Microwave-Synthesized Platinum-Embedded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Dual-Modality Contrast Agents: Computed Tomography and Optical Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
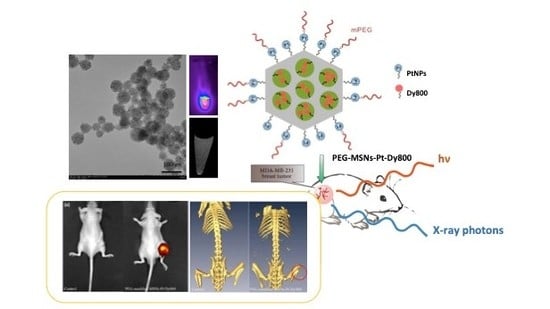
2.1. Synthesis of Dual-Modality MSNs Containing nPtNPs on the Outermost Surface for CT Contrast and NIR Probe (Dy800) in the Nanochannels for OI
2.2. In Vitro Optical and CT Images of Dual-Modality MSNs
2.3. Biocompatibility and Cellular Uptake of MSNs-Pt NPs
2.4. In Vivo Optical and CT Images of Dual-Modality MSNs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of MSNs-NH2 NPs
4.3. Synthesis of Platinum NPs on the MSNs
4.4. Preparation of MSNs-Pt-Dy800 Samples
4.5. PEG Conjugation
4.6. Characterization
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Cellular Uptake and TEM Imaging
4.9. In Vivo Optical Imaging
4.10. CT Imaging
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hun, Y.M.; Jun, Y.W.; Song, H.T.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, S.; Shin, J.S.; Suh, J.S.; Cheon, J. In vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer by using multifunctional magnetic nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12387–12391. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Y.W.; Hun, Y.M.; Choi, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Song, H.T.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, K.S.; Suh, J.S.; Cheon, J. Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5732–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veishe, O.; Sun, C.; Gunn, J.; Kohler, N.; Gabikian, P.; Lee, D.; Bhattarai, N.; Ellenbonge, R.; Sze, R.; Hallahan, A.; et al. Optical and MRI multifunctional nanoprobe for targeting gliomas. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cui, Y.; Levenson, R.M.; Chung, L.W.K.; Nie, S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nature Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovin, T.M. Quantum dots finally come of age. Nature Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattumuri, V.; Katti, K.; Bhaskaran, S.; Boote, J.B.; Casteel, S.W.; Fent, G.M.; Robertson, D.J.; Chandrasekhar, M.; Kannan, R.; Katti, K.V. Gum arabic as a phytochemical construct for the stabilization of gold nanoparticles: In vivo pharmacokinetics and X-ray-contrast-imaging studies. Small 2007, 3, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, W. Delivery of diagnostic agents in computed tomography. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 37, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tung, G.A.; Sun, S. Size and concentration effect of gold nanoparticles on x-ray attenuation as measures on computed tomography. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4167–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, R. A toxicologic review of quantum dots: Toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Porter, A.E.; Muller, K.; Koziol, K.; Skepper, J.N.; Midgley, P.; Welland, M. Imaging carbon nanoparticles and related cytotoxicity. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 151, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, W.S.; Kim, S.; Han, B.S.; Son, W.C.; Jeong, J. Comparison of gene expression profiles in mice liver following intravenous injection of 4 and 100 nm-sized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertegel, A.A.; Siegel, R.W.; Dordick, J.S. Silica nanoparticle size influences the structure and enzymatic activity of adsorbed lysozyme. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6800–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, F.; Rao, S.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Guo, C. PAMAM nanoparticles promote acute lung injury by inducing autophagic cell death through the Akt-TSC2-mTOR signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, B.; Ernst, L.A.; Andreko, S.; Harper, T.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Waggoner, A.S.; Bruchez, M.P. Sentinel lymph node imaging using quantum dots in mouse tumor models. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Mcneil, S.E. Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Tsuji, K.; Yang, M.; Jiang, P.; Moossa, A.R.; Hoffman, M.R. In vivo color-coded imaging of the interaction of colon cancer cells and splenocytes in the formation of liver metastases. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11293–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Lei, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-P.; Wang, C.-W.; Chang, M.-S. IL-24 inhibits the growth of hepatoma cells in vivo. Genes Immun. 2005, 6, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nahrendor, M.; Kelihe, E.; Marinelli, B.; Waterman, P.; Feruglio, P.F.; Fexon, L.; Pivovarov, M.; Swirski, F.K.; Pittet, M.J.; Vinegoni, C.; Weissleder, R. Hybrid PET-optical imaging using targeted probed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7910–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.H.; Miao, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Gambhir, S.S.; Cochran, J.R. A dual-labeled knottin peptide for PET and near-infrared fluorescence imaging of integrin expression in living subjects. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-T.; Noh, Y.-W.; Cho, J.-H.; Han, J.-H.; Choi, B.-S.; Kwon, J.; Hong, K.-S.; Gokarna, A.; Cho, Y.-H.; Chung, B.H. Multiplexed imaging of therapeutic cells with multispectrally encoded magnetofluorescent nanocomposite emulsions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17145–17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.; Song, I.C.; Park, S.P.; Moon, W.K.; et al. Uniform mesoporous dye-doped silica nanoparticles decorated with multiple magnetite nanocrystals for simultaneous enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yu, M.K.; Park, S.; Moon, S.; Min, J.J.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Kang, H.-W.; Jon, S. Thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and application as a dual imaging probe for cancer in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12739–12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-S.; Park, J.C.; Nah, H.; Woo, S.; Oh, J.; Kim, K.M.; Cheon, G.J.; Chang, Y.; Yoo, J.; Cheon, J. A hybrid nanoparticle probe for dual-modality positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6259–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaus, C.; Rossin, R.; Welch, M.J.; Bao, G. In vivo evaluation of (64) Cu-labeled magnetic nanoparticles as a dual-modality PET/MR imaging agent. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Caruso, F. Enzyme encapsulation in nanoporous silica spheres. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 1528–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, D.E.; Dams, M.; Sels, B.F.; Jacobs, P.A. Ordered mesoporous and microporous molecular sieves functionalized with transition metal complexes as catalysts for selective organic transformations. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3615–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Tanaka, N. Acc. Sol-gel with phase separation. Hierarchically porous materials optimized for high-performance liquid chromatography separations. Chem Res. 2007, 40, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bansal, V.; Zelikin, A.N.; Caruso, F. Templated synthesis of single-component polymer capsules and their application in drug delivery. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1741–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Giri, S.; Chen, H.T.; Lin, V.S.Y. Synthesis and functionalization of a mesoporous silica nanoparticle based on the sol-gel process and applications in controlled release. Acc. Chem Res. 2007, 40, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.P.; Hung, Y.; Chou, Y.H.; Huang, D.M.; Hsiao, J.K.; Chang, C.; Chen, Y.C.; Mou, C.Y. High-contrast paramagnetic fluorescent mesoporous silica nanorods as a multifunctional cell-imaging probe. Small 2008, 4, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Hung, Y.; Hsiao, J.K.; Yao, M.; Chung, T.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, S.H.; Hsu, S.C.; Liu, H.M.; Mou, C.Y.; et al. Bifunctional magnetic silica nanoparticles for highly efficient human stem cell labeling. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Choi, E.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Light-activated nanoimpeller-controlled drug release in cancer cells. Small 2008, 4, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-W.; Shau, Y.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Yang, Y.-S.; Shieh, D.-B.; Chen, C.-C. In vitro and in vivo studies of FePt nanoparticles for dual modal CT/MRI molecular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13270–13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Yin, J.J.; Nie, Z. pH dependent catalytic activities of platinum nanoparticles with respect to the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and scavenging of superoxide and singlet oxygen. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11904–11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Meng, L.; Fei, Z.; Dyson, P.J.; Zhang, L. On the origin of the synergy between the Pt nanoparticles and MnO2 nanosheets in Wonton-like 3D nanozyme oxidase mimics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhuang, Q.; Peng, H.; Liu, A.; Xia, X.; Chen, W. Chitosan-stabilized platinum nanoparticles as effective oxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of acid phosphatase. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10292–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Feng, J.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, N. Label-free detection of DNA by combining gated mesoporous silica and catalytic signal amplification of platinum nanoparticles. Analyst 2014, 139, 6088–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qiu, Q.; Sharif, S.; Ying, S.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Y. Solution-phase synthesis of platinum anoparticle-decorated metal-organic framework hybrid nanomaterials as biomimetic nanoenzymes for biosensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24108–24115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.J.; Wu, T.H.; Chien, C.T.; Tu, H.W.; Cha, T.S.; Lin, S.Y. Corrosion-activated chemotherapeutic function of nanoparticulate platinum as a cisplatin resistance-overcoming prodrug with limited autophagy induction. Small 2016, 12, 6124–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.H.; Yang, F.L.; Chang, C.H.; Chen-Yang, Y.W. Microwave-assisted synthesis of silica aerogel supported pt nanoparticles for self-humidifying proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 7669–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irum, M.; Zaheer, M.; Friedrich, M.; Kempe, R. Mesoporous silica nanosphere supported platinum nanoparticles (Pt@MSN): One-pot synthesis and catalytic hydrogen generation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10438–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Hanigan, M.H. Role of cysteine s-conjugate β-lyase in the metabolism of cisplatin. J. Pharm. Exper. Ther. 2003, 306, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, C.-H.; Cheng, S.-H.; Chen, N.-T.; Liao, W.-N.; Lo, L.-W. Microwave-Synthesized Platinum-Embedded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Dual-Modality Contrast Agents: Computed Tomography and Optical Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071560
Chu C-H, Cheng S-H, Chen N-T, Liao W-N, Lo L-W. Microwave-Synthesized Platinum-Embedded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Dual-Modality Contrast Agents: Computed Tomography and Optical Imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071560
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Chia-Hui, Shih-Hsun Cheng, Nai-Tzu Chen, Wei-Neng Liao, and Leu-Wei Lo. 2019. "Microwave-Synthesized Platinum-Embedded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Dual-Modality Contrast Agents: Computed Tomography and Optical Imaging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071560
APA StyleChu, C. -H., Cheng, S. -H., Chen, N. -T., Liao, W. -N., & Lo, L. -W. (2019). Microwave-Synthesized Platinum-Embedded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Dual-Modality Contrast Agents: Computed Tomography and Optical Imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071560