Self-Assembled Benznidazole-Loaded Cationic Nanoparticles Containing Cholesterol/Sialic Acid: Physicochemical Properties, In Vitro Drug Release and In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Surface-Modified Chol/SA NPs
2.2. Physicochemical Stability Study
2.3. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics
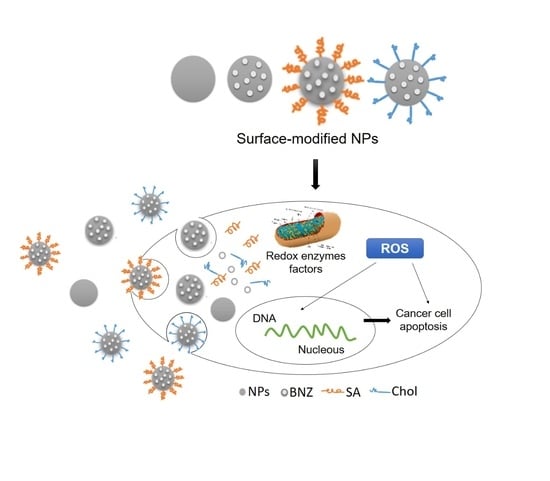
2.4. In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Surface-Modified Chol/SA NPs
4.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
4.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR)
4.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4.6. Drug-Loading Efficiency
4.7. Physicochemical Stability Study
4.8. In Vitro Drug Release
4.9. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics
4.10. In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy
4.10.1. Cell Culture
4.10.2. Cytotoxity Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yokoyama, C.; Sueyoshi, Y.; Ema, M.; Mori, Y. Induction of oxidative stress by anticancer drugs in the presence and absence of cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6066–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.M.; Mazzeti, A.L.; Caldas, S.; Gonçalves, K.R.; Lima, W.G.; Torres, R.M.; Bahia, M.T. Chagas cardiomyopathy: The potential effect of benznidazole treatment on diastolic dysfunction and cardiac damage in dogs chronically infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Acta Trop. 2016, 161, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.S.; Wilkinson, S.R. Activation of benznidazole by trypanosomal type I nitroreductases results in glyoxal formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manarin, R.; Pascutti, M.F.; Ruffino, J.P.; De Las Heras, B.; Boscá, L.; Bottasso, O.; Revelli, S.; Serra, E. Benznidazole blocks NF-kB activation but not AP-1 through inhibition of IKK. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos-Silva, A.M.; de Caland, L.B.; de S L Oliveira, A.L.C.; de Araújo-Júnior, R.F.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Cornélio, A.M.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Designing structural features of novel benznidazole-loaded cationic nanoparticles for inducing slow drug release and improvement of biological efficacy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Andresen, T.L. Factors Controlling Nanoparticle Pharmacokinetics: An Integrated Analysis and Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamrungsap, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Fu, T.; Tan, W. Nanotechnology in therapeutics: A focus on nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, M.L.; Manzo, R.H.; Olivera, M.E. Eudragit E100 as a drug carrier: The remarkable affinity of phosphate ester for dimethylamine. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, U.; Mohanty, A.K.; Pal, S.L.A.L.; Manna, P.K.; Mohanta, G.P. Preparation and in vitro characterization of Felodipine loaded Eudragit® RS100 nanoparticles. Innovare Acad. Sci. 2014, 6, 564–567. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.D.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles evading the reticuloendothelial system: Role of the supported bilayer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajeesh, S.; Lee, T.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Son, D.S.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, S.; Yun, W.S.; Kim, S.; Chang, C.; Li, C.; et al. Efficient intracellular delivery and multiple-target gene silencing triggered by tripodal RNA based nanoparticles: A promising approach in liver-specific RNAi delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasungu, L.; Hoekstra, D. Cationic lipids, lipoplexes and intracellular delivery of genes. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.Y.; Ming, K.; Chan, W.C. Strategies for the intracellular delivery of nanoparticles. Chem Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.R.; Miranda, O.R.; Moyano, D.F.; Walden, C.A.; Giri, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Robertson, J.D.; Rotello, V.M.; Reid, J.M.; Mukherjeeet, P. Modulating pharmacokinetics, tumor uptake and biodistribution by engineered nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecke, A.; Majoros, I.J.; Patri, A.K.; Baker, J.R., Jr.; Holl, M.M.; Orr, B.G. Lipid bilayer disruption by polycationic polymers: The roles of size and chemical functional group. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10348–10354. [Google Scholar]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luxenhofer, R. Polymers and nanomedicine: Considerations on variability and reproducibility when combining complex systems. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2015, 10, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapra, M.; Pawar, A.A.; Venkataraman, C. A single-step aerosol process for in-situ surface modification of nanoparticles: Preparation of stable aqueous nanoparticle suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 464, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Wei, J.; Iida, R.; Ijiro, K.; Niikura, K. Surface engineering of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Polym. J. 2014, 46, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondioli, L.; Costantino, L.; Ballestrazzi, A.; Lucchesi, D.; Boraschi, D.; Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S.; Tosi, G.; Vandelli, M. PLGA nanoparticles surface decorated with the sialic acid, N-acetylneuraminic acid. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, C.L.; Marín, M.J.; Rejzek, M.; Crocker, P.R.; Field, R.; Russell, D. Detection of mSiglec-E, in solution and expressed on the surface of Chinese hamster ovary cells, using sialic acid functionalised gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2016, 141, 5799–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; Roitberg, A.E. Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase as a drug target against Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis). Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.D.; Cho, H.J. Cholesterol-modified poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belletti, D.; Grabrucker, M.; Pederzoli, F.; Menrath, I.; Cappello, V.; Vandelli, M.; Forni, F.; Tosi, G.; Ruozi, B. Exploiting the Versatility of Cholesterol in Nanoparticles Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.; Fei, Y.; Wang, P.N.; Mi, L. The role of surface modification for TiO2 nanoparticles in cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, D.H.; Salah, S.; Elkheshen, S. Formulation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride loaded biodegradable nanoparticles: Optimization of technique and process variables. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senyi, T.; Sonvico, F.; Rossi, A.; Santi, P.; Colombo, P.; Nicoli, S.; Özer, Ö. In Vivo Assessment of Clobetasol Propionate-Loaded Lecithin-Chitosan Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Thakur, P.S.; Padhi, S.; Khuroo, T.; Talegaonkar, S.; Iqbal, Z. Design expert assisted nanoformulation design for co-delivery of topotecan and thymoquinone: Optimization, in vitro characterization and stability assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.; Yadav, R.B.; Kushwaha, K.; Yadav, S.; Sharma, S.; Agrawal, U. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles: Development & statistical optimization of norfloxacin for topical drug delivery system. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Preparation of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 187, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocalinska, A.; Manganaro, M.; Dimastrodonato, V.; Pelucchi, E. Evaluation of defect density by top-view large scale AFM on metamorphic structures grown by MOVPE. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoo, C.M.; Starostin, N.; West, P.; Mecartney, M.L. A comparison of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) methods to characterize nanoparticle size distributions. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Yeap, S.P.; Che, H.X.; Low, S.C. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Guo, T. Preparation of Eudragit L 100-55 enteric nanoparticles by a novel emulsion diffusion method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, U.; Mohanty, A.K.; Manna, P.K.; Mohanta, G.P. Preparation and characterization of nebivolol nanoparticles using Eudragit® RS100. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Jang, I.; Oh, S.-G. Surface modification of silica nanoparticles using phenyl trimethoxy silane and their dispersion stability in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2016, 501, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemarchand, C.; Couvreur, P.; Vauthier, C.; Costantini, D.; Gref, R. Study of emulsion stabilization by graft copolymers using the optical analyzer Turbiscan. Proc. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2003, 254, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, H.; Hirota, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Esumi, K. Effect of dilution on aqueous dispersion of drug particles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 27, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.; Santiago, L.G. Food Hydrocolloids Formation and colloidal stability of ovalbumin-retinol nanocomplexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 130–138. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, H.; Abbaspour, M.; Salemi, S.; Hasani, M. Coalescence process of gold/silver core-shell nanoparticles located on carbon nanotube and graphene surfaces. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schamp, C.T.; Jesser, W.A. Two-phase equilibrium in individual nanoparticles of Bi-Sn. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.M.; Mebed, A.M.; Chatterjee, K.; Li, P.; Murayama, M.; Johnson, W.C. Effect of phase fraction on the tri-junction in two-phase nanoparticle systems. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. A novel method to get methotrexatum/layered double hydroxides intercalation compounds and their release properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarra, J.; Giannuzzi, L.; Rivero, S.; Pinotti, A. Assembly of chitosan support matrix with gallic acid-functionalized nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvez, V.; Corrias, L. The parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel model in R2. Commun. Math. Sci. 2008, 6, 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Soares, K.S.; Oliveira, A.R.; Daniele-Silva, A.; Glaucia-Silva, F.; Caroni, A.L.P.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Self-assembled scorpion venom proteins cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles for use in the immunotherapy. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seju, U.; Kumar, A.; Sawant, K.K. Development and evaluation of olanzapine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementino, A.; Batger, M.; Garrastazu, G.; Pozzoli, M.; Del Favero, E.; Rondelli, V.; Gutfilen, B.; Barboza, T.; Sukkar, M.B.; Souza, S.A.L.; et al. The nasal delivery of nanoencapsulated statins—An approach for brain delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6575–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostendorp, R.L.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. The biological and clinical role of drug transporters at the intestinal barrier. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Tao, W.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Mei, L.; Feng, S.S. The effect of autophagy inhibitors on drug delivery using biodegradable polymer nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Jin, S.; Wang, P.; Du, Z.; Ren, F. Novel Targeted Anti-Tumor Nanoparticles Developed from Folic Acid-Modified 2-Deoxyglucose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 697. [Google Scholar]
- Khmara, I.; Koneracka, M.; Kubovcikova, M.; Zavisova, V.; Antal, I.; Csach, K. Preparation of poly-l-lysine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and their in fl uence on viability of cancer cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 427, 950–960. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Morshed, R.A.; Auffinger, B.; Tobias, A.L.; Lesniak, M.S. Multifunctional nanoparticlesfor brain tumor imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, J.; Alves, G.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A. Blood-brain barrier models and their relevancefor a successful development of CNS drug delivery systems: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes Profirio, D.; Pessine, F.B.T. Formulation of functionalized PLGA nanoparticles with folic acid conjugated chitosan for carboplatin encapsulation. Eur. Pol. J. 2018, 108, 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids: Fascinating sugars in higher animals and man. Proc. Zool. 2004, 107, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiichi, B. Synthesis and function of sialic acid-conjugated cholesterols as ganglioside analogs: Their reconstitution to liposomes and interaction with rat lymphocytes. Proc. Jpn. Acad. 2000, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Leroueil, P.R.; Berry, S.A.; Duthie, K.; Han, G.; Rotello, V.M.; McNerny, D.Q.; Baker, J.R.; Orr, B.G.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Wide varieties of cationic nanoparticles induce defects in supported lipid bilayers. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodeweina, L.; Schmelter, F.; Di Fiore, S.; Hollert, H.; Fischer, R.; Fenske, M. Differences in toxicity of anionic and cationic PAMAM and PPI dendrimers in zebrafish embryos and cancer cell lines. Toxic. App. Pharm. 2016, 305, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.B.; Northeved, H.; Kumar, P.; Permin, A.; Gjetting, T.; Andresen, T.L.; Larsen, S.; Wegener, K.M.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Jantzen, K.; et al. In vivo toxicity of cationic micelles and liposomes. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, P.C.; Davoren, M.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced cytokine production and cytotoxicity of PAMAM dendrimers in J774A.1 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2010, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Hillaireau, H.; Nicolas, J. Influence of surface charge on the potential toxicity of PLGA nanoparticles towards Calu-3 cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2591–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Feng, M.; Pan, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C. Charge shielding effects on gene delivery of polyethylenimine/DNA complexes: PEGylation and phospholipid coating. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos-Senna, E.; Wouessidjewe, D.; Lesieur, S.; Duchêne, D. Preparation of amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanospheres using the emulsification solvent evaporation method. Influence of the surfactant on preparation and hydrophobic drug loading. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 170, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, D.; Tunki, L.; Kulhari, H.; Reddy, B.B.; Sistla, R. Optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by a single emulsification-solvent evaporation method. Data Br. 2016, 6, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Chen, M.; Kaushal, S.; McElroy, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ozkan, C.; Bouvet, M.; Kruse, C.; Grotjahn, D.; Ichim, T.; et al. PLGA nanoparticle-mediated delivery of tumor antigenic peptides elicits effective immune responses. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Thomas, A.C.; Xu, Z.P.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q. In vitro sustained release of LMWH from MgAl-layered double hydroxide nanohybrids. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Han, Y.S.; Park, M.; Park, T.; Hwang, S.J.; Choy, J.H. New inorganic-based drug delivery system of indole-3-acetic acid-layered metal hydroxide nanohybrids with controlled release rate. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, R.; Murthy, R.S.R.; Miglani, B.D.; Viswanathan, K. Novel method to evaluate diffusion controlled release of drug from resinate. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 28, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Kim, W.J. Biodegradable nanoparticles modified by branched polyethylenimine for plasmid DNA delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, K.M.G.; Junior, R.F.A.; Araujo, A.; Oliveira, A.L.C.S.L.; Gasparotto, L.H.S. Environmentally compatible bioconjugated gold nanoparticles as efficient contrast agents for colorectal cancer cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, P.N.; Barbosa, E.G.; De Caland, L.B.; Carpegianni, H.; Garnero, C.; Longhi, M.; De Freitas Fernades-Pedrosa, M.; Da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Host-guest interactions between benznidazole and beta-cyclodextrin in multicomponent complex systems involving hydrophilic polymers and triethanolamine in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 186, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | Drug Loading (%) | Size (nm) ± SD | PdI ± SD | Zeta Potential (mV) ± SD | EE (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | ND | 148.0 ± 2.4 | 0.189 ± 2.1 | +25.2 ± 0.3 | ND |
| NP BNZ | 4.0 | 154.2 ± 1.0 | 0.254 ± 1.0 | +22.1 ± 0.1 | 86.2 ± 2.3 |
| NP BNZSA | 3.7 | 176.9 ± 1.2 | 0.239 ± 1.6 | +21.7 ± 0.1 | 47.5 ± 1.1 |
| NP BNZ Chol | 3.7 | 186.8 ± 2.5 | 0.238 ± 2.5 | +20.0 ± 0.4 | 38.6 ± 1.7 |
| Formulations | Kinetic Models [k value (r2 ± SD)] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Order | Bhaskar | Freundlich | Parabolic Diffusion | |
| NP BNZ | −0.00008 h−1 (0.55 ± 0.04) | −0.0004 h0.65 (0.63 ± 0.02) | 0.0578 h (0.85 ± 0.02) | −0.026 h−0.5 (0.99 ±0.03) |
| NP BNZ SA | −0.0021 h−1 (0.86 ± 0.03) | −0.0095 h0.65 (0.94 ± 0.02) | −0.4246 h (0.86 ± 0.02) | 0.0016 h−0.5 (0.16 ±0.03) |
| NP BNZ CHOL | −0.0023 h−1 (0.83 ± 0.03) | −0.0114 h0.65 (0.93 ± 0.02) | −0.5117 h (0.85 ± 0.02) | −0.0064 h−0.5 (0.41 ± 0.03) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos-Silva, A.M.; de Caland, L.B.; do Nascimento, E.G.; Oliveira, A.L.C.d.S.L.; de Araújo-Júnior, R.F.; Cornélio, A.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Self-Assembled Benznidazole-Loaded Cationic Nanoparticles Containing Cholesterol/Sialic Acid: Physicochemical Properties, In Vitro Drug Release and In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092350
dos Santos-Silva AM, de Caland LB, do Nascimento EG, Oliveira ALCdSL, de Araújo-Júnior RF, Cornélio AM, Fernandes-Pedrosa MF, da Silva-Júnior AA. Self-Assembled Benznidazole-Loaded Cationic Nanoparticles Containing Cholesterol/Sialic Acid: Physicochemical Properties, In Vitro Drug Release and In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092350
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos-Silva, Alaine Maria, Lilia Basílio de Caland, Ednaldo Gomes do Nascimento, Ana Luiza C. de S.L. Oliveira, Raimundo F. de Araújo-Júnior, Alianda Maira Cornélio, Matheus F. Fernandes-Pedrosa, and Arnóbio Antônio da Silva-Júnior. 2019. "Self-Assembled Benznidazole-Loaded Cationic Nanoparticles Containing Cholesterol/Sialic Acid: Physicochemical Properties, In Vitro Drug Release and In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092350
APA Styledos Santos-Silva, A. M., de Caland, L. B., do Nascimento, E. G., Oliveira, A. L. C. d. S. L., de Araújo-Júnior, R. F., Cornélio, A. M., Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. F., & da Silva-Júnior, A. A. (2019). Self-Assembled Benznidazole-Loaded Cationic Nanoparticles Containing Cholesterol/Sialic Acid: Physicochemical Properties, In Vitro Drug Release and In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092350