Synthesis and crystal structures of lanthanide 4-benzyloxy benzoates: Influence of electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups on luminescent properties. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, S.M.; Ding, H.Y.; Chang, W.L.; Lin, H.C. Phenols from the aerial parts of Leonurus sibiricus. Chin. Pharm. J. 2006, 58, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Han, X.; Piao, M.J.; Oh, M.C.; Fernando, P.M.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Jung, U.; Kim, I.G.; Hyun, J.W. Hyperoside Induces Endogenous Antioxidant System to Alleviate Oxidative Stress. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Um, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of hyperoside through the suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Kong, R.; Pan, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Hyperoside induces apoptosis and inhibits growth in pancreatic cancer via Bcl-2 family and NF-kappaB signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7345–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.W.; Wang, X.M.; Ko, H.; Kwon, H.C.; Cha, J.W.; Yang, H.O. Hyperoside protects primary rat cortical neurons from neurotoxicity induced by amyloid beta-protein via the PI3K/Akt/Bad/Bcl(XL)-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 672, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Xiong, Q.J.; Shu, Q.; Wu, W.N.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.G.; Hu, Z.L. Hyperoside protects cortical neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-reperfusion induced injury via nitric oxide signal pathway. Brain Res. 2012, 1469, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Huang, D.; Yang, R.; Zhou, L.; Li, C.; Xiong, Q.; Ziong, Z. Hyperoside protects against chronic mild stress-induced learning and memory deficits. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson′s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eo, H.; Huh, E.; Sim, Y.; Oh, M.S. Ukgansan protects dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity via activation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 factor signaling pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 122, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Michaelis, E.K. Selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2010, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson′s disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2013, 3, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nita, M.; Grzybowski, A. The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of the Age-Related Ocular Diseases and Other Pathologies of the Anterior and Posterior Eye Segments in Adults. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 3164734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Sulfuretin inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death via reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanisms in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 74, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Youle, R.J. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis*. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Tao, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wei, D. Protective effects of hyperoside (quercetin-3-o-galactoside) to PC12 cells against cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide and tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copple, I.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kensler, T.W.; Liby, K.T.; Wigley, W.C. NRF2 as an Emerging Therapeutic Target. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 8165458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2-ARE pathway: A valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sivandzade, F.; Prasad, S.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. NRF2 and NF-B interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Davies, K.J.A.; Forman, H.J. Oxidative stress response and Nrf2 signaling in aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 314–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurutas, E.B. The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: Current state. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jazwa, A.; Cuadrado, A. Targeting heme oxygenase-1 for neuroprotection and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracca, A.; Sgarbi, G.; Solaini, G.; Lenaz, G. Rhodamine 123 as a probe of mitochondrial membrane potential: Evaluation of proton flux through F(0) during ATP synthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1606, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, S.-H.; Lee, S.R.; Park, Y.J.; Ra, M.; Lee, Y.; Pang, C.; Kim, K.H. Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235832
Kwon S-H, Lee SR, Park YJ, Ra M, Lee Y, Pang C, Kim KH. Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235832
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Seung-Hwan, Seoung Rak Lee, Yong Joo Park, Moonjin Ra, Yongjun Lee, Changhyun Pang, and Ki Hyun Kim. 2019. "Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235832
APA StyleKwon, S. -H., Lee, S. R., Park, Y. J., Ra, M., Lee, Y., Pang, C., & Kim, K. H. (2019). Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 5832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235832