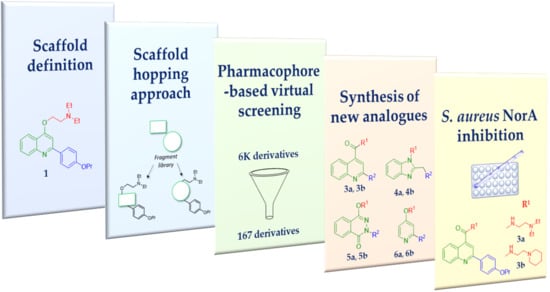
Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
In Silico Scaffold Hopping
3. Chemistry
4. Biological Results
5. Material and Methods
In Silico Scaffold Hopping
6. Chemistry
7. Bacterial Strains, Cell Lines, Culture Media and Antibiotics
8. EtBr Efflux
9. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assays
10. Cytotoxicity Assays
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance 2014; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakkeren, E.; Diard, M.; Hardt, W.-D. Evolutionary causes and consequences of bacterial antibiotic persistence. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, K.B.; Dolk, F.C.K.; Smith, D.R.M.; Robotham, J.V.; Smieszek, T. Actual versus ‘ideal’ antibiotic prescribing for common conditions in English primary care. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.R.; Shrivastava, P.S.; Ramasamy, J. World health organization releases global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. J. Med. Soc. 2018, 32, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roope, L.S.J.; Smith, R.D.; Pouwels, K.B.; Buchanan, J.; Abel, L.; Eibich, P.; Butler, C.C.; Tan, P.S.; Walker, A.S.; Robotham, J.V.; et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance: What economics can contribute. Science 2019, 364, eaau4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kresse, H.; Belsey, M.J.; Rovini, H. The antibacterial drugs market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, R.J.; Melander, C. The Challenge of Overcoming Antibiotic Resistance: An Adjuvant Approach? ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. Antibiotic resistance breakers: Can repurposed drugs fill the antibiotic discovery void? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic Adjuvants: Rescuing Antibiotics from Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Dastidar, S.G.; Fanning, S.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Molnár, J.; Pagès, J.-M.; Schelz, Z.; Spengler, G.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L. Potential role of non-antibiotics (helper compounds) in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections: Mechanisms for their direct and indirect activities. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schillaci, D.; Spanò, V.; Parrino, B.; Carbone, A.; Montalbano, A.; Barraja, P.; Diana, P.; Cirrincione, G.; Cascioferro, S. Pharmaceutical Approaches to Target Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8268–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; Van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saier, M.H. TCDB: The Transporter Classification Database for membrane transport protein analyses and information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D181–D186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neyfakh, A.; Borsch, C.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Fluoroquinolone resistance protein NorA of Staphylococcus aureus is a multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.-Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-Mediated Drug Resistance in Bacteria. Drugs 2004, 64, 159–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamut, A.; Mašič, L.P.; Kikelj, D.; Tomašič, T. Efflux pump inhibitors of clinically relevant multidrug resistant bacteria. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, S.; Buonerba, F.; Goracci, L.; Velilla, I.; Ruzziconi, R.; Schindler, B.D.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cruciani, G. Indole Based Weapons to Fight Antibiotic Resistance: A Structure–Activity Relationship Study. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 867–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonerba, F.; Lepri, S.; Goracci, L.; Schindler, B.D.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cruciani, G. Improved Potency of Indole-Based NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: From Serendipity toward Rational Design and Development. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 60, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hequet, A.; Burchak, O.N.; Jeanty, M.; Guinchard, X.; Le Pihive, E.; Maigre, L.; Bouhours, P.; Schneider, M.; Maurin, M.; Paris, J.-M.; et al. 1-(1H-Indol-3-yl) ethanamine derivatives as potent Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicetti, T.; Cannalire, R.; Pietrella, D.; Latacz, G.; Lubelska, A.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. 2-PhenylquinolineS. Aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: Evaluation of the Importance of Methoxy Group Introduction. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7827–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, T.; Mangiaterra, G.; Cannalire, R.; Cedraro, N.; Pietrella, D.; Astolfi, A.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, F.; Hequet, A.; Voisin-Chiret, A.S.; Bouillon, A.; Lesnard, A.; Cresteil, T.; Jolivalt, C.; Rault, S. First Identification of Boronic Species as Novel Potential Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2536–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, F.; Hequet, A.; Voisin-Chiret, A.S.; Bouillon, A.; Lesnard, A.; Cresteil, T.; Jolivalt, C.; Rault, S. Boronic species as promising inhibitors of the Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump: Study of 6-substituted pyridine-3-boronic acid derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, J.G.; Slotved, H.-C.; Mølgaard, P.; Olsen, C.E.; Christensen, S.B. Chalcone inhibitors of the NorA efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus whole cells and enriched everted membrane vesicles. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4514–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; A Khan, I.; Koul, S.; Taneja, S.C.; Ali, F.; Sharma, S.; Mirza, Z.M.; Sangwan, P.L.; Gupta, P.; Thota, N.; et al. Novel structural analogues of piperine as inhibitors of the NorA efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangwan, P.L.; Koul, J.L.; Koul, S.; Reddy, M.V.; Thota, N.; Khan, I.A.; Kumar, A.; Kalia, N.P.; Qazi, G.N. Piperine analogs as potent Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9847–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Gosetto, F.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Kaatz, G.W.; Patel, D.; Cecchetti, V. Evolution from a Natural Flavones Nucleus to Obtain 2-(4-Propoxyphenyl) quinoline Derivatives as potent inhibitors of the S. Aureus NorA Efflux Pump. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5722–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Seo, S.M. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in genetically related strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 2733–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astolfi, A.; Felicetti, T.; Iraci, N.; Manfroni, G.; Massari, S.; Pietrella, D.; Tabarrini, O.; Kaatz, G.W.; Barreca, M.L.; Sabatini, S.; et al. Pharmacophore-Based Repositioning of Approved Drugs as NovelStaphylococcus aureusNorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestwick Chemical. Available online: http://www.prestwickchemical.com/libraries-screening-lib-drug-frag.html (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: Core Hopping; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. Phase: A novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem. Boil. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: Phase; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Liao, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Ghaleb, H.; Huang, W.; et al. Phenylquinoline transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonists for the treatment of pain: Discovery of 1-(2-phenylquinoline-4-carbonyl)-N-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)pyrrolidine-3-carboxamide. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prime, M.E.; Courtney, S.M.; Brookfield, F.A.; Marston, R.W.; Walker, V.; Warne, J.; Boyd, A.E.; Kairies, N.A.; Von Der Saal, W.; Limberg, A.; et al. Phthalazinone Pyrazoles as Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitors of Aurora-A Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.; Bonnefous, C.; Govek, S.P.; Wu, D.; Pinkerton, A.B.; Kahraman, M.; Cook, T.; Noble, S.A.; Borchardt, A.J.; Prins, T. Heterocyclic Modulators of gpr119 for Treatment of Disease. Application No. PCT/US2009/061281, 20 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Augustin, J.; Rosenstein, R.; Wieland, B.; Schneider, U.; Schnell, N.; Engelke, G.; Entian, K.; Götz, F. Genetic analysis of epidermin biosynthetic genes and epidermin-negative mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis. JBIC J. Boil. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 204, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Greenwood, J.R.; Calkins, D.; Sullivan, A.; Shelley, J.C. Towards the comprehensive, rapid, and accurate prediction of the favorable tautomeric states of drug-like molecules in aqueous solution. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: Epik; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: QikProp; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Schrödinger Release 2017-2: MacroModel; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- M07-A10: Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 10th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015.
- Laudadio, E.; Cedraro, N.; Mangiaterra, G.; Citterio, B.; Mobbili, G.; Minnelli, C.; Bizzaro, D.; Biavasco, F.; Galeazzi, R. Natural Alkaloid Berberine Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexXY-Mediated Aminoglycoside Resistance: In Silico and in Vitro Studies. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, B.; Vaiasicca, S.; Mantovani, M.; Virgili, E.; Bonucci, M.; Ferri, I.H. Bioactive Immunomodulatory Compounds: A Novel Combinatorial Strategy for Integrated Medicine in Oncology? BAIC Exposure in Cancer Cells. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| S. aureus Strains | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compd. | SA-1199 | SA-1199B |
| 3a | 25 | 25 |
| 3b | >50 | 50 |
| 4a | >50 | >50 |
| 4b | >50 | >50 |
| 5a | >50 | >50 |
| 5b | >50 | >50 |
| 6a | 50 | >50 |
| 6b | 50 | 25 |
| 1 | 50 | 25 |
| CPX | 0.16 | 5 |
| Compd. | EtBr Efflux Inhibition (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 50 µM | 10 µM | |
| 3a | 98.1 | 56.6 |
| 3b | 96.4 | 66.2 |
| 4a | 74.5 | 35.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cannalire, R.; Mangiaterra, G.; Felicetti, T.; Astolfi, A.; Cedraro, N.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Vaiasicca, S.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197037
Cannalire R, Mangiaterra G, Felicetti T, Astolfi A, Cedraro N, Massari S, Manfroni G, Tabarrini O, Vaiasicca S, Barreca ML, et al. Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197037
Chicago/Turabian StyleCannalire, Rolando, Gianmarco Mangiaterra, Tommaso Felicetti, Andrea Astolfi, Nicholas Cedraro, Serena Massari, Giuseppe Manfroni, Oriana Tabarrini, Salvatore Vaiasicca, Maria Letizia Barreca, and et al. 2020. "Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197037
APA StyleCannalire, R., Mangiaterra, G., Felicetti, T., Astolfi, A., Cedraro, N., Massari, S., Manfroni, G., Tabarrini, O., Vaiasicca, S., Barreca, M. L., Cecchetti, V., Biavasco, F., & Sabatini, S. (2020). Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197037