Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Virtual Screening Analysis
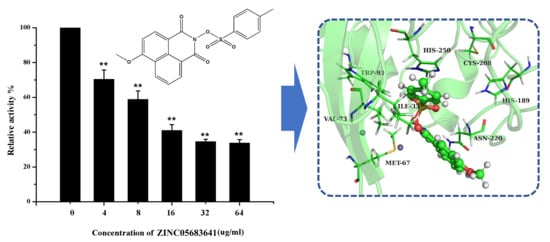
2.2. Nitrocefin Assay
2.3. Antibacterial Activity Assay
2.4. The Potential Binding Mode of Compound ZINC05683641 with NDM-1
2.5. Confirmation of the Binding Mode in the Complex
2.6. Identification of the Competitive Inhibition Mechanism
3. Method and Computation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demain, A.L.; Elander, R.P. The beta-lactam antibiotics: Past, present, and future. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999, 75, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, S.M.; Bonomo, R.A. Three decades of beta-lactamase inhibitors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 160–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spyrakis, F.; Celenza, G.; Marcoccia, F.; Santucci, M.; Cross, S.; Bellio, P.; Cendron, L.; Perilli, M.; Tondi, D. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for the Discovery of Novel Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frere, J.M.; Sauvage, E.; Kerff, F. From “An Enzyme Able to Destroy Penicillin” to Carbapenemases: 70 Years of Beta-lactamase Misbehaviour. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondi, D.; Cross, S.; Venturelli, A.; Costi, M.P.; Cruciani, G.; Spyrakis, F. Decoding the Structural Basis for Carbapenem Hydrolysis by Class A beta-lactamases: Fishing for a Pharmacophore. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 983–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K. New beta-lactamases in gram-negative bacteria: Diversity and impact on the selection of antimicrobial therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambler, R.P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlier, V.; Nicolas, M.H.; Fournier, G.; Philippon, A. Extended broad-spectrum beta-lactamases conferring transferable resistance to newer beta-lactam agents in Enterobacteriaceae: Hospital prevalence and susceptibility patterns. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.F.; Meroueh, S.O.; Mobashery, S. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: Compelling opportunism, compelling opportunity. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palzkill, T. Metallo-beta-lactamase structure and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Spyrakis, F.; Venturelli, A.; Cross, S.; Tondi, D.; Costi, M.P. The inhibition of extended spectrum beta-lactamases: Hits and leads. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1405–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.W.; Zheng, M.; Wu, S.; Guo, H.; Liu, D.; Xu, D.; Fast, W. Characterization of purified New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 10102–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, A.P.; McCallum, A.K. New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2014, 6, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poirel, L.; Lagrutta, E.; Taylor, P.; Pham, J.; Nordmann, P. Emergence of metallo-beta-lactamase NDM-1-producing multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in Australia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4914–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, T.R.; Toleman, M.A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Metallo-beta-lactamases: The quiet before the storm? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Ray, D.; Anjum, F.; Hassan, M.I. Search of potential inhibitor against New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 from a series of antibacterial natural compounds. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Aitha, M.; Marts, A.R.; Hetrick, A.; Bennett, B.; Crowder, M.W.; Tierney, D.L. Spectroscopic and mechanistic studies of heterodimetallic forms of metallo-beta-lactamase NDM-1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7273–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Worrall, L.J.; Gruninger, R.; Strynadka, N.C. New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase: Structural insights into beta-lactam recognition and inhibition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11362–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; McLeod, S.; MacCormack, K.; Sriram, S.; Gao, N.; Breeze, A.L.; Hu, J. Real-time monitoring of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase activity in living bacterial cells by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 2130–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, K.; Lu, J.; Liang, Z.; Kong, X.; Ye, F.; Jin, L.; Geng, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, H.; et al. A quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics study on the hydrolysis mechanism of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, G.; Shui, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Lou, Z.; Rao, Z. A structural view of the antibiotic degradation enzyme NDM-1 from a superbug. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.M.; Xu, L.W.; Yang, K.W.; Oelschlaeger, P.; He, Y. Rhodanine as a Potent Scaffold for the Development of Broad-Spectrum Metallo-beta-lactamase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, K.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.M.; Su, J.P.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y. A protein structure-guided covalent scaffold selectively targets the B1 and B2 subclass metallo-beta-lactamases. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4802–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Zhang, A.L.; Faheem, M.; Zhang, C.J.; Ai, N.; Buynak, J.D.; Welsh, W.J.; Oelschlaeger, P. Virtual Screening and Experimental Testing of B1 Metallo-beta-lactamase Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2018, 58, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Y.; Thomas, P.W.; Stewart, A.C.; Bergstrom, A.; Cheng, Z.; Miller, C.; Bethel, C.R.; Marshall, S.H.; Credille, C.V.; Riley, C.L.; et al. Dipicolinic Acid Derivatives as Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7267–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, S.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Totrov, M.; Hirst, G.C.; Lomovskaya, O.; Griffith, D.C.; King, P.; Tsivkovski, R.; Sun, D.; Sabet, M.; et al. Discovery of a Cyclic Boronic Acid beta-Lactamase Inhibitor (RPX7009) with Utility vs Class A Serine Carbapenemases. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3682–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosconati, S.; Forli, S.; Perryman, A.L.; Harris, R.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Virtual Screening with AutoDock: Theory and Practice. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwofie, S.K.; Broni, E.; Teye, J.; Quansah, E.; Issah, I.; Wilson, M.D.; Miller, W.A., 3rd; Tiburu, E.K.; Bonney, J.H.K. Pharmacoinformatics-based identification of potential bioactive compounds against Ebola virus protein VP24. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 113, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, C.M.; Rey, J.; Lagorce, D.; Vavrusa, M.; Becot, J.; Sperandio, O.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Tuffery, P.; Miteva, M.A. MTiOpenScreen: A web server for structure-based virtual screening. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W448–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montes-Grajales, D.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Structure-based Identification of Endocrine Disrupting Pesticides Targeting Breast Cancer Proteins. Toxicology 2020, 9, 152459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Swiss. ADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odds, F.C. Synergy, antagonism, and what the chequerboard puts between them. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Cheng, T.L. Refined models of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1 with inhibitors: An QM/MM modeling study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Lu, J.; Ye, F.; Jin, L.; Kong, X.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.Q.; et al. Structure-based computational study of the hydrolysis of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactmase-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftink, M.R.; Ghiron, C.A. Fluorescence quenching studies with proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 114, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Valder, C.R.; Huynh, H.G.; Ren, H.; Allison, W.S. The beta G156C substitution in the F1-ATPase from the thermophilic Bacillus PS3 affects catalytic site cooperativity by destabilizing the closed conformation of the catalytic site. Biochemistry 2003, 41, 14421–14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, J. Pterostilbene restores carbapenem susceptibility in New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-producing isolates by inhibiting the activity of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 4548–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaffner-Barbero, C.; Laura, R.G.-R.; Ruiz-Avila, B.; Huecas, S.; Lppchen, T.; den Blaauwen, t.; Diaz, J.F.; Morreale, A.; Andreu, J.M. Insights into Nucleotide Recognition by Cell Division Protein FtsZ from a mant-GTP Competition Assay and Molecular Dynamics. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 10458–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Punkvang, A.; Saparpakorn, P.; Hannongbua, S.; Wolschann, P.; Beyer, A.; Pungpo, P. Investigating the structural basis of arylamides to improve potency against M. tuberculosis strain through molecular dynamics simulations. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5585–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ligands | Structure | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) | IC50(μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZINC00639379 |  | −10.0 | 207.28 ± 15.51 |
| ZINC03198432 |  | −9.4 | >300 |
| ZINC25558269 |  | −9.2 | N/A a |
| ZINC02938448 |  | −9.2 | >300 |
| ZINC02079077 |  | −9.2 | 107.68 ± 5.64 |
| ZINC12524283 |  | −9.1 | >300 |
| ZINC02953923 |  | −9.1 | >300 |
| ZINC06166781 |  | −9.1 | >300 |
| ZINC25558273 |  | −9.0 | >300 |
| ZINC11865709 |  | −9.0 | >300 |
| ZINC05683641 |  | −9.0 | 13.59 ± 0.52 |
| ZINC02577071 |  | −9.0 | >300 |
| ZINC06421319 |  | −8.9 | N/A |
| ZINC04218138 |  | −8.9 | N/A |
| ZINC20115378 |  | −8.8 | >300 |
| ZINC25558691 |  | −8.8 | N/A |
| ZINC25694564 |  | −8.8 | N/A |
| ZINC01799114 |  | −8.8 | >300 |
| Meropenem | ZINC05683641 | Meropenem (+64 μg/mL ZINC05683641) | Meropenem (+128 μg/mL ZINC05683641) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (μg/mL) | 32 | >512 | 8 | 8 |
| FICI | - | - | 0.375 | 0.50 |
| Energy Components (kcal/mol) | WT | W93A | H250A |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔEele | −12.12 ± 0.96 | −14.11 ± 0.75 | −7.23 ± 1.12 |
| ΔEvdw | −38.05 ± 1.15 | −35.43 ± 0.54 | −34.34 ± 1.18 |
| ΔEMM | −50.17 ± 1.20 | −49.54 ± 1.12 | −41.57 ± 1.34 |
| ΔGsol | 23.21 ± 0.92 | 24.53 ± 0.85 | 19.27 ± 1.13 |
| ΔGbind | −26.96 ± 0.88 | −25.00 ± 0.56 | −22.30 ± 0.99 |
| KA | 4.17 ± 1.02 | 3.05 ± 0.83 * | 2.15 ± 0.88 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Niu, X. Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103567
Wang X, Yang Y, Gao Y, Niu X. Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103567
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiyan, Yanan Yang, Yawen Gao, and Xiaodi Niu. 2020. "Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103567
APA StyleWang, X., Yang, Y., Gao, Y., & Niu, X. (2020). Discovery of the Novel Inhibitor Against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Modelling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103567