Toxicological Evaluation of SiO2 Nanoparticles by Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of NPs in Suspension
2.2. Effects of SiO2 NPs on the Development of Zebrafish Embryo
2.3. Effect on Angiogenesis in Zebrafish Embryos
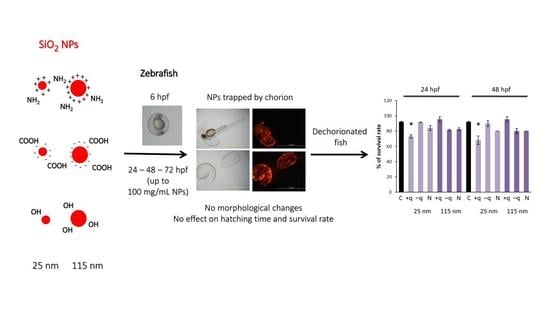
2.4. Protective Effect of Chorion Against SiO2 NPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of NPs Suspensions
3.2. Zebrafish
3.3. Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test (ZFET)
3.4. Evaluation of Survival Rate, Hatching Rate, and Gross Morphological Changes
3.5. Evaluation of NPs Localization
3.6. Evaluation of Development of Subintestinal Vessels and Measurement of Gene Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and VEGF Receptors
3.7. Evaluation of Survival Rate and Gross Morphological Changes after Dechorionation of Zebrafish Embryos
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| EGFP | enhanced green fluorescent protein |
| Flt-1 | Fms-like tyrosine kinase |
| hpf | hours post fertilization |
| KDR | kinase insert domain receptor |
| NPs | nanoparticles |
| PdI | polydispersity index |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SiO2 | silicon dioxide |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| ZFET | zebrafish embryo acute toxicity test |
References
- Pan, J.; Wan, D.; Gong, J. PEGylated liposome coated QDs/mesoporous silica core-shell nanoparticles for molecular imaging. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2011, 47, 3442–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Qu, H.; Manbachi, A.; Butt, H.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Skorobogatiy, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yun, S.H. Nanotechnology in textiles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3042–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.; Roblegg, E. Oral uptake of nanoparticles: Human relevance and the role of in vitro systems. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2297–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietroiusti, A.; Bergamaschi, E.; Campagna, M.; Campagnolo, L.; de Palma, G.; Iavicoli, S.; Leso, V.; Magrini, A.; Miragoli, M.; Pedata, P.; et al. The unrecognized occupational relevance of the interaction between engineered nanomaterials and the gastro-intestinal tract: A consensus paper from a multidisciplinary working group. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Maynard, A.; Donaldson, K.; Castranova, V.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Ausman, K.; Carter, J.; Karn, B.; Kreyling, W.; Lai, D.; et al. Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: Elements of a screening strategy. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2005, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Cambre, M.; Lee, H.J. The Toxicity of nanoparticles depends on multiple molecular and physicochemical mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada-Oikawa, S.; Ichihara, G.; Fukatsu, H.; Shimanuki, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Watanabe, E.; Suzuki, Y.; Murakami, M.; Izuoka, K.; Chang, J.; et al. Titanium dioxide particle type and concentration influence the inflammatory response in caco-2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ude, V.C.; Brown, D.M.; Viale, L.; Kanase, N.; Stone, V.; Johnston, H.J. Impact of copper oxide nanomaterials on differentiated and undifferentiated Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells; assessment of cytotoxicity, barrier integrity, cytokine production and nanomaterial penetration. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempen, P.J.; Greasley, S.; Parker, K.A.; Campbell, J.L.; Chang, H.Y.; Jones, J.R.; Sinclair, R.; Gambhir, S.S.; Jokerst, J.V. Theranostic mesoporous silica nanoparticles biodegrade after pro-survival drug delivery and ultrasound/magnetic resonance imaging of stem cells. Theranostics 2015, 5, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, P.N.; Lin, Y.S.; Dunphy, D.R.; Muñiz, A.J.; Butler, K.S.; Humphrey, K.R.; Lokke, A.J.; Agola, J.O.; Chou, S.S.; Chen, I.M.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for active targeting and delivery to individual leukemia cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8325–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisasola, E.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Beyond traditional hyperthermia: In vivo cancer treatment with magnetic-responsive mesoporous silica nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Ichihara, G.; Shimada, Y.; Tada-Oikawa, S.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Zhang, B.; Suzuki, Y.; Sehsah, R.; Kato, M.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Copper oxide nanoparticles reduce vasculogenesis in transgenic zebrafish through down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and induction of apoptosis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Nishimura, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Umemoto, N.; Shimada, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Kayasuga, K.; Morihara, M.; Katagi, J.; Shiroya, T.; et al. Comparative study of the zebrafish embryonic toxicity test and mouse embryonic stem cell test to screen developmental toxicity of human pharmaceutical drugs. Fundament. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delov, V.; Muth-Köhne, E.; Schäfers, C.; Fenske, M. Transgenic fluorescent zebrafish Tg(fli1:EGFP)y¹ for the identification of vasotoxicity within the zFET. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.M.; Guarienti, M.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Embryo as an in vivo model for behavioral and pharmacological characterization of methylxanthine drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Murakami, S.; Ashikawa, Y.; Sasagawa, S.; Umemoto, N.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, T. Zebrafish as a systems toxicology model for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Congenit. Anom. (Kyoto) 2015, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquet, F.; Strecker, R.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T.; Carr, G.J.; Cenijn, P.; Fochtman, P.; Gourmelon, A.; Hübler, N.; et al. OECD validation study to assess intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Weisbrod, C.J.; Wirth-Heller, A.; Pieles, U. Assessment of uptake and toxicity of fluorescent silica nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y.X.; Sun, M.Z.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhao, X.; Feng, X.Z. SiO2 nanoparticles change colour preference and cause Parkinson’s-like behaviour in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundo, M.V.; Pecoraro, R.; Marino, F.; Salvaggio, A.; Tibullo, D.; Saccone, S.; Bramanti, V.; Buccheri, M.A.; Impellizzeri, G.; Scuderi, V.; et al. Toxicity evaluation of new engineered nanomaterials in zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, B.M.; Schulte-Merker, S. How to Plumb a Pisces: Understanding Vascular Development and Disease Using Zebrafish Embryos. Dev. Cell 2017, 42, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrache Voicu, S.N.; Dinu, D.; Sima, C.; Hermenean, A.; Ardelean, A.; Codrici, E.; Stan, M.S.; Zărnescu, O.; Dinischiotu, A. Silica nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and autophagy but not apoptosis in the MRC-5 cell line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29398–29416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Großgarten, M.; Holzlechner, M.; Vennemann, A.; Balbekova, A.; Wieland, K.; Sperling, M.; Lendl, B.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Karst, U.; Wiemann, M. Phosphonate coating of SiO2 nanoparticles abrogates inflammatory effects and local changes of the lipid composition in the rat lung: A complementary bioimaging study. Part Fibre. Toxicol. 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. The nanosilica hazard: Another variable entity. Part Fibre. Toxicol. 2010, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.H.; Wu, S.H.; Yao, M.; Lu, C.W.; Lin, Y.S.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, D.M. The effect of surfacecharge on the uptake and biological function of mesoporoussilicananoparticles in 3T3-L1 cells and human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhrunkar, S.; Qu, Z.; Popat, A.; Yang, J.; Noonan, O.; Acauan, L.; Ahmad Nor, Y.; Yu, C.; Karmakar, S. Effect of surfacefunctionality of silicananoparticles on cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3642–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y.; He, K.; Li, H.; Gao, F.; Moehling, T.J.; Wu, X.; Duncan, J.; Niu, Q. Exposure to alumina nanoparticles in female mice during pregnancy induces neurodevelopmental toxicity in the offspring. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, M.; Onoda, A.; Takeda, K. Developmental toxicity of nanoparticles on the brain. Yakugaku Zasshi 2017, 137, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, F. The reproductive and developmental toxicity of nanoparticles: A bibliometric analysis. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2018, 34, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhu, R.; Luo, Z.; Ren, B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, S.; You, H. Oxidative stress and apotosis to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and ZnO nanoparticles. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2017, 30, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eryılmaz, O.; Ateş, P.S.; Ünal, İ.; Üstündağ, Ü.; Bay, S.; Alturfan, A.A.; Yiğitbaşı, T.; Emekli-Alturfan, E.; Akalın, M. Evaluation of the interaction between proliferation, oxidant-antioxidant status, Wnt pathway, and apoptosis in zebrafish embryos exposed to silver nanoparticles used in textile industry. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Xu, X.H. In vivo imaging of transport and biocompatibility of single silver nanoparticles in early development of zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, H.; Tian, L.; Guo, C.; Huang, P.; Zhou, X.; Peng, S.; Sun, Z. Toxic effects of silica nanoparticles on zebrafish embryos and larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Tanguay, R.L. The role of chorion on toxicity of silver nanoparticles in the embryonic zebrafish assay. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2014, 29, e2014021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astin, J.W.; Haggerty, M.J.; Okuda, K.S.; Le Guen, L.; Misa, J.P.; Tromp, A.; Hogan, B.M.; Crosier, K.E.; Crosier, P.S. Vegfd can compensate for loss of Vegfc in zebrafish facial lymphatic sprouting. Development 2014, 141, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Ichihara, G.; Hashimoto, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tada-Oikawa, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Chang, J.; Kato, M.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; et al. Synergistic effect of bolus exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles on bleomycin-induced secretion of pro-fibrotic cytokines without lasting fibrotic changes in murine lungs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.A.; Robertson, C.P.; Lepage, T.; Johnson, S.L.; Raible, D.W. Nacre encodes a zebrafish microphthalmia-related protein that regulates neural-crest-derived pigment cell fate. Development 1999, 126, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, N.D.; Weinstein, B.M. In vivo imaging of embryonic vascular development using transgenic zebrafish. Dev. Bio. 2002, 248, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Hirano, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Tanaka, T. A high-throughput fluorescence-based assay system for appetite-regulating gene and drug screening. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.H.; Murray, J. Occupational respiratory disease in mining. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 2004, 54, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnizdo, E.; Sullivan, P.A.; Bang, K.M.; Wagner, G. Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and employment by industry and occupation in the US population: A study of data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnizdo, E.; Vallyathan, V. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease due to occupational exposure to silica dust: A review of epidemiological and pathological evidence. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| NPs | Hydrodynamic Size (nm) | PdI | Intensity of Particles of less than 100 nm (%) | Volume of Particles of less than 100 nm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 nm +q | 171.3 ± 8.58 | 0.394 ± 0.076 | 18.7 ± 1.9 | 33.9 ± 4.4 |
| 25 nm −q | 166.8 ± 2.05 | 0.113 ± 0.013 | 4.63 ± 0.75 | 10.5 ± 1.6 |
| 25 nm N | 132.2 ± 6.99 | 0.294 ± 0.060 | 28.5 ± 0.26 | 45.4 ± 4.8 |
| 115 nm +q | 228.9 ± 5.06 | 0.326 ± 0.021 | – | – |
| 115 nm −q | 152.7 ± 1.19 | 0.140 ± 0.006 | – | – |
| 115 nm N | 127.2 ± 1.10 | 0.081 ± 0.015 | – | – |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vranic, S.; Shimada, Y.; Ichihara, S.; Kimata, M.; Wu, W.; Tanaka, T.; Boland, S.; Tran, L.; Ichihara, G. Toxicological Evaluation of SiO2 Nanoparticles by Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040882
Vranic S, Shimada Y, Ichihara S, Kimata M, Wu W, Tanaka T, Boland S, Tran L, Ichihara G. Toxicological Evaluation of SiO2 Nanoparticles by Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040882
Chicago/Turabian StyleVranic, Sandra, Yasuhito Shimada, Sahoko Ichihara, Masayuki Kimata, Wenting Wu, Toshio Tanaka, Sonja Boland, Lang Tran, and Gaku Ichihara. 2019. "Toxicological Evaluation of SiO2 Nanoparticles by Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040882
APA StyleVranic, S., Shimada, Y., Ichihara, S., Kimata, M., Wu, W., Tanaka, T., Boland, S., Tran, L., & Ichihara, G. (2019). Toxicological Evaluation of SiO2 Nanoparticles by Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Test. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040882