Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review
Abstract
:1. Overview
2. Materials and Methods
3. Search Results
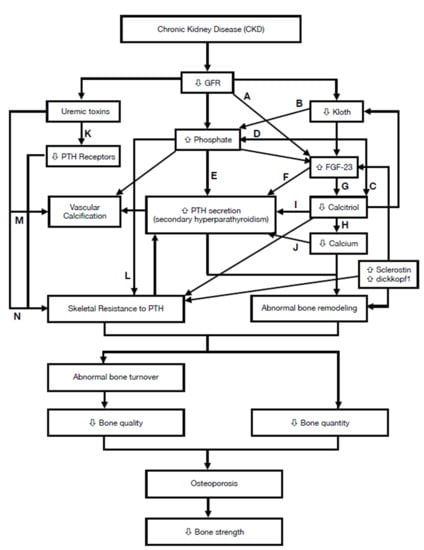
4. Characteristics of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD)
4.1. Abnormalities of Calcium, Phosphorus, PTH, or Vitamin D Metabolism
4.1.1. Disorders of Calcium Balance
4.1.2. Disorder of Phosphorus Metabolism
4.1.3. Disorder of Parathyroid Hormone Metabolism
4.1.4. Disorder of Vitamin D Metabolism
4.2. Abnormalities in Bone Turnover, Mineralization, Volume, Volume Linear Growth, or Strength
4.2.1. TMV Characteristics of Renal Osteodystrophy
4.2.2. Bone Turnover in CKD
Prevalence of Low-Turnover Bone Disease in CKD
Evaluation of Bone Turnover
4.2.3. Evaluation of Bone Strength
4.3. Vascular or Other Soft Tissue Calcification
4.3.1. Risk Factors
4.3.2. Protectors
4.4. Evaluating Fracture Risk in CKD
5. Management of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD)
5.1. Lifestyle Modification
5.2. Exercise and Physical Therapy
5.3. Correction of Biochemical Abnormalities of CKD-MBD
5.3.1. Phosphate
5.3.2. Calcium or Cinacalcet
5.3.3. Vitamin D
5.3.4. Parathyroidectomy
5.4. Choices of Pharmacologic Treatment
5.4.1. Antiresorptive
Bisphosphonates
Denosumab
Raloxifene
5.4.2. Anabolic Agents
Teriparatide
Abaloparatide
Romosozumab
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group. KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moe, S.; Drueke, T.; Cunningham, J.; Goodman, W.; Martin, K.; Olgaard, K.; Ott, S.; Sprague, S.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G.; et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sidibe, A.; Auguste, D.; Desbiens, L.C.; Fortier, C.; Wang, Y.P.; Jean, S.; Moore, L.; Mac-Way, F. Fracture Risk in Dialysis and Kidney Transplanted Patients: A Systematic Review. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nih Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA 2001, 285, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najar, M.S.; Mir, M.M.; Muzamil, M. Prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with chronic kidney disease (stages 3–5) in comparison with age- and sex-matched controls: A study from Kashmir Valley Tertiary Care Center. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2017, 28, 538–544. [Google Scholar]
- Nickolas, T.L.; McMahon, D.J.; Shane, E. Relationship between moderate to severe kidney disease and hip fracture in the United States. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3223–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra de Carvalho, K.S.; Vasco, R.F.V.; Custodio, M.R.; Jorgetti, V.; Moyses, R.M.A.; Elias, R.M. Chronic kidney disease is associated with low BMD at the hip but not at the spine. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, P.; Nickolas, T.L. Management of Osteoporosis in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.M.; Long, J.; Montez-Rath, M.; Leonard, M.; Chertow, G.M. Hip Fracture in Patients with Non-Dialysis-Requiring Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Lips, P.; Vervloet, M.G.; van Schoor, N.M.; de Jongh, R.T. Association of renal function with bone mineral density and fracture risk in the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, R.K.; Sloane, R.; Pieper, C.; Van Houtven, C.; LaFleur, J.; Adler, R.; Colon-Emeric, C. Competing Risks of Fracture and Death in Older Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.M. Renal Osteodystrophy or Kidney-Induced Osteoporosis? Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Quinones, H.; Griffith, C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Klotho deficiency causes vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, S.; Cianciolo, G.; De Pascalis, A.; Guglielmo, C.; Urena Torres, P.A.; Bover, J.; Tartaglione, L.; Pasquali, M.; La Manna, G. Bone, inflammation and the bone marrow niche in chronic kidney disease: What do we know? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, O.; Isakova, T.; Rhee, E.; Shah, A.; Holmes, J.; Collerone, G.; Juppner, H.; Wolf, M. Fibroblast growth factor-23 mitigates hyperphosphatemia but accentuates calcitriol deficiency in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P.; D’Haese, P.; Brandenburg, V. Sclerostin and DKK1: New players in renal bone and vascular disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglione, L.; Pasquali, M.; Rotondi, S.; Muci, M.L.; Covic, A.; Mazzaferro, S. Positioning novel biologicals in CKD-mineral and bone disorders. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colditz, J.; Thiele, S.; Baschant, U.; Garbe, A.I.; Niehrs, C.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Rauner, M. Osteogenic Dkk1 Mediates Glucocorticoid-Induced but Not Arthritis-Induced Bone Loss. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.; Levi, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin. Nephrol. 2005, 63, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llach, F. Secondary hyperparathyroidism in renal failure: The trade-off hypothesis revisited. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 25, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fukagawa, M. Uremic Toxicity and Bone in CKD. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malluche, H.H.; Mawad, H.; Koszewski, N.J. Update on vitamin D and its newer analogues: Actions and rationale for treatment in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Kazama, J.J.; Fukagawa, M. Molecular Abnormalities Underlying Bone Fragility in Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3485785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveh-Many, T.; Rahamimov, R.; Livni, N.; Silver, J. Parathyroid cell proliferation in normal and chronic renal failure rats. The effects of calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Bakris, G.L.; Molitch, M.; Smulders, M.; Tian, J.; Williams, L.A.; Andress, D.L. Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, M.; Nemeth, E.; Martin, D. The calcium-sensing receptor: A key factor in the pathogenesis of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2005, 288, F253–F264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canadillas, S.; Canalejo, A.; Santamaria, R.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Estepa, J.C.; Martin-Malo, A.; Bravo, J.; Ramos, B.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. Calcium-sensing receptor expression and parathyroid hormone secretion in hyperplastic parathyroid glands from humans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Block, G.A.; Hulbert-Shearon, T.E.; Levin, N.W.; Port, F.K. Association of serum phosphorus and calcium x phosphate product with mortality risk in chronic hemodialysis patients: A national study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 31, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Kim, J.; Ireland, E.; Chazot, C.; Drueke, T.; de Francisco, A.; Kronenberg, F.; Marcelli, D.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Schernthaner, G.; et al. Serum iPTH, calcium and phosphate, and the risk of mortality in a European haemodialysis population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sessa, A.; Esposito, A.; Iavicoli, G.D.; Lettieri, E.; Dente, G.; Costa, C.; Bergallo, M.; Rossano, R.; Capuano, M. Immunosuppressive agents and bone disease in renal transplant patients with hypercalcemia. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill Gallant, K.M.; Spiegel, D.M. Calcium Balance in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.J.; Gonzalez, E.A. Metabolic bone disease in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruska, K.A.; Teitelbaum, S.L. Renal osteodystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Maeda, A.; Ohtomo, S.; Hirata, M.; Kusano, K.; Kato, S.; Ogata, E.; Segawa, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Fukushima, N. Circulating FGF-23 is regulated by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phosphorus in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paloian, N.J.; Giachelli, C.M. A current understanding of vascular calcification in CKD. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014, 307, F891–F900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isakova, T.; Wahl, P.; Vargas, G.S.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Scialla, J.; Xie, H.; Appleby, D.; Nessel, L.; Bellovich, K.; Chen, J.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P.; Cashman, K.D.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Bianchi, M.L.; Stepan, J.; El-Hajj Fuleihan, G.; Bouillon, R. Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, P23–P54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaClair, R.E.; Hellman, R.N.; Karp, S.L.; Kraus, M.; Ofner, S.; Li, Q.; Graves, K.L.; Moe, S.M. Prevalence of calcidiol deficiency in CKD: A cross-sectional study across latitudes in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, G.; Mantella, D.; Manni, M.; Balducci, A.; Nofroni, I.; Sardella, D.; Ballanti, P.; Bonucci, E. 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and bone histomorphometry in hemodialysis renal osteodystrophy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacome-Galarza, C.E.; Percin, G.I.; Muller, J.T.; Mass, E.; Lazarov, T.; Eitler, J.; Rauner, M.; Yadav, V.K.; Crozet, L.; Bohm, M.; et al. Developmental origin, functional maintenance and genetic rescue of osteoclasts. Nature 2019, 568, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenberg, D.; Boonen, S. The bone quality framework: Determinants of bone strength and their interrelationships, and implications for osteoporosis management. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Frazao, J.M.; Monier-Faugere, M.C.; Gil, C.; Galvao, J.; Oliveira, C.; Baldaia, J.; Rodrigues, I.; Santos, C.; Ribeiro, S.; et al. Effects of sevelamer hydrochloride and calcium carbonate on renal osteodystrophy in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Moyses, R.M.; Neves, K.R.; Canziani, M.E.; Draibe, S.A.; Jorgetti, V.; Carvalho, A.B. K/DOQI-recommended intact PTH levels do not prevent low-turnover bone disease in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasovski, G.B.; Bervoets, A.R.; Behets, G.J.; Ivanovski, N.; Sikole, A.; Dams, G.; Couttenye, M.M.; De Broe, M.E.; D’Haese, P.C. Spectrum of renal bone disease in end-stage renal failure patients not yet on dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, S.M.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Jorgetti, V.; Carvalho, A.B.; Malluche, H.H.; Ferreira, A.; D’Haese, P.C.; Drueke, T.B.; Du, H.; Manley, T.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Histology in Patients With CKD Treated by Dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malluche, H.H.; Mawad, H.W.; Monier-Faugere, M.C. Renal osteodystrophy in the first decade of the new millennium: Analysis of 630 bone biopsies in black and white patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moe, S.M.; Drueke, T.B. A bridge to improving healthcare outcomes and quality of life. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Moyses, R.M.; Neves, C.L.; Jorgetti, V.; Draibe, S.A.; Canziani, M.E.; Carvalho, A.B. Osteoporosis in hemodialysis patients revisited by bone histomorphometry: A new insight into an old problem. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gal-Moscovici, A.; Popovtzer, M.M. New worldwide trends in presentation of renal osteodystrophy and its relationship to parathyroid hormone levels. Clin. Nephrol. 2005, 63, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrli, F.W.; Leonard, M.B.; Saha, P.K.; Gomberg, B.R. Quantitative high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging reveals structural implications of renal osteodystrophy on trabecular and cortical bone. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qunibi, W.; Moustafa, M.; Muenz, L.R.; He, D.Y.; Kessler, P.D.; Diaz-Buxo, J.A.; Budoff, M.; CARE-2 Investigators. A 1-year randomized trial of calcium acetate versus sevelamer on progression of coronary artery calcification in hemodialysis patients with comparable lipid control: The Calcium Acetate Renagel Evaluation-2 (CARE-2) study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, H.J.; Brunner, U. Calcified and ossified phlebosclerosis. VASA 1992, 21, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vervloet, M.; Cozzolino, M. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: Different bricks in the wall? Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, G.M.; Guerin, A.P.; Marchais, S.J.; Metivier, F.; Pannier, B.; Adda, H. Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: Impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, W.G.; Goldin, J.; Kuizon, B.D.; Yoon, C.; Gales, B.; Sider, D.; Wang, Y.; Chung, J.; Emerick, A.; Greaser, L.; et al. Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.J.; Covic, A.; Sambrook, P.A.; Ackrill, P. Vascular calcification in long-term haemodialysis patients in a single unit: A retrospective analysis. Nephron 1997, 77, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.A.; Sandberg, K.R.; Dumler, F.; Yanez, J.E. Determinants of coronary vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: A systematic review. J. Nephrol. 2004, 17, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ok, E.; Asci, G.; Bayraktaroglu, S.; Toz, H.; Ozkahya, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Kircelli, F.; Sevinc Ok, E.; Ceylan, N.; Duman, S.; et al. Reduction of Dialysate Calcium Level Reduces Progression of Coronary Artery Calcification and Improves Low Bone Turnover in Patients on Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimura, E.; Okuno, S.; Kitatani, K.; Tsuchida, T.; Yamakawa, T.; Shioi, A.; Inaba, M.; Nishizawa, Y. Significant association between the presence of peripheral vascular calcification and lower serum magnesium in hemodialysis patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2007, 68, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, H.; Toto, R.; Peshock, R.; Cooper, R.; Victor, R. Association between chronic kidney disease and coronary artery calcification: The Dallas Heart Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.H.; O’Neill, W.C. Increased Peripheral Arterial Calcification in Patients Receiving Warfarin. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, K.; Wada, Y. Evaluation of aortic calcification with lanthanum carbonate vs. calcium-based phosphate binders in maintenance hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An open-label randomized controlled trial. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2014, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, P.; Chertow, G.M.; Torres, P.U.; Csiky, B.; Naso, A.; Nossuli, K.; Moustafa, M.; Goodman, W.G.; Lopez, N.; Downey, G.; et al. The ADVANCE study: A randomized study to evaluate the effects of cinacalcet plus low-dose vitamin D on vascular calcification in patients on hemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, W.C.; Sigrist, M.K.; McIntyre, C.W. Plasma pyrophosphate and vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collin-Osdoby, P. Regulation of vascular calcification by osteoclast regulatory factors RANKL and osteoprotegerin. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.L.; Lok, C.E.; Langsetmo, L.; Cheung, A.M.; Szabo, E.; Pearce, D.; Fusaro, M.; Wald, R.; Weinstein, J.; Jamal, S.A. Bone mineral density predicts fractures in chronic kidney disease. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, K.L.; Garg, A.X.; Zou, G.; Langsetmo, L.; Leslie, W.D.; Fraser, L.A.; Adachi, J.D.; Morin, S.; Goltzman, D.; Lentle, B.; et al. Comparison of fracture risk prediction among individuals with reduced and normal kidney function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iimori, S.; Mori, Y.; Akita, W.; Kuyama, T.; Takada, S.; Asai, T.; Kuwahara, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tsukamoto, Y. Diagnostic usefulness of bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in predicting fracture in CKD stage 5D patients—A single-center cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, P.A.U.; Cohen-Solal, M. Evaluation of fracture risk in chronic kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.A.; West, S.L.; Nickolas, T.L. The clinical utility of FRAX to discriminate fracture status in men and women with chronic kidney disease. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, K.L.; Leslie, W.D.; Hodsman, A.B.; Rush, D.N.; Garg, A.X. FRAX predicts fracture risk in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2014, 97, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, Y.; Inaba, M.; Nakatsuka, K.; Nagasue, K.; Okuno, S.; Yoshihara, A.; Miura, M.; Miyauchi, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Miki, T.; et al. FGF-23 in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, T.; Nisbeth, U.; Ljunggren, O.; Juppner, H.; Jonsson, K.B. Circulating concentration of FGF-23 increases as renal function declines in patients with chronic kidney disease, but does not change in response to variation in phosphate intake in healthy volunteers. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Seigneux, S.; Courbebaisse, M.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Wilhelm-Bals, A.; Metzger, M.; Khodo, S.N.; Hasler, U.; Chehade, H.; Dizin, E.; Daryadel, A.; et al. Proteinuria Increases Plasma Phosphate by Altering Its Tubular Handling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyal, R.; Jialal, I. Hyperphosphatemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, A.; Moriniere, P.; Ben Hamida, F.; el Esjer, N.; Shenovda, M.; Ghazali, A.; Bouzernidj, M.; Achard, J.M.; Westeel, P.F. Use of alkaline calcium salts as phosphate binder in uremic patients. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1992, 38, S50–S61. [Google Scholar]
- Komaba, H.; Goto, S.; Fujii, H.; Hamada, Y.; Kobayashi, A.; Shibuya, K.; Tominaga, Y.; Otsuki, N.; Nibu, K.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Depressed expression of Klotho and FGF receptor 1 in hyperplastic parathyroid glands from uremic patients. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canalejo, R.; Canalejo, A.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Estepa, J.C.; Mendoza, F.J.; Munoz-Castaneda, J.R.; Shalhoub, V.; Almaden, Y.; Rodriguez, M. FGF23 fails to inhibit uremic parathyroid glands. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.H.; Patel, S.R.; Young, E.W.; Vanholder, R. The biological action of calcitriol in renal failure. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denda, M.; Finch, J.; Brown, A.J.; Nishii, Y.; Kubodera, N.; Slatopolsky, E. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and 22-oxacalcitriol prevent the decrease in vitamin D receptor content in the parathyroid glands of uremic rats. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slatopolsky, E.; Weerts, C.; Thielan, J.; Horst, R.; Harter, H.; Martin, K.J. Marked suppression of secondary hyperparathyroidism by intravenous administration of 1,25-dihydroxy-cholecalciferol in uremic patients. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.; Felsenfeld, A.; Drezner, M.K.; Llach, F. Altered divalent ion metabolism in early renal failure: Role of 1,25(OH)2D. Kidney Int. 1985, 27, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yano, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Chihara, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Kitazawa, S.; Maeda, S.; Kitazawa, R. Association of decreased calcium-sensing receptor expression with proliferation of parathyroid cells in secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogusev, J.; Duchambon, P.; Hory, B.; Giovannini, M.; Goureau, Y.; Sarfati, E.; Drueke, T.B. Depressed expression of calcium receptor in parathyroid gland tissue of patients with hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Teng, J.; Ji, J.; Ding, X. Indoxyl Sulfate Enhance the Hypermethylation of Klotho and Promote the Process of Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yamato, H.; Mori, Y.; Komaba, H.; Watanabe, H.; Maruyama, T.; Fukagawa, M. p-Cresyl sulfate induces osteoblast dysfunction through activating JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Bone 2013, 56, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, S.L.; Jamal, S.A.; Lok, C.E. Tests of neuromuscular function are associated with fractures in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, P.; Nickolas, T.L. Updates in CKD-Associated Osteoporosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, J.; Bailone, L.; Lopez-Baez, V.; Benito, S.; Ciceri, P.; Galassi, A.; Cozzolino, M. Osteoporosis, bone mineral density and CKD-MBD: Treatment considerations. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiwe, S.; Jacobson, S.H. Exercise training in adults with CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.W.; Huang, T.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Liou, H.H.; Chou, Y.H.; Sue, Y.M.; Hung, P.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Ho, P.C.; Tsai, K.J. Exercise Alleviates Osteoporosis in Rats with Mild Chronic Kidney Disease by Decreasing Sclerostin Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roshanravan, B.; Gamboa, J.; Wilund, K. Exercise and CKD: Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction and Practical Application of Exercise to Prevent and Treat Physical Impairments in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.M.; Martin, B.R.; Wastney, M.E.; McCabe, G.P.; Moe, S.M.; Weaver, C.M.; Peacock, M. Oral calcium carbonate affects calcium but not phosphorus balance in stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, M.E.; Almaden, Y.; Canadillas, S.; Canalejo, A.; Siendones, E.; Lopez, I.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Martin, D.; Rodriguez, M. The calcimimetic R-568 increases vitamin D receptor expression in rat parathyroid glands. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 292, F1390–F1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi, R.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Dinur, M.; Martin, D.; Naveh-Many, T.; Silver, J. Increased parathyroid hormone gene expression in secondary hyperparathyroidism of experimental uremia is reversed by calcimimetics: Correlation with posttranslational modification of the trans acting factor AUF1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagano, N. Pharmacological and clinical properties of calcimimetics: Calcium receptor activators that afford an innovative approach to controlling hyperparathyroidism. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 109, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.M.; Abdalla, S.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.S.; Block, G.A.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Floege, J.; Herzog, C.A.; London, G.M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Effects of Cinacalcet on Fracture Events in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: The EVOLVE Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.M.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.S.; Kubo, Y.; Block, G.A.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Drueke, T.B.; Herzog, C.A.; London, G.M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Cinacalcet, Fibroblast Growth Factor-23, and Cardiovascular Disease in Hemodialysis: The Evaluation of Cinacalcet HCl Therapy to Lower Cardiovascular Events (EVOLVE) Trial. Circulation 2015, 132, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuruta, Y.; Okano, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Akiba, T.; Nitta, K. Effects of cinacalcet on bone mineral density and bone markers in hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2013, 17, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behets, G.J.; Spasovski, G.; Sterling, L.R.; Goodman, W.G.; Spiegel, D.M.; De Broe, M.E.; D’Haese, P.C. Bone histomorphometry before and after long-term treatment with cinacalcet in dialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haris, A.; Sherrard, D.J.; Hercz, G. Reversal of adynamic bone disease by lowering of dialysate calcium. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damasiewicz, M.J.; Ebeling, P.R. Management of mineral and bone disorders in renal transplant recipients. Nephrology 2017, 22 (Suppl. 2), 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jo, H.A.; Han, K.H.; So, Y.K.; Jun, H.; Han, S.Y. Effect of Cinacalcet in Kidney Transplant Patients with Hyperparathyroidism. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzado, J.M.; Moreno, P.; Torregrosa, J.V.; Taco, O.; Mast, R.; Gomez-Vaquero, C.; Polo, C.; Revuelta, I.; Francos, J.; Torras, J.; et al. A Randomized Study Comparing Parathyroidectomy with Cinacalcet for Treating Hypercalcemia in Kidney Allograft Recipients with Hyperparathyroidism. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, A.; Urena-Torres, P.; Zillikens, M.C.; Bover, J.; Cohen-Solal, M. Fractures in patients with CKD-diagnosis, treatment, and prevention: A review by members of the European Calcified Tissue Society and the European Renal Association of Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singer, R.F. Vitamin D in dialysis: Defining deficiency and rationale for supplementation. Semin. Dial. 2013, 26, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, G.; Souberbielle, J.C.; Chazot, C. Vitamin D in Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis Patients. Nutrients 2017, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P.; Goldsmith, D.; de Jongh, R. Vitamin D and osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Fafin, C.; Dubois, B.E.; Krzesinski, J.M.; Moranne, O. Efficiency of delivery observed treatment in hemodialysis patients: The example of the native vitamin D therapy. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, D.W.; Goldberg, S.; Faber, M.; Ghossein, C.; Sprague, S.M. A randomized multicenter trial of paricalcitol versus calcitriol for secondary hyperparathyroidism in stages 3-4 CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, L.R.; Abrams, L.; Roe, C.J.; Faugere, M.C.; Fanti, P.; Subayti, Y.; Malluche, H.H. 1,25(OH)2D3 administration in moderate renal failure: A prospective double-blind trial. Kidney Int. 1989, 35, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangoo-Karim, R.; Da Silva Abreu, J.; Yanev, G.P.; Perez, N.N.; Stubbs, J.R.; Wetmore, J.B. Ergocalciferol versus Cholecalciferol for Nutritional Vitamin D Replacement in CKD. Nephron 2015, 130, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetmore, J.B.; Kimber, C.; Mahnken, J.D.; Stubbs, J.R. Cholecalciferol v. ergocalciferol for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) repletion in chronic kidney disease: A randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, D.; Chitalia, N.; Ster, I.C.; Appelbaum, E.; Thadhani, R.; Kaski, J.C.; Goldsmith, D. Impact of Vitamin D on Cardiac structure and function in CKD patients with hypovitaminosis D, a randomised controlled trial and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, pvz080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franca Gois, P.H.; Wolley, M.; Ranganathan, D.; Seguro, A.C. Vitamin D Deficiency in Chronic Kidney Disease: Recent Evidence and Controversies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alshayeb, H.M.; Josephson, M.A.; Sprague, S.M. CKD-mineral and bone disorder management in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.C.; Ma, W.Y.; Yu, J.C.; Wu, C.C.; Chu, P. Bone turnover markers predict changes in bone mineral density after parathyroidectomy in patients with renal hyperparathyroidism. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 2012, 76, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Imai, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Sato, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Igarashi, K.; Harada, Y.; Azuma, Y.; Krust, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell 2007, 130, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoumpra, M.K.; Muniz, J.R.; Barnett, B.L.; Kwaasi, A.A.; Pilka, E.S.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Evdokimov, A.; Walter, R.L.; Von Delft, F.; Ebetino, F.H.; et al. The inhibition of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Elucidating the role of active site threonine 201 and tyrosine 204 residues using enzyme mutants. Bone 2015, 81, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, P.D.; Roux, C.; Boonen, S.; Barton, I.P.; Dunlap, L.E.; Burgio, D.E. Safety and efficacy of risedronate in patients with age-related reduced renal function as estimated by the Cockcroft and Gault method: A pooled analysis of nine clinical trials. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, T.; Muraoka, R.; Sugimoto, T.; Nishizawa, Y. Risedronate therapy in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease with osteoporosis: Post-hoc analysis of data from the risedronate phase III clinical trials. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamal, S.A.; Bauer, D.C.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Hochberg, M.; Ishani, A.; Cummings, S.R. Alendronate treatment in women with normal to severely impaired renal function: An analysis of the fracture intervention trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussaint, N.D.; Lau, K.K.; Strauss, B.J.; Polkinghorne, K.R.; Kerr, P.G. Effect of alendronate on vascular calcification in CKD stages 3 and 4: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.M.; Delmas, P.D.; Eastell, R.; Reid, I.R.; Boonen, S.; Cauley, J.A.; Cosman, F.; Lakatos, P.; Leung, P.C.; Man, Z.; et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergner, R.; Henrich, D.; Hoffmann, M.; Schmidt-Gayk, H.; Lenz, T.; Upperkamp, M. Treatment of reduced bone density with ibandronate in dialysis patients. J. Nephrol. 2008, 21, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, L.M.; Rebholz, C.M.; Jirru, E.; Liu, M.C.; Zhang, A.; Gayleard, J.; Chu, Y.; Robinson, K.A. Benefits and Harms of Osteoporosis Medications in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, M.; Xu, J.H.; Shu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Cui, X.J. Bisphosphonates for prevention of osteopenia in kidney-transplant recipients: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth-Manikowski, S.M.; Francis, J.M.; Gautam, A.; Gordon, C.E. Outcomes of bisphosphonate therapy in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 30, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, D.L.; Boyle, W.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Kostenuik, P.J.; Dougall, W.C.; Sullivan, J.K.; San Martin, J.; Dansey, R. Bench to bedside: Elucidation of the OPG-RANK-RANKL pathway and the development of denosumab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobacchi, C.; Menale, C.; Villa, A. The RANKL-RANK Axis: A Bone to Thymus Round Trip. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, Y.Y.; Yoshida, H.; Sarosi, I.; Tan, H.L.; Timms, E.; Capparelli, C.; Morony, S.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; Van, G.; Itie, A.; et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 1999, 397, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, M.; Reddy, S.; Berkman, N.; Cullen, K.; Middleton, J.C.; Nicholson, W.K.; Kahwati, L.C. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews. In Screening to Prevent Osteoporotic Fractures: An Evidence Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fontalis, A.; Kenanidis, E.; Prousali, E.; Potoupnis, M.; Tsiridis, E. Safety and efficacy of denosumab in osteoporotic patients previously treated with other medications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Crandall, C.J.; Ganz, D.A. Cost-effectiveness of denosumab versus oral alendronate for elderly osteoporotic women in Japan. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudoin, C.; Jean, S.; Bessette, L.; Ste-Marie, L.G.; Moore, L.; Brown, J.P. Denosumab compared to other treatments to prevent or treat osteoporosis in individuals at risk of fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samelson, E.J.; Miller, P.D.; Christiansen, C.; Daizadeh, N.S.; Grazette, L.; Anthony, M.S.; Egbuna, O.; Wang, A.; Siddhanti, S.R.; Cheung, A.M.; et al. RANKL inhibition with denosumab does not influence 3-year progression of aortic calcification or incidence of adverse cardiovascular events in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and high cardiovascular risk. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G.A.; Bone, H.G.; Fang, L.; Lee, E.; Padhi, D. A single-dose study of denosumab in patients with various degrees of renal impairment. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.A.; Ljunggren, O.; Stehman-Breen, C.; Cummings, S.R.; McClung, M.R.; Goemaere, S.; Ebeling, P.R.; Franek, E.; Yang, Y.C.; Egbuna, O.I.; et al. Effects of denosumab on fracture and bone mineral density by level of kidney function. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, T.R.; Flogaitis, I.; Moore, A.E.; Hampson, G. The effect of previous treatment with bisphosphonate and renal impairment on the response to denosumab in osteoporosis: A ‘real-life’ study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.L.; Chen, N.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chou, K.J.; Lee, P.T.; Fang, H.C.; Renn, J.H. An open-label, prospective pilot clinical study of denosumab for severe hyperparathyroidism in patients with low bone mass undergoing dialysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Festuccia, F.; Jafari, M.T.; Moioli, A.; Fofi, C.; Barberi, S.; Amendola, S.; Sciacchitano, S.; Punzo, G.; Mene, P. Safety and efficacy of denosumab in osteoporotic hemodialysed patients. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.A.; Nair, L.R.; Thomas, L.; Garla, V.; Palabindala, V.; Agarwal, M.; Fulop, T. Denosumab-Associated Severe Hypocalcemia in a Patient with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 355, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, B.B.; Davis, J.; Burns, K.D. Severe hypocalcemia following denosumab injection in a hemodialysis patient. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrosbree, J.E.; Elder, G.J.; Eisman, J.A.; Center, J.R. Acute hypocalcaemia following denosumab in heart and lung transplant patients with osteoporosis. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanmoku, K.; Shinzato, T.; Kubo, T.; Shimizu, T.; Yagisawa, T. Effects of denosumab on hypercalcemia and bone mineral density loss in kidney transplant recipients. Clin. Nephrol. 2019, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Acharya, P.; Aeddula, N.R.; Torres-Ortiz, A.; Bathini, T.; Sharma, K.; Ungprasert, P.; Watthanasuntorn, K.; Suarez, M.L.G.; Salim, S.A.; et al. Effects of denosumab on bone metabolism and bone mineral density in kidney transplant patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2019, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, H.; Ioannidis, G.; Lau, A.; Treleaven, D.; Gangji, A.; Ribic, C.; Wong-Pack, M.; Papaioannou, A.; Adachi, J.D. Correction to: Comparison of the clinical effectiveness and safety between the use of denosumab vs bisphosphonates in renal transplant patients. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobel, C.; Frey, D.; Graf, N.; Wuthrich, R.P.; Bonani, M. Follow-Up of Bone Mineral Density Changes in de novo Kidney Transplant Recipients Treated with Two Doses of the Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor kappaB Ligand Inhibitor Denosumab. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.; Chiang, C.Y.; Booth, J.; Mount, P.F. Hypocalcemia post denosumab in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 4–5. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, K.; Yajima, A.; Tsuchiya, K. Management of Osteoporosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 3271–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhanot, R.D.; Kaur, J.; Bhat, Z. Severe Hypocalcemia and Dramatic Increase in Parathyroid Hormone after Denosumab in a Dialysis Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2019, 2019, 3027419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, A.L.; Baker, S.T.; Stewardson, A.J.; Johnson, D.F. Denosumab-associated hypocalcaemia: Incidence, severity and patient characteristics in a tertiary hospital setting. Pharm. Drug Saf. 2016, 25, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, T.; Nakano, C. Is denosmab really effective and safe in the care of CKD-MBD? Clin. Calcium 2016, 26, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, D.M.; Rosen, C.J. Clinical Practice. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, D.P. Mining the complexities of the estrogen signaling pathways for novel therapeutics. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4237–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishani, A.; Blackwell, T.; Jamal, S.A.; Cummings, S.R.; Ensrud, K.E.; Investigators, M. The effect of raloxifene treatment in postmenopausal women with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghverdi, F.; Farbodara, T.; Mortaji, S.; Soltani, P.; Saidi, N. Effect of raloxifene on parathyroid hormone in osteopenic and osteoporotic postmenopausal women with chronic kidney disease stage 5. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 8, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, E.; Valera, R.; Alonzo, E.; Bajares-Lilue, M.; Carlini, R.; Capriles, F.; Martinis, R.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Weisinger, J.R. Effects of raloxifene on bone metabolism and serum lipids in postmenopausal women on chronic hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanchetta, J.R.; Bogado, C.E.; Ferretti, J.L.; Wang, O.; Wilson, M.G.; Sato, M.; Gaich, G.A.; Dalsky, G.P.; Myers, S.L. Effects of teriparatide [recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-34)] on cortical bone in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardella, T.J.; Juppner, H. Molecular properties of the PTH/PTHrP receptor. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 12, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodsman, A.B.; Bauer, D.C.; Dempster, D.W.; Dian, L.; Hanley, D.A.; Harris, S.T.; Kendler, D.L.; McClung, M.R.; Miller, P.D.; Olszynski, W.P.; et al. Parathyroid hormone and teriparatide for the treatment of osteoporosis: A review of the evidence and suggested guidelines for its use. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cejka, D.; Jager-Lansky, A.; Kieweg, H.; Weber, M.; Bieglmayer, C.; Haider, D.G.; Diarra, D.; Patsch, J.M.; Kainberger, F.; Bohle, B.; et al. Sclerostin serum levels correlate positively with bone mineral density and microarchitecture in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejka, D.; Herberth, J.; Branscum, A.J.; Fardo, D.W.; Monier-Faugere, M.C.; Diarra, D.; Haas, M.; Malluche, H.H. Sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 in renal osteodystrophy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, D.M.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Ensrud, K.E.; Greenspan, S.L.; Palermo, L.; Hue, T.; Lang, T.F.; McGowan, J.A.; Rosen, C.J.; PaTH Study Investigators. One year of alendronate after one year of parathyroid hormone (1-84) for osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, P.D.; Schwartz, E.N.; Chen, P.; Misurski, D.A.; Krege, J.H. Teriparatide in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and mild or moderate renal impairment. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, A.; Ishida, T.; Taketsuna, M.; Yoshiki, F.; Enomoto, H. Safety and effectiveness of daily teriparatide in a prospective observational study in patients with osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in Japan: Final report. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cejka, D.; Kodras, K.; Bader, T.; Haas, M. Treatment of Hemodialysis-Associated Adynamic Bone Disease with Teriparatide (PTH1-34): A Pilot Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcu, P.; Dion, N.; Ste-Marie, L.G.; Goltzman, D.; Radziunas, I.; Miller, P.D.; Jamal, S.A. Teriparatide and bone turnover and formation in a hemodialysis patient with low-turnover bone disease: A case report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamalis, P.; Economidou, D.; Dimitriadis, C.; Memmos, D.; Papagianni, A.; Efstratiadis, G. Treatment of adynamic bone disease in a haemodialysis patient with teriparatide. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.; Ubara, Y.; Hoshino, J.; Mise, K.; Hayami, N.; Suwabe, T.; Kawada, M.; Imafuku, A.; Hiramatsu, R.; Hasegawa, E.; et al. Once-weekly teriparatide in hemodialysis patients with hypoparathyroidism and low bone mass: A prospective study. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejka, D.; Benesch, T.; Krestan, C.; Roschger, P.; Klaushofer, K.; Pietschmann, P.; Haas, M. Effect of teriparatide on early bone loss after kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattersley, G.; Dean, T.; Corbin, B.A.; Bahar, H.; Gardella, T.J. Binding Selectivity of Abaloparatide for PTH-Type-1-Receptor Conformations and Effects on Downstream Signaling. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.D.; Hattersley, G.; Riis, B.J.; Williams, G.C.; Lau, E.; Russo, L.A.; Alexandersen, P.; Zerbini, C.A.; Hu, M.Y.; Harris, A.G.; et al. Effect of Abaloparatide vs. Placebo on New Vertebral Fractures in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leder, B.Z.; O’Dea, L.S.; Zanchetta, J.R.; Kumar, P.; Banks, K.; McKay, K.; Lyttle, C.R.; Hattersley, G. Effects of abaloparatide, a human parathyroid hormone-related peptide analog, on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk, B.; Smertka, M.; Chudek, J. Sclerostin: Intracellular mechanisms of action and its role in the pathogenesis of skeletal and vascular disorders. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClung, M.R.; Grauer, A.; Boonen, S.; Bolognese, M.A.; Brown, J.P.; Diez-Perez, A.; Langdahl, B.L.; Reginster, J.Y.; Zanchetta, J.R.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandeira, L.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Bilezikian, J.P. Romosozumab for the treatment of osteoporosis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, F.; Crittenden, D.B.; Adachi, J.D.; Binkley, N.; Czerwinski, E.; Ferrari, S.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Lau, E.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Miyauchi, A.; et al. Romosozumab Treatment in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, V.M.; Verhulst, A.; Babler, A.; D’Haese, P.C.; Evenepoel, P.; Kaesler, N. Sclerostin in chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder think first before you block it! Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factor | Main Effect | Category |
|---|---|---|
| ↓ Kloth | ↑ FGF-23 level [13] | Humoral |
| ↑ FGF-23 1 | ↑ phosphate excretion [14] ↓ calcitriol synthesis [14,15] | Humoral |
| ↑ Sclerostin | ↓ bone formation [14,16] ↑ osteoclastogenesis [17] | Humoral |
| ↑ dickkopf1 | ↓ bone formation [16,18] | Humoral |
| ↑ phosphate | ↑ SPTH 3 [19] ↓ calcitriol synthesis [20] | Mineral |
| ↑ uremic toxins 2 | ↓ PTH receptor [21] ↑ skeletal resistance to PTH [21] | Uremia |
| ↓ 1,25(OH)2 D | ↑ PTH secretion [20,22] ↓ calcium [23] | Humoral |
| ↓ calcium | ↑ SPTH [23] ↑ abnormal bone remodeling [23] | Mineral |
| ↑Skeletal resistance to PTH | ↑ SPTH [24] | Humoral |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186846
Hsu C-Y, Chen L-R, Chen K-H. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186846
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chia-Yu, Li-Ru Chen, and Kuo-Hu Chen. 2020. "Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186846
APA StyleHsu, C. -Y., Chen, L. -R., & Chen, K. -H. (2020). Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186846