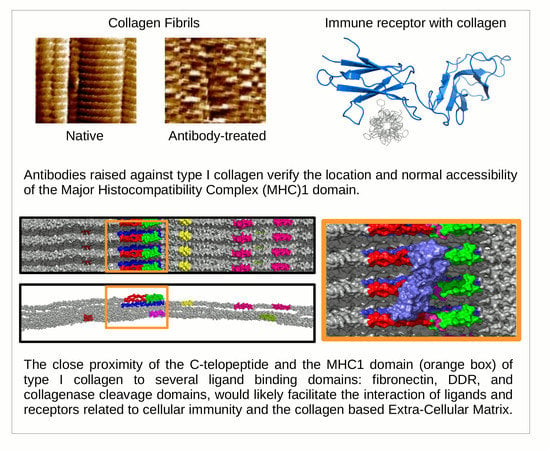
Ultrastructural Location and Interactions of the Immunoglobulin Receptor Binding Sequence within Fibrillar Type I Collagen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Collagen Fibril Structure
1.2. Receptor Binding with the Collagen Fibril
1.3. Approaches to Observing Collagen Structure and Receptor Sites
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Elasticity and Adhesive Behavior of Collagen Fiber
2.2. Topography of Native Collagen Fibers
2.3. Topography of Gold-Labeled Collagen Fibers
2.4. X-Ray Diffraction and Fourier Analyses
2.5. Interpretations from AFM and XRD Studies
- 0.32 which is just prior to the C-terminal telopeptide region with a cluster of modestly exposed GPP/GPR sequences on M4 and M5;
- 0.42 is at the end of the highly exposed GPO/GPP(4/5) region and the start of the non-helical telopeptide (M5), the middle of the fibronectin binding/MMP interaction domain of which the C-terminal portion is also a DDR interaction site (M4);
- 0.99–1.0/0.0 is the lowest trough of the up/down formation of the collagen fibril surface (Figure 6) and rich in lysine residues and some reoccurring GDK sequences. Its trough-like features could lead to more unspecific type interactions with the probe.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Immunogold-Labeled Collagen Fibrils
3.2. Imaging and Topographic Analysis
3.3. Nanoindentation and Elasticity Analysis
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction
3.5. Molecular Visualization
4. Immunoglobulin-Like Collagen Receptor—Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| DDR | Discoidin domain receptor |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| GPP | Glycine – Proline – Proline |
| GPR | Glycine – Proline – Arginine |
| GPVI | Glycoprotein VI |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| OSCAR | Human osteoclast-associated receptor |
| GPO | Glycine-proline-hydroxyproline |
| OPSS PEG | Orthopyridyl disulfide polyethylene glycol |
| pMA-PEG | Para-mercapto-aniline polyethylene glycol 5000 |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| DI Water | Deionized water |
| vWF | Von Willebrand Factor |
References
- Orgel, J.; San Antonio, J.; Antipova, O. Molecular and structural mapping of collagen fibril interactions. Connect. Tissue Res. 2011, 52, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgel, J.P.R.O.; Irving, T.C.; Miller, A.; Wess, T.J. Microfibrillar structure of type I collagen in situ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9001–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orgel, J.P.; Wess, T.J.; Miller, A. The in situ conformation and axial location of the intermolecular cross-linked non-helical telopeptides of type I collagen. Structure 2000, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horii, K.; Kahn, M.L.; Herr, A.B. Structural basis for platelet collagen responses by the immune-type receptor glycoprotein VI. Blood 2006, 108, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wienke, D.; MacFadyen, J.R.; Isacke, C.M. Identification and characterization of the endocytic transmembrane glycoprotein Endo180 as a novel collagen receptor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3592–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.; Qi, J.; Chen, C.C.; Lu, G.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Structural basis of collagen recognition by human osteoclast-associated receptor and design of osteoclastogenesis inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orgel, J.P.R.O.; Madhurapantula, R.S. A structural prospective for collagen receptors such as DDR and their binding of the collagen fibril. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 118478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.M.; Orgel, J.P.; Fertala, A.; McAuliffe, J.D.; Turner, K.R.; Di Lullo, G.A.; Chen, S.; Antipova, O.; Perumal, S.; Ala-Kokko, L.; et al. Candidate cell and matrix interaction domains on the collagen fibril, the predominant protein of vertebrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21187–21197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perumal, S.; Antipova, O.; Orgel, J.P.R.O. Collagen fibril architecture, domain organization, and triple-helical conformation govern its proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orgel, J.; Antipova, O.; Sagi, I.; Bitler, A.; Qiu, D.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; San Antonio, J. Collagen fibril surface displays a constellation of sites capable of promoting fibril assembly, stability, and hemostasis. Connect.proline Tissue Res. 2011, 52, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.M.; Moroi, M.; Soejima, K.; Nakagaki, T.; Miura, Y.; Berndt, M.C.; Gardiner, E.E.; Howes, J.M.; Pugh, N.; Bihan, D.; et al. Constitutive dimerization of glycoprotein VI (GPVI) in resting platelets is essential for binding to collagen and activation in flowing blood. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30000–30013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Jung, S.M.; Moroi, M. Analysis of the interaction of platelet collagen receptor glycoprotein VI (GPVI) with collagen. A dimeric form of GPVI, but not the monomeric form, shows affinity to fibrous collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46197–46204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulter, N.; Pollitt, A.Y.; Owen, D.; Gardiner, E.E.; Andrews, R.; Shimizu, H.; Ishikawa, D.; Bihan, D.; Farndale, R.W.; Moroi, M.; et al. Clustering of glycoprotein VI (GPVI) dimers upon adhesion to collagen as a mechanism to regulate GPVI signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orgel, J.P.; Miller, A.; Irving, T.C.; Fischetti, R.F.; Hammersley, A.P.; Wess, T.J. The in situ supermolecular structure of type I collagen. Structure 2001, 9, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boraschi-Diaz, I.; Wang, J.; Mort, J.S.; Komarova, S.V. Collagen type I as a ligand for receptor-mediated signaling. Front. Phys. 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, A.J.; Matthews, W.G.; Koob, T.J. Determination of the elastic modulus of native collagen fibrils via radial indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 181902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, S.; Zink, A.; Janko, M.; Heckl, W.M.; Thalhammer, S. Structural investigations on native collagen type I fibrils using AFM. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Brockwell, D.J.; Radford, S.E.; Thomson, N.H. Effects of hydration on the mechanical response of individual collagen fibrils. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 233902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipova, O.; Orgel, J.P.R.O. In situ D-periodic molecular structure of type II collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7087–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orgel, J.P.; Irving, T.C. Advances in Fiber Diffraction of Macromolecular Assembles. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.; MacRae, T.; Suzuki, E. Chain conformation in the collagen molecule. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 129, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgel, J.P.R.O.; Persikov, A.V.; Antipova, O. Variation in the helical structure of native collagen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, J. Collagen structure: New tricks from a very old dog. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1001–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.R.; Reiber, A. Influence of saline and pH on collagen type I fibrillogenesis in vitro: Fibril polymorphism and colloidal gold labelling. Micron 2007, 38, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, S.W.; Lin, Y.J.; Tibudan, M.; Huang, Y.; Nakaema, M.; Swarup, V.; Keiderling, T.A. SERS biodetection using gold–silica nanoshells and nitrocellulose membranes. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. Study on the original height and compression elasticity of the DNA strands with atomic force microscopy. Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 2008, 25, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Orgel, J.P.R.O.; Eid, A.; Antipova, O.; Bella, J.; Scott, J.E. Decorin core protein (decoron) shape complements collagen fibril surface structure and mediates its binding. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.X.; Chen, L.; Di Costanzo, L.; Christie, C.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.K.; et al. Protein Data Bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D520–D528. [Google Scholar]
- Hoop, C.; Zhu, J.; Nunes, A.; Case, D.; Baum, J. Revealing Accessibility of Cryptic Protein Binding Sites within the Functional Collagen Fibril. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, A.H.; Edelman, E.R.; Stultz, C.M. Collagen fragments modulate innate immunity. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 406–411. [Google Scholar]







| Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Source Tissue | |
|---|---|---|
| Results reported here | 1.1 ± 0.2 (overlap) 1.2 ± 0.2 (gap) | Rat tail tendon |
| Heim et al., 2006 [16] | 1–2 | Inner dermis of sea cucumber |
| Strasser et al., 2007 [17] | ~1.2 | Calf skin |
| Grant et al., 2007 [18] | 1.9 ± 0.5 | Bovine achilles tendon |
| Incubation Time | n | Adhesion Force (nN) | Percentage Error (%) | Percentage Change from Native (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native (0 min) | 40 | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 13.3 | - |
| 20 min | 40 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 15.1 | 17.8 |
| 1 h | 40 | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 7.5 | 48.9 |
| 2 h | 40 | 8.2 ± 0.4 | 4.9 | 82.2 |
| Incubation Time | n | Adhesion Force (nN) | Percentage Error (%) | Percentage Change from Native (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native (0 min) | 40 | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 12.5 | - |
| 20 min | 40 | 5.0 ± 0.7 | 14.0 | 4.2 |
| 1 h | 40 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 7.5 | 10.4 |
| 2 h | 40 | 5.6 ± 0.2 | 3.6 | 16.6 |
| Fractional Peak Position | Fibril Accessibility | Candidate Amino Acid Sequences (Monomer (M) and Sequence) | Functional Binding Region of Collagen D-Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.31–0.33 | Just prior to C-term telopeptide. M4, M5 | M4 GPP(2) M5 GPPGPR | Near (N-terminal) fibronectin binding site (M4) |
| 0.42–0.44 | Interdomain, helical/non-helical of M5 near C-term telopeptide. M3, M4, M5 | M4 GVVGLPGQRGER M5 GPO(orP)(5) SGY/YYR | Middle of the fibronectin binding/MMP interaction domain (M4) |
| 0.84–085 | Highly accessible area in gap region, just before (n-terminal) decoron d-band binding site | M4 GPP(GAP)3GPVGPA | Directly over DDR/VWF on M3 and adjacent to decoron binding on M4 |
| 0.99–0.1 | Lowest trough of the up/down formation of the collagen fibril surface, near N-term telopeptide | M4 GPRGDK/GSRGAAGPP M5 GPRGDK/GETGEQ | Near N-terminal telopeptide, possible decorin binding region |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Madhurapantula, R.S.; Kalyanasundaram, A.; Sabharwal, T.; Antipova, O.; Bishnoi, S.W.; Orgel, J.P.R.O. Ultrastructural Location and Interactions of the Immunoglobulin Receptor Binding Sequence within Fibrillar Type I Collagen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114166
Zhu J, Madhurapantula RS, Kalyanasundaram A, Sabharwal T, Antipova O, Bishnoi SW, Orgel JPRO. Ultrastructural Location and Interactions of the Immunoglobulin Receptor Binding Sequence within Fibrillar Type I Collagen. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114166
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jie, Rama S. Madhurapantula, Aruna Kalyanasundaram, Tanya Sabharwal, Olga Antipova, Sandra W. Bishnoi, and Joseph P. R. O. Orgel. 2020. "Ultrastructural Location and Interactions of the Immunoglobulin Receptor Binding Sequence within Fibrillar Type I Collagen" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114166
APA StyleZhu, J., Madhurapantula, R. S., Kalyanasundaram, A., Sabharwal, T., Antipova, O., Bishnoi, S. W., & Orgel, J. P. R. O. (2020). Ultrastructural Location and Interactions of the Immunoglobulin Receptor Binding Sequence within Fibrillar Type I Collagen. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114166