Acid Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI Is Unsuitable for the Functional Assays That Require Long-Term Culture of Basophils and Entire Removal of Surface IgE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FcɛRI on Basophils Are Almost Saturated with IgE
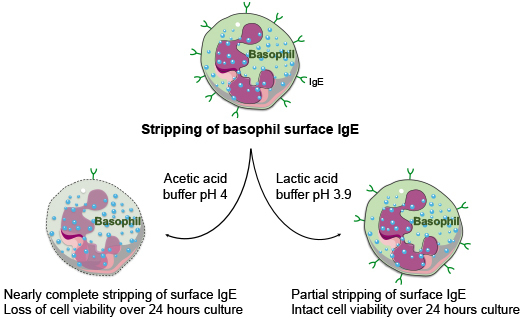
2.2. Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI of Basophils by Acetic Acid Buffer (pH 4)
2.3. Response of the IgE Stripped Human Peripheral Blood Basophils to IL-3 Stimulation
2.4. Effect of Lactic Acid on the Elution of IgE and the Activation of Basophils
2.5. Acetic Acid Buffer (pH 4) and Lactic Acid Differentially Affect the Viability of Basophils Cultured in the Presence of IL-3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Basophils from the Blood
4.2. Acid Stripping of IgE and Culture of Basophils
4.3. Binding of Exogenous IgE to Basophils
4.4. Analyses of Phenotype of Basophils
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAFF | B cell activating factor |
| CNBr | Cyanogen bromide |
| FcεRI | Type I high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor |
| FVD | Fixable viable dye |
| HSA | Human Serum Albumin |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| TSLP | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
References
- Karasuyama, H.; Miyake, K.; Yoshikawa, S.; Yamanishi, Y. Multifaceted roles of basophils in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voehringer, D. Protective and pathological roles of mast cells and basophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Bayry, J. Autoimmunity: Basophils in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, J.T. Basophils: Emerging roles in the pathogenesis of allergic disease. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaveri, S.V.; Mouthon, L.; Bayry, J. Basophils and nephritis in lupus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, N.; Hardwick, D.; Daugas, E.; Illei, G.G.; Rivera, J. Basophils and the T helper 2 environment can promote the development of lupus nephritis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellefigues, C.; Dema, B.; Lamri, Y.; Saidoune, F.; Chavarot, N.; Loheac, C.; Pacreau, E.; Dussiot, M.; Bidault, C.; Marquet, F.; et al. Prostaglandin D2 amplifies lupus disease through basophil accumulation in lymphoid organs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balam, S.; Schiechl-Brachner, G.; Buchtler, S.; Halbritter, D.; Schmidbauer, K.; Talke, Y.; Neumayer, S.; Salewski, J.N.; Winter, F.; Karasuyama, H.; et al. IL-3 Triggers Chronic Rejection of Cardiac Allografts by Activation of Infiltrating Basophils. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3514–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, B.J.; Davies, A.M.; Bax, H.J.; Karagiannis, S.N. IgE Antibodies: From Structure to Function and Clinical Translation. Antibodies 2019, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henault, J.; Riggs, J.M.; Karnell, J.L.; Liarski, V.M.; Li, J.; Shirinian, L.; Xu, L.; Casey, K.A.; Smith, M.A.; Khatry, D.B.; et al. Self-reactive IgE exacerbates interferon responses associated with autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayry, J. Lupus pathogenesis: Role of IgE autoantibodies. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasser, P.; Eggel, A. Targeting IgE in allergic disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 54, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritter, C.; Battig, M.; Kraemer, R.; Stadler, B.M. IgE hidden in immune complexes with anti-IgE autoantibodies in children with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 88, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.C.; Ramadani, F.; Santos, A.F.; Pillai, P.; Ohm-Laursen, L.; Harper, C.E.; Fang, C.; Dodev, T.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Ying, S.; et al. “Auto-anti-IgE”: Naturally occurring IgG anti-IgE antibodies may inhibit allergen-induced basophil activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacGlashan, D. Autoantibodies to IgE and FcεRI and the natural variability of spleen tyrosine kinase expression in basophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiebiger, E.; Maurer, D.; Holub, H.; Reininger, B.; Hartmann, G.; Woisetschläger, M.; Kinet, J.P.; Stingl, G. Serum IgG autoantibodies directed against the alpha chain of FcεRI: A selective marker and pathogenetic factor for a distinct subset of chronic urticaria patients? J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.P.; Pachlopnik, J.M.; Vogel, M.; Dahinden, M.; Wurm, F.; Stadler, B.M.; Miescher, S.M. Conditional autoimmunity mediated by human natural anti-FcεRIalpha autoantibodies? FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, C.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Karnam, A.; Das, M.; Gilardin, L.; Maddur, M.S.; Wymann, S.; Vonarburg, C.; Chevailler, A.; Dimitrov, J.D.; et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin induces IL-4 in human basophils by signaling through surface-bound IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galeotti, C.; Karnam, A.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Chevailler, A.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Anti-IgE IgG autoantibodies isolated from therapeutic normal IgG intravenous immunoglobulin induce basophil activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, C.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. IVIG-mediated effector functions in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, F.; Powell-Richards, A. Elucidation of the epitope locations of human autoanti-IgE: Recognition of two epitopes located within the C epsilon 2 and the C epsilon 4 domains. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1991, 95, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malveaux, F.J.; Conroy, M.C.; Adkinson, N.F., Jr.; Lichtenstein, L.M. IgE receptors on human basophils. Relationship to serum IgE concentration. J. Clin. Investig. 1978, 62, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruzansky, J.J.; Grammer, L.C.; Patterson, R.; Roberts, M. Dissociation of IgE from receptors on human basophils. I. Enhanced passive sensitization for histamine release. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, R.; Forsythe, P.A.; Rankin, J.A.; Boyars, M.C.; Lett-Brown, M.A.; Grant, J.A. Sensitivity of basophils to histamine releasing factor(s) of various origin: Dependency on allergic phenotype of the donor and surface-bound IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hide, M.; Francis, D.M.; Grattan, C.E.; Hakimi, J.; Kochan, J.P.; Greaves, M.W. Autoantibodies against the high-affinity IgE receptor as a cause of histamine release in chronic urticaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hide, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamura, Y.; Koro, O.; Yamamoto, S. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity against human sweat antigen in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2002, 82, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greer, A.M.; Wu, N.; Putnam, A.L.; Woodruff, P.G.; Wolters, P.; Kinet, J.P.; Shin, J.S. Serum IgE clearance is facilitated by human FcepsilonRI internalization. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanase, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, A.; Iwamoto, K.; Takahagi, S.; Hide, M. Activation of Human Peripheral Basophils in Response to High IgE Antibody Concentrations without Antigens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacGlashan, D.W., Jr. Releasability of human basophils: Cellular sensitivity and maximal histamine release are independent variables. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 91, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, L.A.; Schuyler, M.; Wilson, B.S.; Oliver, J.M. Roles for the high affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI, of human basophils in the pathogenesis and therapy of allergic asthma: Disease promotion, protection or both? Open Allergy J. 2010, 3, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voehringer, D. Basophil modulation by cytokine instruction. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Kim, S.; Do, J.S.; Wang, L.; Lantz, C.; Urban, J.F.; Le Gros, G.; Min, B. T cell-derived IL-3 plays key role in parasite infection-induced basophil production but is dispensable for in vivo basophil survival. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, B.M.; Liang, H.E.; Bando, J.K.; Wu, D.; Cheng, L.E.; McKerrow, J.K.; Allen, C.D.; Locksley, R.M. Genetic analysis of basophil function in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Das, M.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Galeotti, C.; Karnam, A.; Maddur, M.S.; Bruneval, P.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Regulatory T cells induce activation rather than suppression of human basophils. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaan0829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Hener, P.; Michea, P.; Karasuyama, H.; Chan, S.; Soumelis, V.; Li, M. Skin thymic stromal lymphopoietin initiates Th2 responses through an orchestrated immune cascade. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, T.; Galli, S.J. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Karsan, A.; Duronio, V.; Chu, F.; Walker, D.C.; Bai, T.R.; Schellenberg, R.R. Interleukin-3, but not granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-5, inhibits apoptosis of human basophils through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: Requirement of NF-κB-dependent and -independent pathways. Immunology 2002, 107, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, C.; Yamaguchi, M.; Iikura, M.; Izumi, S.; Kudo, K.; Nagase, H.; Ishii, A.; Walls, A.F.; Ra, C.; Iwata, T.; et al. Activation markers of human basophils: CD69 expression is strongly and preferentially induced by IL-3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redrup, A.C.; Howard, B.P.; MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Lichtenstein, L.M.; Schroeder, J.T. Differential regulation of IL-4 and IL-13 secretion by human basophils: Their relationship to histamine release in mixed leukocyte cultures. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Didichenko, S.A.; Spiegl, N.; Brunner, T.; Dahinden, C.A. IL-3 induces a Pim1-dependent antiapoptotic pathway in primary human basophils. Blood 2008, 112, 3949–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephen-Victor, E.; Das, M.; Sharma, M.; Galeotti, C.; Fohrer-Ting, H.; Sendid, B.; Darnige, L.; Terris, B.; Badoual, C.; Bruneval, P.; et al. Demystification of enigma on antigen-presenting cell features of human basophils: Data from secondary lymphoid organs. Haematologica 2017, 102, e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salabert-Le Guen, N.; Hemont, C.; Delbove, A.; Poli, C.; Braudeau, C.; Fantou, A.; Amouriaux, K.; Beriou, G.; Martin, J.C.; Colas, L.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin does not activate human basophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salter, B.M.; Oliveria, J.P.; Nusca, G.; Smith, S.G.; Watson, R.M.; Comeau, M.; Sehmi, R.; Gauvreau, G.M. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activation of basophils in patients with allergic asthma is IL-3 dependent. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, I.; Nawata, Y.; Koike, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tomioka, H.; Yoshida, S. Relationship between anti-IgE autoantibody and severity of bronchial asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1989, 90, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, W.; Stadler, B.M.; Schopf, E.; Kapp, A. IgE autoantibodies in atopic dermatitis—Occurrence of different antibodies against the CH3 and the CH4 epitopes of IgE. Allergy 1995, 50, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawata, Y.; Koike, T.; Yanagisawa, T.; Iwamoto, I.; Itaya, T.; Yoshida, S.; Tomioka, H. Anti-IgE autoantibody in patients with bronchial asthma. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1984, 58, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Izaki, S.; Toyoshima, S.; Endo, T.; Kanegae, K.; Nunomura, S.; Kashiwakura, J.I.; Sasaki-Sakamoto, T.; Nakamura, R.; Akiyama, H.; Ra, C.; et al. Differentiation between control subjects and patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria based on the ability of anti-IgE autoantibodies (AAbs) to induce FcεRI crosslinking, as compared to anti-FcεRIα AAbs. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, F.; Smith, S.J. In vitro basophil histamine-releasing activity of circulating IgG1 and IgG4 autoanti-IgE antibodies from asthma patients and the demonstration that anti-IgE modulates allergen-induced basophil activation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1994, 24, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B.L.; Kaufman, L.D.; Marchese, M.J.; Roth, W.; Kaplan, A.P. Anti-IgE autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Prevalence and biologic activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, J.A.; Wilson, P.B.; Dore, P.; Pumphrey, R.S. Evidence for circulating complexes containing IgE in patients with atopic dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1985, 76, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passante, E.; Frankish, N. The RBL-2H3 cell line: Its provenance and suitability as a model for the mast cell. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, T.; Huang, R.; Aveskogh, M.; Nilsson, K.; Hellman, L. Phenotypic characterization of KU812, a cell line identified as an immature human basophilic leukocyte. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, C.G.; Haard, J.; Matsson, P.; Karlsson, T.; Nilsson, K.; Johansson, S.G. Demonstration of specific high-affinity Fc epsilon-receptors on the human basophil-like leukemia cell line KU812 by flow cytometry. Allergy 1995, 50, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaka, T.; Ishizaka, K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. IV. Dissociation of IgE molecules from basophil receptors at acid pH. J. Immunol. 1974, 112, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galeotti, C.; Karnam, A.; Das, M.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Acid Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI Is Unsuitable for the Functional Assays That Require Long-Term Culture of Basophils and Entire Removal of Surface IgE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020510
Galeotti C, Karnam A, Das M, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Acid Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI Is Unsuitable for the Functional Assays That Require Long-Term Culture of Basophils and Entire Removal of Surface IgE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(2):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020510
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaleotti, Caroline, Anupama Karnam, Mrinmoy Das, Srini V. Kaveri, and Jagadeesh Bayry. 2020. "Acid Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI Is Unsuitable for the Functional Assays That Require Long-Term Culture of Basophils and Entire Removal of Surface IgE" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 2: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020510
APA StyleGaleotti, C., Karnam, A., Das, M., Kaveri, S. V., & Bayry, J. (2020). Acid Stripping of Surface IgE Antibodies Bound to FcεRI Is Unsuitable for the Functional Assays That Require Long-Term Culture of Basophils and Entire Removal of Surface IgE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(2), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020510