Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ghrelin, Regulator of Nutritional Condition
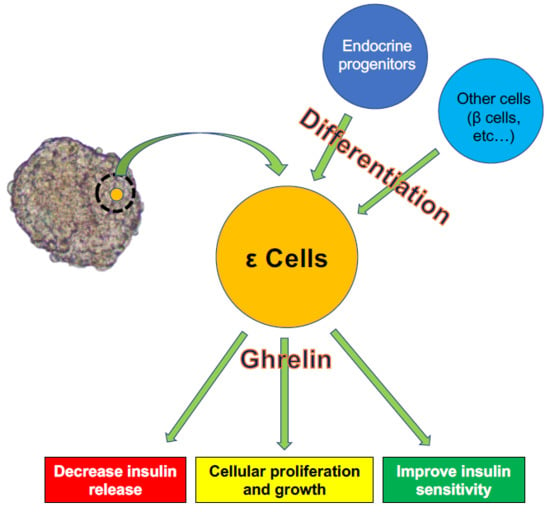
3. ε Cell Development
4. Role of Ghrelin in Interactions between ε Cells and Other Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | acylated ghrelin |
| AgRP | agouti-related protein |
| Arx | aristaless-related homeobox |
| DE | definitive endoderm |
| E | embryonic day |
| GHS-R | growth hormone secretagogue receptor |
| MAFA | V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A |
| NGN-3 | neurogenin-3 |
| Nkx2.2 | Nk2 homeobox 2 |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| OB | Obestatin |
| Pax4 | paired box protein Pax-4 |
| Pax6 | paired box protein Pax-6 |
| PDX-1 | pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1 |
| POMC | pro-opio-melanocortin |
| PP | pancreatic polypeptide |
| UAG | unacylated ghrelin |
References
- Napolitano, T.; Silvano, S.; Vieira, A.; Balaji, S.; Garrido-Utrilla, A.; Friano, M.E.; Atlija, J.; Collombat, P. Role of ghrelin in pancreatic development and function. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 2), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Xavier, G. The Cells of the Islets of Langerhans. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.L.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Elghazi, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; Sussel, L. Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing beta cells in two mouse models of pancreas development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauge-Evans, A.C.; King, A.J.; Carmignac, D.; Richardson, C.C.; Robinson, I.C.; Low, M.J.; Christie, M.R.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. Somatostatin secreted by islet delta-cells fulfills multiple roles as a paracrine regulator of islet function. Diabetes 2009, 58, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromada, J.; Hoy, M.; Buschard, K.; Salehi, A.; Rorsman, P. Somatostatin inhibits exocytosis in rat pancreatic alpha-cells by G(i2)-dependent activation of calcineurin and depriming of secretory granules. J. Physiol. 2001, 535, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Bengtsson, M.; Partridge, C.; Salehi, A.; Braun, M.; Cox, R.; Eliasson, L.; Johnson, P.R.; Renstrom, E.; Schneider, T.; et al. R-type Ca(2+)-channel-evoked CICR regulates glucose-induced somatostatin secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, F.; Karaca, M.; Novials, A.; Maldonado, R.; Maechler, P.; Rubi, B. Pancreatic polypeptide regulates glucagon release through PPYR1 receptors expressed in mouse and human alpha-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wierup, N.; Svensson, H.; Mulder, H.; Sundler, F. The ghrelin cell: A novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2002, 107, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin: Much more than a hunger hormone. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Fukue, Y.; Teranishi, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Kojima, M. Molecular forms of hypothalamic ghrelin and its regulation by fasting and 2-deoxy-d-glucose administration. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2510–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shintani, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Ebihara, K.; Aizawa-Abe, M.; Miyanaga, F.; Takaya, K.; Hayashi, T.; Inoue, G.; Hosoda, K.; Kojima, M.; et al. Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes 2001, 50, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, A.M.; Small, C.J.; Abbott, C.R.; Dhillo, W.S.; Seal, L.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Batterham, R.L.; Taheri, S.; Stanley, S.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Inomata, N.; Ohnuma, N.; Tanaka, S.; Itoh, Z.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Masaki, T.; Kakuma, T.; Yoshimatsu, H. Centrally administered ghrelin suppresses sympathetic nerve activity in brown adipose tissue of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 349, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatar, D.; Patel, K.; Taub, D.D. The effects of ghrelin on inflammation and the immune system. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornonville de la Cour, C.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Sandvik, A.K.; Bakke, I.; Zhao, C.M.; Chen, D.; Hakanson, R. A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control. Regul. Pept. 2001, 99, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyasu, H.; Takaya, K.; Tagami, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Akamizu, T.; Suda, M.; Koh, T.; Natsui, K.; Toyooka, S.; et al. Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4753–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, V.; Miljic, D.; Pekic, S.; Pesko, P.; Djurovic, M.; Doknic, M.; Damjanovic, S.; Micic, D.; Cvijovic, G.; Glodic, J.; et al. Low plasma ghrelin level in gastrectomized patients is accompanied by enhanced sensitivity to the ghrelin-induced growth hormone release. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Sawaguchi, A.; Mondal, M.S.; Suganuma, T.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, F.; Salio, C.; Lossi, L.; Merighi, A. Ghrelin in central neurons. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiras-Fernandez, A.; Kreth, S.; Weis, F.; Ledderose, C.; Pottinger, T.; Dieguez, C.; Beiras, A.; Reichart, B. Altered myocardial expression of ghrelin and its receptor (GHSR-1a) in patients with severe heart failure. Peptides 2010, 31, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, M.; Fulcheri, E.; Allia, E.; Cerrato, M.; Pucci, A.; Papotti, M. Ghrelin expression in fetal, infant, and adult human lung. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2002, 50, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Fujioka, H.; Ishimura, T.; Takenaka, A.; Fujisawa, M. Ghrelin expression in human testis and serum testosterone level. J. Androl. 2007, 28, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Dezaki, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Arima, T.; Matsuo, H.; et al. Ghrelin is present in pancreatic alpha-cells of humans and rats and stimulates insulin secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andralojc, K.M.; Mercalli, A.; Nowak, K.W.; Albarello, L.; Calcagno, R.; Luzi, L.; Bonifacio, E.; Doglioni, C.; Piemonti, L. Ghrelin-producing epsilon cells in the developing and adult human pancreas. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.A.; Kobberup, S.; Wong, R.; Lopez, A.D.; Quayum, N.; Still, T.; Kutchma, A.; Jensen, J.N.; Gianani, R.; Beattie, G.M.; et al. Global gene expression profiling and histochemical analysis of the developing human fetal pancreas. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, M.; Allia, E.; Gugliotta, P.; Funaro, A.; Broglio, F.; Deghenghi, R.; Muccioli, G.; Ghigo, E.; Papotti, M. Expression of ghrelin and of the GH secretagogue receptor by pancreatic islet cells and related endocrine tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, R.S.; Jenny, M.; Collombat, P.; Mansouri, A.; Tomasetto, C.; Madsen, O.D.; Mellitzer, G.; Gradwohl, G.; Serup, P. Genetic determinants of pancreatic epsilon-cell development. Dev. Biol. 2005, 286, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ikeda, Y. PDX1, Neurogenin-3, and MAFA: Critical transcription regulators for beta cell development and regeneration. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Aguirre, A.L.; Canales-Aguirre, A.A.; Padilla-Camberos, E.; Esquivel-Solis, H.; Diaz-Martinez, N.E. Development of the endocrine pancreas and novel strategies for beta-cell mass restoration and diabetes therapy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Dubauskaite, J.; Melton, D.A. Direct evidence for the pancreatic lineage: NGN3+ cells are islet progenitors and are distinct from duct progenitors. Development 2002, 129, 2447–2457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apelqvist, A.; Li, H.; Sommer, L.; Beatus, P.; Anderson, D.J.; Honjo, T.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Lendahl, U.; Edlund, H. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature 1999, 400, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pictet, R.R.W. Development of the Embryonic Endocrine Pancreas; Steiner, D.F.F.N., Ed.; American Physiological Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, T.A.; Artner, I.; Henderson, E.; Means, A.; Sander, M.; Stein, R. The MafA transcription factor appears to be responsible for tissue-specific expression of insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2930–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Zavacki, A.M.; Marinelarena, A.; Hollister-Lock, J.; El Khattabi, I.; Marsili, A.; Weir, G.C.; Sharma, A.; Larsen, P.R.; Bonner-Weir, S. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic beta-cell development and glucose-responsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruin, J.E.; Saber, N.; O’Dwyer, S.; Fox, J.K.; Mojibian, M.; Arora, P.; Rezania, A.; Kieffer, T.J. Hypothyroidism Impairs Human Stem Cell-Derived Pancreatic Progenitor Cell Maturation in Mice. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussel, L.; Kalamaras, J.; Hartigan-O’Connor, D.J.; Meneses, J.J.; Pedersen, R.A.; Rubenstein, J.L.; German, M.S. Mice lacking the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.2 have diabetes due to arrested differentiation of pancreatic beta cells. Development 1998, 125, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.T.; Mastracci, T.L.; Vinton, C.; Doyle, M.L.; Anderson, K.R.; Loomis, Z.L.; Schrunk, J.M.; Minic, A.D.; Prabakar, K.R.; Pugliese, A.; et al. Ghrelin is dispensable for embryonic pancreatic islet development and differentiation. Regul. Pept. 2009, 157, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastracci, T.L.; Wilcox, C.L.; Arnes, L.; Panea, C.; Golden, J.A.; May, C.L.; Sussel, L. Nkx2.2 and Arx genetically interact to regulate pancreatic endocrine cell development and endocrine hormone expression. Dev. Biol. 2011, 359, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastracci, T.L.; Anderson, K.R.; Papizan, J.B.; Sussel, L. Regulation of Neurod1 contributes to the lineage potential of Neurogenin3+ endocrine precursor cells in the pancreas. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.S.; Loomis, Z.L.; Lee, J.E.; Sussel, L. Genetic identification of a novel NeuroD1 function in the early differentiation of islet alpha, PP and epsilon cells. Dev. Biol. 2007, 312, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Elghazi, L.; Parker, S.E.; Kizilocak, H.; Asano, M.; Sussel, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B. The concerted activities of Pax4 and Nkx2.2 are essential to initiate pancreatic beta-cell differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2004, 266, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.T.; Chao, C.S.; Anderson, K.R.; Kaufman, F.; Johnson, C.W.; Sussel, L. Nkx2.2 activates the ghrelin promoter in pancreatic islet cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Elghazi, L.; Martin, S.; Martins, I.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Geng, X.; Sleeman, M.; Collombat, P.; Houghton, J.; Sosa-Pineda, B. Ghrelin is a novel target of Pax4 in endocrine progenitors of the pancreas and duodenum. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez Gutierrez, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, A.H.; Tong, J.; Niu, J.; Gray, S.M.; Wei, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, M.; Adler, C.; et al. Gene Signature of the Human Pancreatic epsilon Cell. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaham, O.; Menuchin, Y.; Farhy, C.; Ashery-Padan, R. Pax6: A multi-level regulator of ocular development. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 2012, 31, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, M.N.; Mi, D.; Mason, J.O.; Price, D.J. Regulation of cerebral cortical neurogenesis by the Pax6 transcription factor. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisa, A.; Avrahami, D.; Eden, N.; Zhang, J.; Feleke, E.; Dahan, T.; Cohen-Tayar, Y.; Stolovich-Rain, M.; Kaestner, K.H.; Glaser, B.; et al. PAX6 maintains beta cell identity by repressing genes of alternative islet cell types. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collombat, P.; Mansouri, A.; Hecksher-Sorensen, J.; Serup, P.; Krull, J.; Gradwohl, G.; Gruss, P. Opposing actions of Arx and Pax4 in endocrine pancreas development. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2591–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnes, L.; Hill, J.T.; Gross, S.; Magnuson, M.A.; Sussel, L. Ghrelin expression in the mouse pancreas defines a unique multipotent progenitor population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Baragli, A.; Settanni, F.; Scarlatti, F.; Ghigo, E. Unraveling the role of the ghrelin gene peptides in the endocrine pancreas. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Solenberg, P.J.; Perkins, D.R.; Willency, J.A.; Knierman, M.D.; Jin, Z.; Witcher, D.R.; Luo, S.; Onyia, J.E.; Hale, J.E. Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6320–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kakei, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Endogenous ghrelin in pancreatic islets restricts insulin release by attenuating Ca2+ signaling in beta-cells: Implication in the glycemic control in rodents. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, H.; Funahashi, H.; Hirayama, M.; Takenoya, F.; Kita, T.; Kato, S.; Sakurai, J.; Lee, E.Y.; Inoue, S.; Date, Y.; et al. Morphological analysis of ghrelin and its receptor distribution in the rat pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2005, 126, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Gallo, D.; Trovato, L.; Biancone, L.; Cantaluppi, V.; Nano, R.; Annunziata, M.; Campiglia, P.; Arnoletti, E.; et al. Obestatin promotes survival of pancreatic beta-cells and human islets and induces expression of genes involved in the regulation of beta-cell mass and function. Diabetes 2008, 57, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronberg, M.; Tsolakis, A.V.; Magnusson, L.; Janson, E.T.; Saras, J. Distribution of obestatin and ghrelin in human tissues: Immunoreactive cells in the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and mammary glands. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesmundo, I.; Gallo, D.; Favaro, E.; Ghigo, E.; Granata, R. Obestatin: A new metabolic player in the pancreas and white adipose tissue. Iubmb Life 2013, 65, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holst, B.; Egerod, K.L.; Jin, C.; Petersen, P.S.; Ostergaard, M.V.; Hald, J.; Sprinkel, A.M.; Storling, J.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Holst, J.J.; et al. G protein-coupled receptor 39 deficiency is associated with pancreatic islet dysfunction. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoortere, I.; Thijs, T.; Moechars, D.; De Smet, B.; Ver Donck, L.; Peeters, T.L. Effect of peripheral obestatin on food intake and gastric emptying in ghrelin-knockout mice. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 153, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broglio, F.; Benso, A.; Castiglioni, C.; Gottero, C.; Prodam, F.; Destefanis, S.; Gauna, C.; van der Lely, A.J.; Deghenghi, R.; Bo, M.; et al. The endocrine response to ghrelin as a function of gender in humans in young and elderly subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Blockade of pancreatic islet-derived ghrelin enhances insulin secretion to prevent high-fat diet-induced glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Smith, R.G. Ablation of ghrelin improves the diabetic but not obese phenotype of ob/ob mice. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dezaki, K.; Kakei, M.; Yada, T. Ghrelin uses Galphai2 and activates voltage-dependent K+ channels to attenuate glucose-induced Ca2+ signaling and insulin release in islet beta-cells: Novel signal transduction of ghrelin. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, M.; Ronchi, C.L.; Gebbia, C.; Cappiello, V.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Peracchi, M. Stimulatory effects of ghrelin on circulating somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGruccio, M.R.; Mawla, A.M.; Donaldson, C.J.; Noguchi, G.M.; Vaughan, J.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; van der Meulen, T.; Huising, M.O. Comprehensive alpha, beta and delta cell transcriptomes reveal that ghrelin selectively activates delta cells and promotes somatostatin release from pancreatic islets. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Svendsen, B.; Lam, B.Y.; Yeo, G.S.; Holst, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Transcriptomic profiling of pancreatic alpha, beta and delta cell populations identifies delta cells as a principal target for ghrelin in mouse islets. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Biancone, L.; Trovato, L.; Nano, R.; Bertuzzi, F.; Destefanis, S.; Annunziata, M.; Martinetti, M.; Catapano, F.; et al. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells and human islets: Involvement of 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, and phosphatidyl inositol 3-Kinase/Akt signaling. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irako, T.; Akamizu, T.; Hosoda, H.; Iwakura, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Tojo, K.; Tajima, N.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin prevents development of diabetes at adult age in streptozotocin-treated newborn rats. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauna, C.; Delhanty, P.J.; van Aken, M.O.; Janssen, J.A.; Themmen, A.P.; Hofland, L.J.; Culler, M.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Unacylated ghrelin is active on the INS-1E rat insulinoma cell line independently of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a and the corticotropin releasing factor 2 receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2006, 251, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhanty, P.J.; Sun, Y.; Visser, J.A.; van Kerkwijk, A.; Huisman, M.; van Ijcken, W.F.; Swagemakers, S.; Smith, R.G.; Themmen, A.P.; van der Lely, A.J. Unacylated ghrelin rapidly modulates lipogenic and insulin signaling pathway gene expression in metabolically active tissues of GHSR deleted mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.W.; Yang, Q.; Mody, N.; Graham, T.E.; Hsu, C.H.; Xu, Z.; Houstis, N.E.; Kahn, B.B.; Rosen, E.D. The adipokine lipocalin 2 is regulated by obesity and promotes insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.T.; Araujo, E.P.; Stoppiglia, L.F.; Pauli, J.R.; Ropelle, E.; Rocco, S.A.; Marin, R.M.; Franchini, K.G.; Carvalheira, J.B.; Saad, M.J.; et al. Inhibition of UCP2 expression reverses diet-induced diabetes mellitus by effects on both insulin secretion and action. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, E.T.; Jessen, N.; Moller, N.; Jorgensen, J.O.L. Unacylated Ghrelin does not Acutely Affect Substrate Metabolism or Insulin Sensitivity in Men with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Davis, H.W.; Summer, S.; Benoit, S.C.; Haque, A.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Tschop, M.H.; D’Alessio, D. Acute administration of unacylated ghrelin has no effect on Basal or stimulated insulin secretion in healthy humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Volante, M.; Settanni, F.; Gauna, C.; Ghe, C.; Annunziata, M.; Deidda, B.; Gesmundo, I.; Abribat, T.; van der Lely, A.J.; et al. Unacylated ghrelin and obestatin increase islet cell mass and prevent diabetes in streptozotocin-treated newborn rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Julien, M.; Nano, R.; Togliatto, G.; Trombetta, A.; Gallo, D.; Piemonti, L.; Brizzi, M.F.; Abribat, T.; et al. Des-acyl ghrelin fragments and analogues promote survival of pancreatic beta-cells and human pancreatic islets and prevent diabetes in streptozotocin-treated rats. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragli, A.; Grande, C.; Gesmundo, I.; Settanni, F.; Taliano, M.; Gallo, D.; Gargantini, E.; Ghigo, E.; Granata, R. Obestatin enhances in vitro generation of pancreatic islets through regulation of developmental pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, T.; Damdindorj, B.; Rita, R.S.; Kurashina, T.; Ando, A.; Taguchi, M.; Koizumi, M.; Sone, H.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; et al. Ghrelin signalling in beta-cells regulates insulin secretion and blood glucose. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16 (Suppl. 1), 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, N.I.; Ebrahim, N.; Mohammed, O.M.; Sabry, D. Combination of Obestatin and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevents Aggravation of Endocrine Pancreatic Damage in Type II Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Stem. Cells 2017, 10, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asfar, R.K.; Kamal, M.M.; Abd El-Razek, R.S.; El-Demerdash, E.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Obestatin can potentially differentiate Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakata, N.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Kodama, S. Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081867
Sakata N, Yoshimatsu G, Kodama S. Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081867
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakata, Naoaki, Gumpei Yoshimatsu, and Shohta Kodama. 2019. "Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081867
APA StyleSakata, N., Yoshimatsu, G., & Kodama, S. (2019). Development and Characteristics of Pancreatic Epsilon Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081867