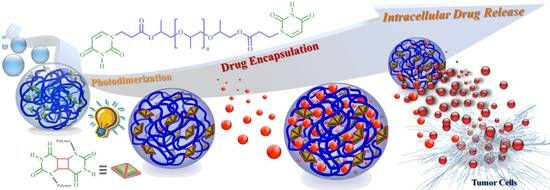
Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miragoli, M.; Ceriotti, P.; Iafisco, M.; Vacchiano, M.; Salvarani, N.; Alogna, A.; Carullo, P.; Ramirez-Rodríguez, G.B.; Patrício, T.; Esposti, L.D.; et al. Inhalation of peptide-loaded nanoparticles improves heart failure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibori, H.; Eliyahu, S.; Krivitsky, A.; Ben-Shushan, D.; Epshtein, Y.; Tiram, G.; Blau, R.; Ofek, P.; Lee, J.S.; Ruppin, E.; et al. Amphiphilic nanocarrier-induced modulation of PLK1 and MiR-34a leads to improved therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenbaum, I.; Harnoy, A.J.; Tirosh, E.; Buzhor, M.; Segal, M.; Frid, L.; Shaharabani, R.; Avinery, R.; Beck, R.; Amir, R.J. Encapsulation and covalent binding of molecular payload in enzymatically activated micellar nanocarriers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskas, L.M.; McLeod, V.M.; Porter, C.J.H.; Boyd, B.J. Association of chemotherapeutic drugs with dendrimer nanocarriers: An assessment of the merits of covalent conjugation compared to noncovalent encapsulation. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2012, 9, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechty, W.B.; Kryscio, D.R.; Slaughter, B.V.; Peppas, N.A. Polymers for drug delivery systems. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010, 1, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madaan, K.; Kumar, S.; Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting: Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Inorganic nanomaterials for bioimaging, targeted drug delivery and therapeutics. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14071–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Ruiz-Molina, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in porous nanoparticles for drug delivery in antitumoral applications: Inorganic nanoparticles and nanoscale metal-organic frameworks. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artif. Cell. Nanomed. B. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.C.; Chan, D.P.Y.; Shoichet, M.S. Polymeric micelle stability. Nano Today 2012, 7, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tian, H. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular polymers in aqueous solution. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Duval, K.; Fan, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Z. Dimeric drug polymeric micelles with acid-active tumor targeting and FRET-traceable drug release. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Ge, L.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Translatable high drug loading drug delivery systems based on biocompatible polymer nanocarriers. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfam, M.; Matini, T.; Monteiro, P.F.; Riva, R.; Collins, H.; Spriggs, K.; Howdle, S.M.; Jérôme, C.; Alexander, C. Bioreducible cross-linked core polymer micelles enhance in vitro activity of methotrexate in breast cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Su, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhu, B.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Tu, C.; Yan, D.; Zhu, X. Supramolecular copolymer micelles based on the complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases for drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, W.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C.; Huang, F. A pillararene-based ternary drug-delivery system with photocontrolled anticancer drug release. Small 2015, 11, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Yin, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular polymer chemistry: From structural control to functional assembly. Prog.Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.A.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M.; et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.C.; Wang, J.H.; Chuang, W.T.; Liao, Z.S.; Huang, J.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Fan, W.L.; Lee, D.J. Dynamic supramolecular self-assembly: Hydrogen bonding-induced contraction and extension of functional polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.L.; Yu, A.C.; Agmon, G.; Appel, E.A. Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Zimmerman, S.C. Hydrogen bonding modules for use in supramolecular polymers. Isr. J. Chem. 2013, 53, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, R.; O’Reilly, R.K. Nucleobase containing synthetic polymers: Advancing biomimicry via controlled synthesis and self-assembly. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7665–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Shen, J. Functional supramolecular polymers for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 498–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Lee, D.J.; Chen, J.K. Self-assembled supramolecular polymers with tailorable properties that enhance cell attachment and proliferation. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Tang, C. Supramolecular nucleobase-functionalized polymers: Synthesis and potential biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020, 8, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, S.; Devalapally, H.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Yuan, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. Redox-responsive polymers for drug delivery: From molecular design to applications. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Kao, W.Y.; Hwang, S.M.; Liao, L.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Liang, M.C.; Chen, J.K.; Lee, D.J. Highly efficient drug delivery systems based on functional supramolecular polymers: In vitro evaluation. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Zhang, R. Remote light-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug delivery: Advances and perspectives. Small 2019, 15, 1903060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deirram, N.; Zhang, C.; Kermaniyan, S.S.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Such, G.K. pH-Responsive polymer nanoparticles for drug delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-H.; Luo, G.-F.; Lei, Q.; Jia, H.-Z.; Hong, S.; Wang, Q.-R.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. MMP-2 responsive polymeric micelles for cancer-targeted intracellular drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Wu, S.; Meng, F.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Core-crosslinked amphiphilic biodegradable copolymer based on the complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases: Synthesis, self-assembly and in vitro drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24832–24840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.L.; Kwon, G.S. Relative aggregation state and hemolytic activity of amphotericin B encapsulated by poly(ethylene oxide)-block–poly (N-hexyl-l-aspartamide)-acyl conjugate micelles: effects of acyl chain length. J. Control. Release 2003, 87, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, H.M.; Lavasanifar, A. Polymeric micelles for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2006, 3, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, B.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, A.W.; Chen, J.K.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Dual stimuli-responsive nucleobase-functionalized polymeric systems as efficient tools for manipulating micellar self-assembly behavior. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, B.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, A.W.; Muhabie, A.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Highly stable photosensitive supramolecular micelles for tunable, efficient controlled drug release. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Johnston, P.; Saito, K. Photo-reversible dimerisation reactions and their applications in polymeric systems. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, Q.; Gao, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Yu, S.; He, C.; Chen, X. pH-Responsive poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(L-lactide) supramolecular micelles based on host–guest interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8404–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Huang, J.J.; Chen, J.K.; Lee, A.W.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Self-assembled pH-responsive polymeric micelles for highly efficient, noncytotoxic delivery of doxorubicin chemotherapy to inhibit macrophage activation: In vitro investigation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alemayehu, Y.A.; Fan, W.-L.; Ilhami, F.B.; Chiu, C.-W.; Lee, D.-J.; Cheng, C.-C. Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
Alemayehu YA, Fan W-L, Ilhami FB, Chiu C-W, Lee D-J, Cheng C-C. Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(13):4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlemayehu, Yihalem Abebe, Wen-Lu Fan, Fasih Bintang Ilhami, Chih-Wei Chiu, Duu-Jong Lee, and Chih-Chia Cheng. 2020. "Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 13: 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
APA StyleAlemayehu, Y. A., Fan, W. -L., Ilhami, F. B., Chiu, C. -W., Lee, D. -J., & Cheng, C. -C. (2020). Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(13), 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677