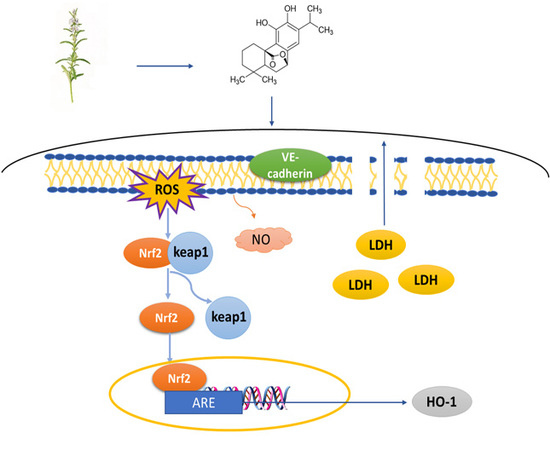
Carnosol as a Nrf2 Activator Improves Endothelial Barrier Function Through Antioxidative Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Carnosol Has the Antioxidant Activity in ABTS Assay
2.2. Carnosol Can Protect HMVEC Cells Against t-BHP Induced Cell Injury
2.3. Carnosol Increases the Expression of VE-Cadherin in HMVEC Cells
2.4. Carnosol Reduces the ROS Production and Promotes NO Release in t-BHP-Induced Cell Injury in HMVEC Cells
2.5. Carnosol Has the Potential of Interrupting Nrf2-Keap1 Protein−Protein Interaction and Stimulating ARE-Mediated Luciferase Activity
2.6. Carnosol Stimulates the Expression of Cytoprotective Genes and Proteins.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Line and Culture
4.3. Antioxidant Activity by ABTS Method
4.4. CCK-8 Assay for Cell Viability Evaluation
4.5. Determination of LDH
4.6. Annexin V-FITC/PI Double Staining
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Measurement of ROS and NO Generation
4.9. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.10. Luciferase Reporter Activity Assay
4.11. mRNA Quantification by Real-Time PCR
4.12. Assessment Expression of HO-1 and Nrf2 Proteins
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMVEC | human microvascular endothelial cells |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| VE-cadherin | vascular endothelial cadherin |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 |
| Keap1 | kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| ARE | antioxidant-responsive element |
| t-BHP | tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
| ABTS | 2,2’-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| TBHQ | Tertiary butylhydroquinone |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| GSH | glutathione |
| GCLC | glutamate-cystein ligase catalytic |
| GST | glutathione-S-transferase |
| NQO1 | NADP(H) quinone oxidoreductase 1 |
References
- Patel, H.; Chen, J.; Das, K.C.; Kavdia, M. Hyperglycemia induces differential change in oxidative stress at gene expression and functional levels in huvec and hmvec. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dai, F.; Liu, H.; Ren, W.; Chang, J.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Road, J. Dephosphorylation of y685-ve-cadherin involved in pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier injury induced by angiotensin ii. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannotta, M.; Trani, M.; Dejana, E. Ve-cadherin and endothelial adherens junctions: Active guardians of vascular integrity. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Kim, D.; Yagi, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kurita, J.; Iida, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Application of ldh-release assay to cellular-level evaluation of the toxic potential of harmful algal species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Horke, S.; Forstermann, U. Vascular oxidative stress, nitric oxide and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, M.; Kim, S.J. Insulin on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress involves ros/ca2+ and akt/bcl-2 signaling pathways. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Chang, H.C.; Cheng, Y.D.; Lan, W.C.; Yang, S.E.; Ching, H. Aqueous extract of davallia mariesii attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in b35 cells through inhibition of caspase cascade and activation of pi3k/akt/gsk-3beta pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J. The role of nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced endothelial injuries. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.L.; Sinha, S.; Lindner, A.B. The good, the bad, and the ugly of ros: New insights on aging and aging-related diseases from eukaryotic and prokaryotic model organisms. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaria, M.; Cho, D.Y.; Haque, M.E.; Karthivashan, G.; Kim, I.S.; Ganesan, P.; Choi, D.K. Neuropharmacological potential and delivery prospects of thymoquinone for neurological disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruno, A.; Yagishita, Y.; Yamamoto, M. The keap1-nrf2 system and diabetes mellitus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 566, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Qian, Q.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Rabbani, N.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Thornalley, P.J. Activation of nf-e2-related factor-2 reverses biochemical dysfunction of endothelial cells induced by hyperglycemia linked to vascular disease. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuoka, F.; Motohashi, H.; Ishii, T.; Aburatani, H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Genetic evidence that small maf proteins are essential for the activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Mcmahon, M.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Cancer chemoprevention mechanisms mediated through the keap1-nrf2 pathway. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1713–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.X.; Li, G.H.; Sun, B.; Xu, Y.W.; Li, A.L.; Li, Y.R.; Ren, D.M.; Wang, X.N.; Wen, X.S.; Lou, H.X. Identification of novel nrf2 activators from cinnamomum chartophyllum h. W. Li and their potential application of preventing oxidative insults in human lung epithelial cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskovic, A.; Milanovic, I.; Pavlovic, N.; Cebovic, T.; Vukmirovic, S.; Mikov, M. Antioxidant activity of rosemary (rosmarinus officinalis l.) essential oil and its hepatoprotective potential. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Horcajada, M.N.; Scalfo, F.M.; Ameye, L.; Offord, E.; Henrotin, Y. Carnosol inhibits pro-inflammatory and catabolic mediators of cartilage breakdown in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and mediates cross-talk between subchondral bone osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Plos One 2015, 10, e0136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, F.; Scanu, A.; Zamudio-Cuevas, Y.; Punzi, L.; Spinella, P. Anti-inflammatory effects of polyphenols in arthritis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 98, doi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; He, X.; Lian, L.; Wu, X.; Lan, P. Carnosol inhibits cell adhesion molecules and chemokine expression by tumor necrosis factor-α in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through the nuclear factor-κb and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro, I.; Lopez-Sanz, L.; Bernal, S.; Oguiza, A.; Recio, C.; Melgar, A.; Jimenez-Castilla, L.; Egido, J.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Gomez-Guerrero, C. Nrf2 activation provides atheroprotection in diabetic mice through concerted upregulation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and autophagy mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Das, A.; Sinha, M.; Saha, S. Biological efficacy of medicinal plant extracts in preventing oxidative damage. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7904349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Kumar, G.; Sharma, A.; Sak, K.; Tuli, H.S.; Mukherjee, T.K. Mechanistic insight into carnosol-mediated pharmacological effects: Recent trends and advancements. Life Sci. 2017, 169, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari Fakhrabadi, M.; Zeinali Ghotrom, A.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Hadi Nodoushan, H.; Nadjarzadeh, A. Effect of coenzyme q10 on oxidative stress, glycemic control and inflammation in diabetic neuropathy: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2014, 84, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.K.; Singh, U.K. Oxidative stress: Meeting multiple targets in pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Kowluru, A.; Mishra, M.; Kumar, B. Oxidative stress and epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 48, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, C.Y.; Hourihan, J.M.; Blackwell, T.K. Oxidative stress assays (arsenite and tbhp) in caenorhabditis elegans. Bio. Protoc. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manu, T.M.; Anand, T.; Khanum, F. Attenuation of cytotoxicity induced by tbhp in h9c2 cells by bacopa monniera and bacoside a. Pathophysiology 2018, 25, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Liu, F. Betulinic acid alleviates myocardial hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via inducing nrf2/ho-1 and inhibiting p38 and jnk pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 838, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.L.; Du, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.H.; Yang, X.L.; Zheng, R.H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.S.; Liu, H.R. Endothelial dysfunction induced by antibodies against angiotensin at1 receptor in immunized rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schor, N.F. Apoptosis in the Nervous System. In The Neurology of Neuroblastoma; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Cai, B.; Deng, P.; Wu, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cai, W.; Schaper, J.; Schaper, W. Nitric oxide increases arterial endotheial permeability through mediating ve-cadherin expression during arteriogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. Antioxidants as therapies: Can we improve on nature? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selimoglu-Buet, D.; Badaoui, B.; Benayoun, E.; Toma, A.; Fenaux, P.; Quesnel, B.; Etienne, G.; Braun, T.; Abermil, N.; Morabito, M.; et al. Accumulation of classical monocytes defines a subgroup of mds that frequently evolves into cmml. Blood 2017, 130, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanson, A.L.; Marica, B. Dietary regulation of keap1/nrf2/are pathway: Focus on plant-derived compounds and trace minerals. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3777–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; de la Vega, M.R.; Wen, Q.; Bharara, M.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, S.; Wong, P.K.; Wondrak, G.T.; Zheng, H.; et al. An essential role of nrf2 in diabetic wound healing. Diabetes 2016, 65, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullinan, S.B.; Zhang, D.; Hannink, M.; Arvisais, E.; Kaufman, R.J.; Diehl, J.A. Nrf2 is a direct perk substrate and effector of perk-dependent cell survival. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 7198–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.E.; Wang, Q.J.; Gao, J.; Ban, S.R.; Li, Q.S. Synthesis of novel nitrogen-containing heterocycle bromophenols and their interaction with keap1 protein by molecular docking. Molecules 2017, 22, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Chu, H.X.; Xi, M.Y.; Yang, T.T.; Jia, J.M.; Huang, J.J.; Guo, X.K.; Zhang, X.J.; You, Q.D.; Sun, H.P. Insight into the intermolecular recognition mechanism between keap1 and ikkbeta combining homology modelling, protein-protein docking, molecular dynamics simulations and virtual alanine mutation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75076. [Google Scholar]
- Amata, E.; Pittala, V.; Marrazzo, A.; Parenti, C.; Prezzavento, O.; Arena, E.; Nabavi, S.M.; Salerno, L. Role of the nrf2/ho-1 axis in bronchopulmonary dysplasia and hyperoxic lung injuries. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Dihydromyricetin protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from injury through erk and akt mediated nrf2/ho-1 signaling pathway. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Sequence (5’–3’) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| HO-1 F | ACTGCGTTCCTGCTCAACAT | 133 |
| HO-1 R | GGGCAGAATCTTGCACTTTGT | |
| Nrf2 F | TCTGCCAACTACTCCCAGGT | 124 |
| Nrf2 R | ACGTAGCCGAAGAAACCTCA | |
| eNOS F | GCCGGAACAGCACAAGAGTTA | 147 |
| eNOS R | GCCCGAACACACAGAACCT | |
| GAPDH F | CTTTGTCAAGCTCATTTCCTGG | 133 |
| GAPDH R | TCTTCCTCTTGTGCTCTTGC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, N.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; et al. Carnosol as a Nrf2 Activator Improves Endothelial Barrier Function Through Antioxidative Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040880
Li X, Zhang Q, Hou N, Li J, Liu M, Peng S, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Zhao B, Wang S, et al. Carnosol as a Nrf2 Activator Improves Endothelial Barrier Function Through Antioxidative Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040880
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xi, Qiao Zhang, Ning Hou, Jing Li, Min Liu, Sha Peng, Yuxin Zhang, Yinzhen Luo, Bowen Zhao, Shifeng Wang, and et al. 2019. "Carnosol as a Nrf2 Activator Improves Endothelial Barrier Function Through Antioxidative Mechanisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040880
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, Q., Hou, N., Li, J., Liu, M., Peng, S., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Zhao, B., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., & Qiao, Y. (2019). Carnosol as a Nrf2 Activator Improves Endothelial Barrier Function Through Antioxidative Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040880