N-Butylidenephthalide Inhibits the Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs through Activation of AMPK and Prevents Stenosis in an Arteriovenous Fistula Rat Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
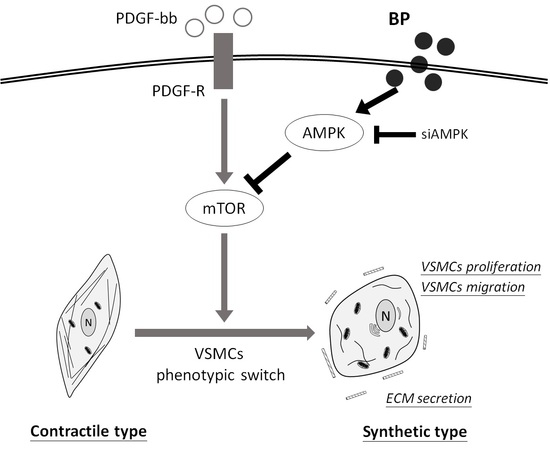
2.1. n-Butylidenephthalide (BP) Inhibited the PDGF-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells’ (VSMCs’) Phenotypic Switch
2.2. BP Inhibited the Functional Characteristics of the Synthetic VSMCs
2.3. BP Inhibited Thrombosis, Neointimal Hyperplasia and Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs in an Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) Rat Model
2.4. BP Inhibited the PDGF-Induced VSMCs’ Phenotypic Switch through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Axis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. Migration Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Transient Transfection of siRNA
4.8. Animal Model
4.9. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | N-butylidenephthalide |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| AMPK | 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| AVF | Arteriovenous fistula |
References
- Rensen, S.S.; Doevendans, P.A.; van Eys, G.J. Regulation and characteristics of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic diversity. Neth. Heart J. 2007, 15, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, K.A.; Merenick, B.L.; Ding, M.; Fetalvero, K.M.; Rzucidlo, E.M.; Kozul, C.D.; Brown, D.J.; Chiu, H.Y.; Shyu, M.; Drapeau, B.L.; et al. Rapamycin promotes vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation through insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt2 feedback signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36112–36120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halka, A.T.; Turner, N.J.; Carter, A.; Ghosh, J.; Murphy, M.O.; Kirton, J.P.; Kielty, C.M.; Walker, M.G. The effects of stretch on vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in vitro. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2008, 17, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.M.; Chen, W.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Ouyang, C.H. Antiplatelet effect of butylidenephthalide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 924, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Choi, A.O.; Jones, R.L.; Lin, G. Mechanisms underlying the vasorelaxing effects of butylidenephthalide, an active constituent of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 537, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.S.; Lin, P.C.; Chang, L.F.; Harn, H.J.; Shiuan, D.; Chiou, T.W.; Jeng, J.R. Inhibitory effect of n-butylidenephthalide on neointimal hyperplasia in balloon injured rat carotid artery. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjobsted, R.; Hingst, J.R.; Fentz, J.; Foretz, M.; Sanz, M.N.; Pehmoller, C.; Shum, M.; Marette, A.; Mounier, R.; Treebak, J.T.; et al. AMPK in skeletal muscle function and metabolism. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1741–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, K.W.; Yin, S.C.; Ting, C.T.; Lin, S.J.; Hsueh, C.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.L. Berberine inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced growth and migration partly through an AMPK-dependent pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairaq, A.; Shawky, N.M.; Osman, I.; Pichavaram, P.; Segar, L. AdipoRon, an adiponectin receptor agonist, attenuates PDGF-induced VSMC proliferation through inhibition of mTOR signaling independent of AMPK: Implications toward suppression of neointimal hyperplasia. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, J.D.; Narine, A.; Shaver, P.R.; Fox, J.C.; Vuncannon, J.R.; Tulis, D.A. AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration and vascular remodeling following injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H369–H381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, J.Y.; Choi, H.C. Metformin-induced AMP-activated protein kinase activation regulates phenylephrine-mediated contraction of rat aorta. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkower, K.I.; Herber, R.L. Cell migration and invasion assays as tools for drug discovery. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lok, C.E.; Huber, T.S.; Lee, T.; Shenoy, S.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Abreo, K.; Allon, M.; Asif, A.; Astor, B.C.; Glickman, M.H.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Vascular Access: 2019 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, S1–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Song, P.; Okon, I.S.; Xiao, L.; Zou, M.H. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Alpha 2 Deletion Induces VSMC Phenotypic Switching and Reduces Features of Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, K.A.; Rzucidlo, E.M.; Merenick, B.L.; Fingar, D.C.; Brown, D.J.; Wagner, R.J.; Powell, R.J. The mTOR/p70 S6K1 pathway regulates vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C507–C517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salabei, J.K.; Cummins, T.D.; Singh, M.; Jones, S.P.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hill, B.G. PDGF-mediated autophagy regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype and resistance to oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2013, 451, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, J.M.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Jin, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Song, S.H.; Shin, H.K.; Bae, S.S. Platelet-derived growth factor regulates vascular smooth muscle phenotype via mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.J.; Martin, K.A.; Powell, R.J.; Rzucidlo, E.M. Lovastatin induces VSMC differentiation through inhibition of Rheb and mTOR. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C119–C127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, B. Regulation of autophagy by Ca2+. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decuypere, J.P.; Kindt, D.; Luyten, T.; Welkenhuyzen, K.; Missiaen, L.; De Smedt, H.; Bultynck, G.; Parys, J.B. mTOR-Controlled Autophagy Requires Intracellular Ca2+ Signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e610020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croatt, A.J.; Grande, J.P.; Hernandez, M.C.; Ackerman, A.W.; Katusic, Z.S.; Nath, K.A. Characterization of a model of an arteriovenous fistula in the rat: The effect of L-NAME. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2530–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.-H.; Xu, Y.-X.; Chen, J.-Y.; Harn, H.-J.; Chiou, T.-W. N-Butylidenephthalide Inhibits the Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs through Activation of AMPK and Prevents Stenosis in an Arteriovenous Fistula Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197403
Yang H-H, Xu Y-X, Chen J-Y, Harn H-J, Chiou T-W. N-Butylidenephthalide Inhibits the Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs through Activation of AMPK and Prevents Stenosis in an Arteriovenous Fistula Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197403
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hsin-Han, Yue-Xuan Xu, Jie-Yi Chen, Horng-Jyh Harn, and Tzyy-Wen Chiou. 2020. "N-Butylidenephthalide Inhibits the Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs through Activation of AMPK and Prevents Stenosis in an Arteriovenous Fistula Rat Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197403
APA StyleYang, H. -H., Xu, Y. -X., Chen, J. -Y., Harn, H. -J., & Chiou, T. -W. (2020). N-Butylidenephthalide Inhibits the Phenotypic Switch of VSMCs through Activation of AMPK and Prevents Stenosis in an Arteriovenous Fistula Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197403