GO Nanosheets: Promising Nano Carrier for the S29, 1-(2-Chloro-2-(4-chlorophenyl-ethyl)-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine, Therapeutic Agent in Neuroblastoma
Abstract
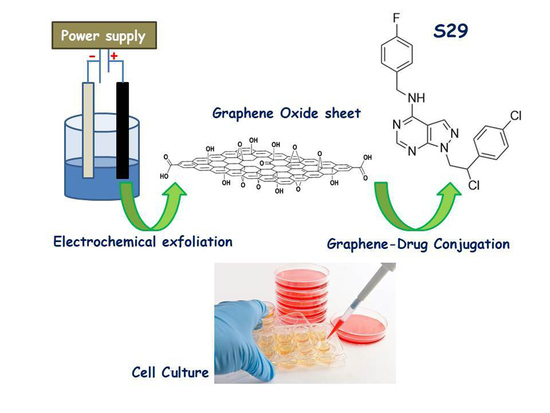
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Conjugation of GO Nanosheets with S29
2.2. Chromatographic Analysis and Binding of GO with S29
2.3. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.4. GO Uptake in Cells
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection
2.7. Cell Cycle with PI
2.8. Wound Healing Assay
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of GO and Conjugation with S29
3.2. Determination of Binding and Stability of GO-S29 Conjugates
3.3. Uptake of GO by SKNBE (2) Cells
3.4. Additive Effect between GO and S29 in Inducing Cell Death
3.5. The Combination of GO and S29 Inhibits SKNBE (2) Proliferation
3.6. The Combination of GO and S29 Induces ROS Production in SKNBE (2) Cells
3.7. The Combination of GO and S29 Inhibits SKNBE (2) Migration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valentini, F.; Calcaterra, A.; Ruggiero, V.; Pichichero, E.; Martino, A.; Iosi, F.; Bertuccini, L.; Antonaroli, S.; Mardente, S.; Zicari, A.; et al. Functionalized Graphene Derivatives: Antibacterial Properties and Cytotoxicity. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor, E.R.; Mousa, S.A. Current management of neuroblastoma and future direction. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 138, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S.J.; Parsons, J.T. Src family kinases, key regulators of signal transduction. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7906–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarra, M.; Celano, M.; Maiuolo, J.; Schenone, S.; Botta, M.; Angelucci, A.; Bramanti, B.; Russo, D. Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects afforded by novel Src-kinase inhibitors inhuman neuroblastoma cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jallal, H.; Valentino, M.L.; Chen, G.; Boschelli, F.; Ali, S.; Rabbani, S.A. A Src/Abl kinase inhibitor, SKI-606, blocks breast cancer invasion, growth, and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.S.; Swerdolw, T.M.; Duffy, R.; Weinmann, F.Y.; Lee, S. Targeting Multiple Kinase Pathways in Leukemic Progenitors and Stem Cells Is Essential for Improved Treatment of Ph+ Leukemia in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16870–16875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Bernasconi, P.; Clauser, K.R.; Mani, D.R.; Finn, S.P.; Beroukhim, R.; Burns, M.; Julian, B.; Peng, X.P.; Hieronymus, H.; et al. Bead-based profiling of tyrosine kinase phosphorylation identifies SRC as a potential target for glioblastoma therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S. Src Kinase Signaling in Leukaemia. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreafico, A.; Schenone, S.; Serchi, T.; Orlandini, M.; Angelucci, A.; Magrini, D.; Bernardini, G.; Collodel, G.; Di Stefano, A.; Tintori, C.; et al. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of new pyrazolo-[3,4-d]-pyrimidine derivative Src kinase inhibitors in human osteosarcoma cells. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Schenone, S.; Angelucci, A.; Cozzi, M.; Caracciolo, V.; Pentimalli, F.; Puca, A.; Pucci, B.; La Montagna, R.; Bologna, M.; et al. New pyrazolo-[3,4-d]-pyrimidine derivative Src kinase inhibitors lead to cell cycle arrest and tumor growth reduction of human medulloblastoma cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenone, S.; Brullo, C.; Bruno, O.; Bondavalli, F.; Mosti, L.; Maga, G.; Crespan, E.; Carraro, F.; Manetti, F.; Tintori, C.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies of 4-amino substituted 1H-pyrazolo-[3,4-d]-pyrimidines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, G.A.; Locatelli, G.; Maga, S.; Schenone, M.; Modugno, S.; Forli, F.; Corelli, M.; Botta, M. A Combination of docking/dynamics Simulations and Pharmacophoric Modeling to Discover New Dual c-Src/Abl Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3278–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, F.; Mari, E.; Zicari, A.; Calcaterra, A.; Talamo, M.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Mardente, S. Metal Free Graphene Oxide (GO) Nanosheets and Pristine-Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes (p-SWCNTs) Biocompatibility Investigation: A Comparative Study in Different Human Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mari, E.; Mardente, S.; Morgante, E.; Tafani, M.; Lococo, E.; Fico, F.; Valentini, F.; Zicari, A. Graphene Oxide Nanoribbons Induce Autophagic Vacuoles in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1995–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, N. Fluorescence and Sensing Applications of Graphene Oxide and Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mileo, A.M.; Di Venere, D.; Mardente, S.; Miccadei, S. Artichoke Polyphenols Sensitize Human Breast Cancer Cells to Chemotherapeutic Drugs via a ROS-Mediated Downregulation of Flap Endonuclease 1. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Bhowmik, P.; Zhao, B.; Hamon, M.A. Determination of the acidic sites of purified single-walled carbon nanotubes by acid–base titration. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 345, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, F.A.; Sundberg, R.J. Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Springer: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1992; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Fransson, A.; Glaessgen, D.; Alfredsson, J.; Wiman, K.; Lagerktantz, S.B.; Mohell, N. Strong synergy with APR-246 and DNA-damaging drugs in primary cancer cells from patients with TP53 mutant High-Grade Serous ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2016, 99, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung-Mi, O.; Eunhee, K.; Sungkun, C. Ginsenoside Compound K induces Ros-mediated apoptosis and autophagic inhibition in human neuroblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4279. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, D.S.; Van Etten, R.A. Tyrosin kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, T.W.; Hubbard, S.R. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Mechanisms of activation and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Musumeci, F.; Schenone, S.; Grossi, G.; Brullo, C.; Sanna, M. Analogs, formulations and derivatives of imatinib: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desogus, A.; Schenone, S.; Brullo, C.; Tintori, C.; Musumeci, F. Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megison, M.L.; Gillory, L.A.; Beierle, E.A. Cell survival signaling in neuroblastoma. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borriello, L.; Robert, C.; Seeger, R.C.; Asgharzadeh, S.; De Clerck, Y.A. More than the genes, the tumor microenvironment in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 380, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tadyszak, K.; Wychowaniec, J.K.; Litowczenko, J. Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villanueva-Flores, F.; Castro-Lugo, A.; Ramírez, O.T.; Palomares, L.A. Understanding cellular interactions with nanomaterials: Towards a rational design of medical nanodevices. Nanotechnology 2020, 3, 132002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadia, S.; Serpooshanb, V.; Taoa, W.; Hamalyc, M.A.; Alkawareekd, M.Y.; Dreadene, E.C.; Brownf, E.; Alkilanyd, A.M.; Farokhzada, O.C.; Mahmoudia, M. Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles: Journey Inside the Cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Bai, J.; Jiang, X.; Nienhaus, G.U. Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles by Membrane Penetration: A Study Combining Confocal Microscopy with FTIR Spectroelectrochemistry. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zong, C.; Shen, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, B.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Z. Mechanism of Cellular Uptake of Graphene Oxide Studied by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Small 2012, 8, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniyal, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, W. Comprehensive Review on Graphene Oxide for Use in Drug Delivery System. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 3665–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, A.; Andrews, N.G.; Raghavan, V. Natural polymer functionalized graphene oxide for co-delivery of anticancer drugs: In-vitro and in-vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Deng, X.; Huang, W.; Qing, X.; Shao, Z. The Physicochemical Properties of Graphene Nanocomposites Influence the Anticancer Effect. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 7254534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejabat, M.; Charbgoo, F.; Ramezani, M. Graphene as multifunctional delivery platform in cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2017, 105, 2355–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, M.; Farfalle, A.; Saletta, F.; Valli, E.; Pantuso, E.; Nicoletta, F.P.; Iemma, F.; Vittorio, O.; Cirillo, G. Functionalized Carbon Nanostructures Versus Drug Resistance: Promising Scenarios in Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Sanders, A.; Katoh, M.; Ungefroren, H.; Gieseler, F.; Prince, M.; Thompson, S.; Zollo, M.; Spano, D.; Dhawan, P.; et al. Tissue invasion and metastasis: Molecular, biological and clinical perspectives. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 244–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, S.A.; Welch, D.R. Metastasis: Recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet 2007, 369, 1742–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Elemental Analysis (% w/w) a | Si n.d. S n.d. Ca n.d. Cr n.d. Fe n. d. Co n. d. |
|---|---|
| Thickness (nm) b | (1.20 ± 0.30; a bilayer) |
| Area (nm2) c | (0.10–3.00) |
| weight loss% (TGA) d | (2.80 ± 0.50) |
| acidic sites (nmol/mg) e | (63.22 ± 2.70) |
| extent of defect (ID/IG) f | 0.10 |
| Z-potential (ξ/mV) | −38.47 |
| GO | GO/S29 Composite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTIR | FTIR | ||||
| Carboxylic acids, C(=O)OH: νOH 3300-2500 cm−1; νC(=O)1717 cm−1; δ-in-p-C-O-H 1424 cm−1; ν-C-O 1301 cm−1; δ-out-of-p- -O-H 946 cm−1 | Amide, νC(=O)N 1550 cm−1 | ||||
| Chetons, C(=O)R: normal νC(=O) 1715 cm−1; ν and δC-CO-C 1213 cm−1 Aldheids, C(=O)H: νC-H 2715 cm−1; νC(=O) 1728 cm−1; δC-H 1381 cm−1 | Amide, νC=(O) 1650 cm-1 | ||||
| Ethers, -C-O-C: asymmetrical νC-O-C 1125 cm−1 | Amide, Overtone, νC(=O)N 3090 cm−1 | ||||
| Alcohols, C-OH: νOH 3350 cm−1; νC-O 1054 cm−1 | Amide, vNH 3290 cm−1 | ||||
| XPS | XPS | ||||
| Functional groups | Peak Binding Energy (eV) | At (%) | Functional groups | Peak Binding Energy (eV) | At (%) |
| C(=O)O | 289.3 | 5.0 | Amide –N–(C=O) | C1s 287.84 | 10.0 |
| C(=O) | 287.8 | 8.0 | |||
| C-O | 286.5 | 16.0 | Amide –N–(C=O) | N1s 400.50 | 7.0 |
| C-OH | 285.2 | 18.0 | |||
| At (%): Atomic percentage (%) | |||||
| SKN BE (2) | Pre-G1 (A) | G0-G1(B) (Dyploid) | G2-M (C-D) (Hyperploidy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 5 ± 6% | 67 ± 8% | 28 ± 9% |
| S29 10 μM | 16 ± 6% | 72 ± 6% | 12 ± 5% |
| GO 2 μg/mL | 8 ± 4% | 62 ± 2% | 30 ± 6% |
| GO 2 μg/mL + S29 10 μM | 38 ± 7% | 60 ± 3% | 2 ± 2% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mardente, S.; Aventaggiato, M.; Mari, E.; Francioso, A.; Tafani, M.; Mosca, L.; Zicari, A.; Malyshev, I.; Kuznetsova, L.; Valentini, F. GO Nanosheets: Promising Nano Carrier for the S29, 1-(2-Chloro-2-(4-chlorophenyl-ethyl)-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine, Therapeutic Agent in Neuroblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176430
Mardente S, Aventaggiato M, Mari E, Francioso A, Tafani M, Mosca L, Zicari A, Malyshev I, Kuznetsova L, Valentini F. GO Nanosheets: Promising Nano Carrier for the S29, 1-(2-Chloro-2-(4-chlorophenyl-ethyl)-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine, Therapeutic Agent in Neuroblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176430
Chicago/Turabian StyleMardente, Stefania, Michele Aventaggiato, Emanuela Mari, Antonio Francioso, Marco Tafani, Luciana Mosca, Alessandra Zicari, Igor Malyshev, Larisa Kuznetsova, and Federica Valentini. 2020. "GO Nanosheets: Promising Nano Carrier for the S29, 1-(2-Chloro-2-(4-chlorophenyl-ethyl)-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine, Therapeutic Agent in Neuroblastoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176430
APA StyleMardente, S., Aventaggiato, M., Mari, E., Francioso, A., Tafani, M., Mosca, L., Zicari, A., Malyshev, I., Kuznetsova, L., & Valentini, F. (2020). GO Nanosheets: Promising Nano Carrier for the S29, 1-(2-Chloro-2-(4-chlorophenyl-ethyl)-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidin-4-amine, Therapeutic Agent in Neuroblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176430