Contribution of Palmitic Acid to Epidermal Morphogenesis and Lipid Barrier Formation in Human Skin Equivalents
Abstract
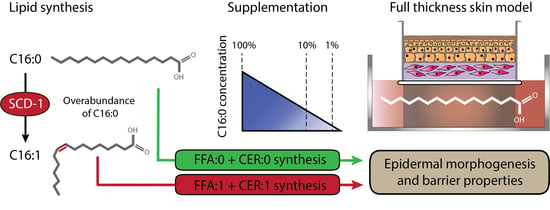
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FTMs Generated with Various PA Levels Displayed Similar Epidermal Architecture
2.2. Strong Reduction in PA Supplementation Level Compromised the Epidermal Morphogenesis
2.3. Supplementation of FTMs with Various PA Levels Resulted in an Equal Composition of FFA in the SC
2.4. Variations in Supplemented PA did not alter the Composition of CERs in the SC
2.5. FTMs Supplemented with Reduced PA Exhibited a Similar Lipid Organization
2.6. Reduction of Supplemented PA Resulted in a Similar Expression of Lipid Processing Enzymes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of FTMs
4.2. Immunohistochemical Analyses
4.3. Gene Expression Analyses
4.4. Lipidomics Analyses
4.4.1. Lipid Extraction
4.4.2. FFA Analysis
4.4.3. CER Analysis
4.5. Small Angle X-Ray Diffraction
4.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.7. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SC | Stratum corneum |
| NHS | Native human skin |
| HSE | Human skin equivalent |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| CER | Ceramide |
| LPP | Long periodicity phase |
| SPP | Short periodicity phase |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| PA | Palmitic acid |
| SCD-1 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 |
| FTM | Full thickness model |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| saFFA | Saturated free fatty acid |
| muFFA | Monounsaturated free fatty acid |
| puFFA | Polyunsaturated free fatty acid |
| MCL | Mean carbon chain length |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| ISTD | Internal standard |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| amu | Atomic mass unit |
| saCER | Saturated ceramide |
| muCER | Monounsaturated ceramide |
| SAXD | Small angle X-ray diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| ELOVL | Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein |
| CERS | Ceramide synthase |
| SREBP | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| MGAT | Monoacyglycerol acyltransferases |
| DGAT | Diacylglycerol acyltransferases |
| GPAT | Glycerol phosphate acyltransferase |
| ACAT | Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| UPLC | Ultra performance liquid chromatography |
| FFPE | Formalin fixed paraffin embedded |
References
- Lilienblum, W.; Dekant, W.; Foth, H.; Gebel, T.; Hengstler, J.G.; Kahl, R.; Kramer, P.-J.; Schweinfurth, H.; Wollin, K.-M. Alternative methods to safety studies in experimental animals: Role in the risk assessment of chemicals under the new european chemicals legislation (reach). Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Directive. Directive 2003/15/ec of the european parliament and of the council of 27 february 2003 amending council directive 76/768/eec on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to cosmetic products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2003, 66, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst, M.; Rietveld, M.; Gruijl, F.; El Ghalbzouri, A. A shift from papillary to reticular fibroblasts enables tumour–stroma interaction and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Mahmoud, A.; Vuia, A.; Rübbelke, M.; Schmidt, E.; Schaller, M.; Kandarova, H.; Haberland, A.; Schäfer, U.; Bock, U. Reconstructed epidermis versus human and animal skin in skin absorption studies. Toxicol. Vitr. 2005, 19, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer-Korting, M.; Bock, U.; Diembeck, W.; Düsing, H.-J.; Gamer, A.; Haltner-Ukomadu, E.; Hoffmann, C.; Kaca, M.; Kamp, H.; Kersen, S. The use of reconstructed human epidermis for skin absorption testing: Results of the validation study. Altern. Lab. Anim 2008, 36, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehues, H.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Brandner, J.M.; Zeeuwen, P.L.; van den Bogaard, E.H. 3d skin models for 3r research: The potential of 3d reconstructed skin models to study skin barrier function. Exp. Dermatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakoersing, V.S.; Gooris, G.S.; Mulder, A.; Rietveld, M.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Unraveling barrier properties of three different in-house human skin equivalents. Tissue Eng. Part C: Methods 2011, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponec, M.; Boelsma, E.; Gibbs, S.; Mommaas, M. Characterization of reconstructed skin models. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 15, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieremet, A.; van Dijk, R.; Boiten, W.; Gooris, G.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A. Characterization of human skin equivalents developed at body’s core and surface temperatures. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieremet, A.; Rietveld, M.; Absalah, S.; van Smeden, J.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A. Improved epidermal barrier formation in human skin models by chitosan modulated dermal matrices. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakoersing, V.S.; Van Smeden, J.; Mulder, A.A.; Vreeken, R.J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Increased presence of monounsaturated fatty acids in the stratum corneum of human skin equivalents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponec, M.; Gibbs, S.; Pilgram, G.; Boelsma, E.; Koerten, H.; Bouwstra, J.; Mommaas, M. Barrier function in reconstructed epidermis and its resemblance to native human skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2001, 14 (Suppl. 1), 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiten, W.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.; Bouwstra, J.; van Smeden, J. Quantitative analysis of ceramides using a novel lipidomics approach with three dimensional response modelling. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-H.; Khnykin, D. Fatty acid transporters in skin development, function and disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.C.; Pilkington, S.M.; Massey, K.A.; Sassano, G.; Rhodes, L.E.; Nicolaou, A. Distribution of bioactive lipid mediators in human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Role of lipids in the formation and maintenance of the cutaneous permeability barrier. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao-Qiang, M.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Fatty acids are required for epidermal permeability barrier function. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakoersing, V.S.; Smeden, J.; Boiten, W.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Mulder, A.A.; Vreeken, R.J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Modulation of stratum corneum lipid composition and organization of human skin equivalents by specific medium supplements. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vičanová, J.; Weerheim, A.M.; Kempenaar, J.A.; Ponec, M. Incorporation of linoleic acid by cultured human keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1999, 291, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürer, N.; Schliep, V.; Williams, M.L. Differential utilization of linoleic and arachidonic acid by cultured human keratinocytes. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1995, 8, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, S.T.; Williams, M.L. Lipid supplemented medium induces lamellar bodies and precursors of barrier lipids in cultured analogues of human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, A.; Weigert, C.; Staiger, H.; Machicao, F.; Schick, F.; Machann, J.; Stefan, N.; Thamer, C.; Häring, H.-U.; Schleicher, E. Individual stearoyl-coa desaturase 1 expression modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in human myotubes and is associated with skeletal muscle lipid storage and insulin sensitivity in vivo. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.; Volkov, P.; Dayeh, T.; Bacos, K.; Rönn, T.; Nitert, M.D.; Ling, C. Effects of palmitate on genome-wide mrna expression and DNA methylation patterns in human pancreatic islets. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listenberger, L.L.; Han, X.; Lewis, S.E.; Cases, S.; Farese, R.V.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Triglyceride accumulation protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.; Angres, S.; Seltmann, H. Regulation of stearoyl-coenzyme a desaturase and fatty acid delta-6 desaturase-2 expression by linoleic acid and arachidonic acid in human sebocytes leads to enhancement of proinflammatory activity but does not affect lipogenesis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezure, T.; Amano, S. Negative regulation of dermal fibroblasts by enlarged adipocytes through release of free fatty acids. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; van der Spek, J.A.; Bras, W. Structural investigations of human stratum corneum by small-angle x-ray scattering. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, A. Very long-chain fatty acids: Elongation, physiology and related disorders. J. Biochem. 2012, 152, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigolet, M.E.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R. The role of the novel lipokine palmitoleic acid in health and disease. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 173S–181S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Mitsutake, S.; Tsuji, K.; Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. Ceramide biosynthesis in keratinocyte and its role in skin function. Biochimie 2009, 91, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schürer, N.Y.; Monger, D.J.; Hincenbergs, M.; Williams, M.L. Fatty acid metabolism in human keratinocytes cultivated at an air-medium interface. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiekstra, S.W.; dos Santos, G.G.; Scheper, R.J.; Gibbs, S. Potential method to determine irritant potency in vitro – comparison of two reconstructed epidermal culture models with different barrier competency. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, M.; van Smeden, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Portale, G.; Caspers, P.J.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Kezic, S.; Wolterbeek, R. Increase in short-chain ceramides correlates with an altered lipid organization and decreased barrier function in atopic eczema patients. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, J.; Narita, H.; Kondo, N.; Hotta, M.; Takagi, Y.; Masukawa, Y.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y.; Koyano, S.; Yamazaki, S.; et al. Changes in the ceramide profile of atopic dermatitis patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2511–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piccolis, M.; Bond, L.M.; Kampmann, M.; Pulimeno, P.; Chitraju, C.; Jayson, C.B.K.; Vaites, L.P.; Boland, S.; Lai, Z.W.; Gabriel, K.R.; et al. Probing the global cellular responses to lipotoxicity caused by saturated fatty acids. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Shen, L.-F.; Haddad, A.N.S.; Song, I.W.; Chen, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wu, J.-Y.; Yen, J.J.Y.; Chen, Y.-T. Cyclic alopecia and abnormal epidermal cornification in zdhhc13-deficient mice reveal the importance of palmitoylation in hair and skin differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strable, M.S.; Ntambi, J.M. Genetic control of de novo lipogenesis: Role in diet-induced obesity. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grubauer, G.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Relationship of epidermal lipogenesis to cutaneous barrier function. J. Lipid Res. 1987, 28, 746–752. [Google Scholar]
- Man, M.-Q.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Exogenous lipids influence permeability barrier recovery in acetone-treated murine skin. Arch. Dermatol. 1993, 129, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuth, M.; Ortegon, A.M.; Mao-Qiang, M.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R.; Stahl, A. Differential expression of fatty acid transport proteins in epidermis and skin appendages. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popa, I.; Watson, A.L.; Solgadi, A.; Butowski, C.; Allaway, D.; Portoukalian, J. Linoleate-enriched diet increases both linoleic acid esterified to omega hydroxy very long chain fatty acids and free ceramides of canine stratum corneum without effect on protein-bound ceramides and skin barrier function. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Hong, I.; Hwang, J.S.; Choi, J.K.; Rho, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Chang, I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.-O.; Hwang, J.S. Phytosphingosine stimulates the differentiation of human keratinocytes and inhibits tpa-induced inflammatory epidermal hyperplasia in hairless mouse skin. Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Liu, K.-H.; Park, C.S. Phytosphingosine increases biosynthesis of phytoceramide by uniquely stimulating the expression of dihydroceramide c4-desaturase (des2) in cultured human keratinocytes. Lipids 2018, 53, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uche, L.E.; Gooris, G.S.; Beddoes, C.M.; Bouwstra, J.A. New insight into phase behavior and permeability of skin lipid models based on sphingosine and phytosphingosine ceramides. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2019, 1861, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jager, M.W.; Gooris, G.S.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Bras, W.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Novel lipid mixtures based on synthetic ceramides reproduce the unique stratum corneum lipid organization. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Gooris, G.S.; Groen, D.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J.; Demé, B.; Bouwstra, J.A. Stratum corneum lipid matrix: Location of acyl ceramide and cholesterol in the unit cell of the long periodicity phase. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchiyama, M.; Oguri, M.; Mojumdar, E.H.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Free fatty acids chain length distribution affects the permeability of skin lipid model membranes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Helder, R.W.J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Monounsaturated fatty acids reduce the barrier of stratum corneum lipid membranes by enhancing the formation of a hexagonal lateral packing. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- t’Kindt, R.; Jorge, L.; Dumont, E.; Couturon, P.; David, F.; Sandra, P.; Sandra, K. Profiling and characterizing skin ceramides using reversed-phase liquid chromatography–quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, B.M.; Chen, J.; Evans, R.M. Hypolipidemic drugs, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and eicosanoids are ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and δ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4312–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivier, M.; Safonova, I.; Michel, S.; Castiel, I.; Ailhaud, G. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α enhances lipid metabolism in a skin equivalent model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcelo, C.L.; Dunham, W.R. Fatty acid metabolism studies of human epidermal cell cultures. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haisma, E.M.; Rietveld, M.H.; de Breij, A.; van Dissel, J.T.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Nibbering, P.H. Inflammatory and antimicrobial responses to methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro wound infection model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Ghalbzouri, A.; Commandeur, S.; Rietveld, M.H.; Mulder, A.A.; Willemze, R. Replacement of animal-derived collagen matrix by human fibroblast-derived dermal matrix for human skin equivalent products. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Endo, Y.; Ozawa, N.; Sugawara, T.; Kusaka, A.; Sayo, T.; Inoue, S.; Tagami, H. Characteristics of the epidermis and stratum corneum of hairless mice with experimentally induced diabetes mellitus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mieremet, A.; van Dijk, R.; Gooris, G.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A. Shedding light on the effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 on epidermal lipid barrier formation in three-dimensional human skin equivalents. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 189, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkers, T.; Dijk, L.; Absalah, S.; Smeden, J.; Bouwstra, J.A. Topically applied fatty acids are elongated before incorporation in the stratum corneum lipid matrix in compromised skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, S.; Monti, M.; Sesana, S.; Caputo, R.; Carelli, S.; Ghidoni, R. Ceramide composition of the psoriatic scale. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1993, 1182, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, R.W.J.; Boiten, W.A.; van Dijk, R.; Gooris, G.S.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. The effects of LXR agonist T0901317 and LXR antagonist GSK2033 on morphogenesis and lipid properties in full thickness skin models. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Lipids 2019, 1865, 158546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mieremet, A.; Helder, R.; Nadaban, A.; Gooris, G.; Boiten, W.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Contribution of Palmitic Acid to Epidermal Morphogenesis and Lipid Barrier Formation in Human Skin Equivalents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236069
Mieremet A, Helder R, Nadaban A, Gooris G, Boiten W, El Ghalbzouri A, Bouwstra JA. Contribution of Palmitic Acid to Epidermal Morphogenesis and Lipid Barrier Formation in Human Skin Equivalents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236069
Chicago/Turabian StyleMieremet, Arnout, Richard Helder, Andreea Nadaban, Gert Gooris, Walter Boiten, Abdoelwaheb El Ghalbzouri, and Joke A. Bouwstra. 2019. "Contribution of Palmitic Acid to Epidermal Morphogenesis and Lipid Barrier Formation in Human Skin Equivalents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236069
APA StyleMieremet, A., Helder, R., Nadaban, A., Gooris, G., Boiten, W., El Ghalbzouri, A., & Bouwstra, J. A. (2019). Contribution of Palmitic Acid to Epidermal Morphogenesis and Lipid Barrier Formation in Human Skin Equivalents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236069