Structural Perspectives on the Mechanism of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Domain Architecture of sGC
3. Activity Profile of sGC
4. Crystal Structures of Individual sGC Domains
4.1. The H-NOX Domain
4.2. The PAS and CC Domains
4.3. The CAT Domain
5. Low-Resolution Structures of Full-Length sGC
6. High-Resolution Cryo-EM Structures of Full-Length sGC
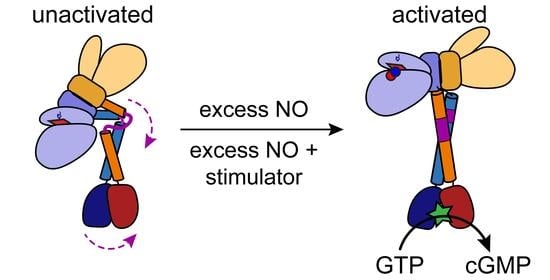
6.1. General Architecture of Full-Length sGC in the Unactivated and Activated States
6.2. The α H-NOX Domain
6.3. The β H-NOX Domain
6.4. The PAS Domains
6.5. The CC Domains
6.6. The CAT Domains
7. Insight into the 1-NO State from Small Angle X-Ray Scattering
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, W.P.; Mittal, C.K.; Katsuki, S.; Murad, F. Nitric Oxide Activates Guanylate Cyclase and Increases Guanosine 3ʹ:5ʹ-Cyclic Monophosphate Levels in Various Tissue Preparations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3203–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohlen, H.G. Nitric Oxide and the Cardiovascular System. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 803–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, J.R.; Chernova, T.; Forsythe, I.D. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Brain Function, Dysfunction, and Dementia. Neuroscientist 2010, 16, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buys, E.; Sips, P. New Insights into the Role of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase in Blood Pressure Regulation. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasch, J.P.; Pacher, P.; Evgenov, O.V. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase as an Emerging Therapeutic Target in Cardiopulmonary Disease. Circulation 2011, 123, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Aissa, M.; Lee, S.H.; Bennett, B.M.; Thatcher, G.R.J. Targeting NO/cGMP Signaling in the CNS for Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2770–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Koziol-White, C.J.; Asosingh, K.; Cheng, G.; Ruple, L.; Groneberg, D.; Friebe, A.; Comhair, S.A.A.; Stasch, J.-P.; Panettieri, R.A.; et al. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase as an Alternative Target for Bronchodilator Therapy in Asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2355–E2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papapetropoulos, A.; Simoes, D.C.M.; Xanthou, G.; Roussos, C.; Gratziou, C. Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Expression Is Reduced in Allergic Asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L179–L184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conole, D.; Scott, L.J. Riociguat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2013, 73, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, B.G.; Marletta, M.A. Physiological Activation and Deactivation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Nitric Oxide 2018, 77, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, B.; Humbert, P.; Harteneck, C.; Foerster, J.; Malkewitz, J.; Bohme, E.; Schultz, G.; Koesling, D. Mutation of His-105 in the β1 Subunit Yields a Nitric Oxide-Insensitive Form of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2592–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Marletta, M.A. Localization of the Heme Binding Region in Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 15959–15964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Schelvis, J.P.M.; Babcock, G.T.; Marletta, M.A. Identification of Histidine 105 in the β1 Subunit of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase as the Heme Proximal Ligand. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 4502–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koglin, M.; Behrends, S. A Functional Domain of the α1 Subunit of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Is Necessary for Activation of the Enzyme by Nitric Oxide and YC-1 but Is Not Involved in Heme Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12590–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Möglich, A.; Ayers, R.A.; Moffat, K. Structure and Signaling Mechanism of Per-ARNT-Sim Domains. Structure 2009, 17, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Truebestein, L.; Leonard, T.A. Coiled-coils: The Long and Short of It. BioEssays 2016, 38, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, J.M.; Arndt, K.M. Coiled Coil Domains: Stability, Specificity, and Biological Implications. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winger, J.A.; Marletta, M.A. Expression and Characterization of the Catalytic Domains of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase: Interaction with the Heme Domain. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 4083–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, A.; Leipelt, M.; Russwurm, M.; Steegborn, C. Crystal Structure of the Guanylyl Cyclase Cya2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15720–15725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winger, J.A.; Derbyshire, E.R.; Lamers, M.H.; Marletta, M.A.; Kuriyan, J. The Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of a Eukaryotic Guanylate Cyclase. BMC Struct. Biol. 2008, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allerston, C.K.; von Delft, F.; Gileadi, O. Crystal Structures of the Catalytic Domain of Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeger, F.; Quintyn, R.; Tanimoto, A.; Williams, G.J.; Tainer, J.A.; Wysocki, V.H.; Garcin, E.D. Interfacial Residues Promote an Optimal Alignment of the Catalytic Center in Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase: Heterodimerization Is Required but Not Sufficient for Activity. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, S.P.L.; Winger, J.A.; Marletta, M.A. Tonic and Acute Nitric Oxide Signaling through Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Is Mediated by Nonheme Nitric Oxide, ATP, and GTP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13064–13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derbyshire, E.R.; Fernhoff, N.B.; Deng, S.; Marletta, M.A. Nucleotide Regulation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Substrate Specificity. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7519–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sürmeli, N.B.; Müskens, F.M.; Marletta, M.A. The Influence of Nitric Oxide on Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Regulation by Nucleotides: Role of the Pseudosymmetric Site. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15570–15580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russwurm, M.; Koesling, D. NO Activation of Guanylyl Cyclase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4443–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernhoff, N.B.; Derbyshire, E.R.; Marletta, M.A. A Nitric Oxide/Cysteine Interaction Mediates the Activation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21602–21607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keefer, L.K.; Nims, R.W.; Davies, K.M.; Wink, D.A. “NONOates” (1-Substituted Diazen-1-Ium-1,2-Diolates) as Nitric Oxide Donors: Convenient Nitric Oxide Dosage Forms. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 268, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzer, R.; Böhme, E.; Hofmann, F.; Schultz, G. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Purified from Bovine Lung Contains Heme and Copper. FEBS Lett. 1981, 132, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, J.R.; Marletta, M.A. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase from Bovine Lung: Activation with Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide and Spectral Characterization of the Ferrous and Ferric States. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5636–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.-N.; Wu, C.-C.; Kuo, S.-C.; Lee, F.-Y.; Teng, C.-M. YC-1, A Novel Activator of Platelet Guanylate Cyclase. Blood 1994, 84, 4226–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasch, J.-P.; Becker, E.M.; Alonso-Alija, C.; Apeler, H.; Dembowsky, K.; Feurer, A.; Gerzer, R.; Minuth, T.; Perzborn, E.; Pleiß, U.; et al. NO-Independent Regulatory Site on Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Nature 2001, 410, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, T.; Perl, N.R.; Barden, T.C.; Carvalho, A.; Fretzen, A.; Germano, P.; Im, G.-Y.J.; Jin, H.; Kim, C.; Lee, T.W.-H.; et al. Discovery of IWP-051, a Novel Orally Bioavailable sGC Stimulator with Once-Daily Dosing Potential in Humans. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobin, J.V.; Zimmer, D.P.; Shea, C.; Germano, P.; Bernier, S.G.; Liu, G.; Long, K.; Miyashiro, J.; Ranganath, S.; Jacobson, S.; et al. Pharmacological Characterization of IW-1973, a Novel Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulator with Extensive Tissue Distribution, Antihypertensive, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antifibrotic Effects in Preclinical Models of Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 365, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buys, E.S.; Zimmer, D.P.; Chickering, J.; Graul, R.; Chien, Y.T.; Profy, A.; Hadcock, J.R.; Masferrer, J.L.; Milne, G.T. Discovery and Development of next Generation sGC Stimulators with Diverse Multidimensional Pharmacology and Broad Therapeutic Potential. Nitric Oxide 2018, 78, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, A.; Schultz, G.; Koesling, D. Sensitizing Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase to Become a Highly CO-Sensitive Enzyme. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 6863–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.N.; Garthwaite, J. What Is the Real Physiological NO Concentration in Vivo? Nitric Oxide 2009, 21, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Brandish, P.E.; Ballou, D.P.; Marletta, M.A. A Molecular Basis for Nitric Oxide Sensing by Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14753–14758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, K.; Schrammel, A.; Koesling, D.; Mayer, B. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Synergistic Activation of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase by YC-1 and Nitric Oxide in Endothelial Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, L.M.; Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L. Ancient Conserved Domains Shared by Animal Soluble Guanylyl Cyclases and Bacterial Signaling Proteins. BMC Genom. 2003, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plate, L.; Marletta, M.A. Nitric Oxide-Sensing H-NOX Proteins Govern Bacterial Communal Behavior. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karow, D.S.; Pan, D.; Tran, R.; Pellicena, P.; Presley, A.; Mathies, R.A.; Marletta, M.A. Spectroscopic Characterization of the Soluble Guanylate Cyclase-like Heme Domains from Vibrio Cholerae and Thermoanaerobacter Tengcongensis. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 10203–10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicena, P.; Karow, D.S.; Boon, E.M.; Marletta, M.A.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal Structure of an Oxygen-Binding Heme Domain Related to Soluble Guanylate Cyclases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12854–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nioche, P.; Berka, V.; Vipond, J.; Minton, N.; Tsai, A.-L.; Raman, C.S. Femtomolar Sensitivity of a NO Sensor from Clostridium Botulinum. Science 2004, 306, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzik, M.A.; Jonnalagadda, R.; Kuriyan, J.; Marletta, M.A. Structural Insights into the Role of Iron–Histidine Bond Cleavage in Nitric Oxide-Induced Activation of H-NOX Gas Sensor Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4156–E4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hespen, C.W.; Bruegger, J.J.; Phillips-Piro, C.M.; Marletta, M.A. Structural and Functional Evidence Indicates Selective Oxygen Signaling in Caldanaerobacter Subterraneus H-NOX. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hespen, C.W.; Bruegger, J.J.; Guo, Y.; Marletta, M.A. Native Alanine Substitution in the Glycine Hinge Modulates Conformational Flexibility of Heme Nitric Oxide/Oxygen (H-NOX) Sensing Proteins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Suess, D.L.M.; Herzik, M.A.; Iavarone, A.T.; Britt, R.D.; Marletta, M.A. Regulation of Nitric Oxide Signaling by Formation of a Distal Receptor–Ligand Complex. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nambu, J.R.; Lewis, J.O.; Wharton, K.A.; Crews, S.T. The Drosophila Single-Minded Gene Encodes a Helix-Loop-Helix Protein That Acts as a Master Regulator of CNS Midline Development. Cell 1991, 67, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The Protein Families Database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sayed, N.; Baskaran, P.; Beuve, A.; van den Akker, F. PAS-Mediated Dimerization of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Revealed by Signal Transduction Histidine Kinase Domain Crystal Structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Key, J.; Hefti, M.; Purcell, E.B.; Moffat, K. Structure of the Redox Sensor Domain of Azotobacter Vinelandii NifL at Atomic Resolution: Signaling, Dimerization, and Mechanism. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3614–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, R.; Weichsel, A.; Montfort, W.R. Crystal Structure of the Alpha Subunit PAS Domain from Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Underbakke, E.S.; Iavarone, A.T.; Chalmers, M.J.; Pascal, B.D.; Novick, S.; Griffin, P.R.; Marletta, M.A. Nitric Oxide-Induced Conformational Changes in Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Structure 2014, 22, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Beuve, A.; van den Akker, F. Crystal Structure of the Signaling Helix Coiled-Coil Domain of the β1 Subunit of the Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase. BMC Struct. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, B.G.; Roberts, S.A.; Ahmed, A.; Breci, L.; Li, W.; Weichsel, A.; Brailey, J.L.; Wysocki, V.H.; Tama, F.; Montfort, W.R. Molecular Model of a Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Fragment Determined by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering and Chemical Cross-Linking. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 1568–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Ruoho, A.E.; Hurley, J.H. Structure of the Adenylyl Cyclase Catalytic Core. Nature 1997, 386, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, J.J.G.; Sunahara, R.K.; Gilman, A.G.; Sprang, S.R. Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domains of Adenylyl Cyclase in a Complex with Gsα·GTPγS. Science 1997, 278, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesmer, J.J.G.; Sunahara, R.K.; Johnson, R.A.; Gosselin, G.; Gilman, A.G.; Sprang, S.R. Two-Metal-Ion Catalysis in Adenylyl Cyclase. Science 1999, 285, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ruoho, A.E.; Rao, V.D.; Hurley, J.H. Catalytic Mechanism of the Adenylyl and Guanylyl Cyclases: Modeling and Mutational Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13414–13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunahara, R.K.; Beuve, A.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Sprang, S.R.; Garbers, D.L.; Gilman, A.G. Exchange of Substrate and Inhibitor Specificities between Adenylyl and Guanylyl Cyclases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16332–16338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, M.G.; Underbakke, E.S.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; Marletta, M.A. Single-Particle EM Reveals the Higher-Order Domain Architecture of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2960–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kühlbrandt, W. The Resolution Revolution. Science 2014, 343, 1443–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, B.G.; Yokom, A.L.; Rosenberg, D.J.; Morris, K.L.; Hammel, M.; Hurley, J.H.; Marletta, M.A. Allosteric Activation of the Nitric Oxide Receptor Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Mapped by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. eLife 2019, 8, e50634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.-X.; Chen, L. Structural Insights into the Mechanism of Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Nature 2019, 574, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Murata, L.B.; Weichsel, A.; Brailey, J.L.; Roberts, S.A.; Nighorn, A.; Montfort, W.R. Allostery in Recombinant Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase from Manduca sexta. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 20968–20977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabel, U.; Weeger, M.; La, M.; Schmidt, H.H.H.W. Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase: Functional Expression and Revised Isoenzyme Family. Biochem. J. 1998, 335, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haase, T.; Haase, N.; Kraehling, J.R.; Behrends, S. Fluorescent Fusion Proteins of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Indicate Proximity of the Heme Nitric Oxide Domain and Catalytic Domain. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, P.; Heckler, E.J.; van den Akker, F.; Beuve, A. Identification of Residues in the Heme Domain of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase That Are Important for Basal and Stimulated Catalytic Activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underbakke, E.S.; Iavarone, A.T.; Marletta, M.A. Higher-Order Interactions Bridge the Nitric Oxide Receptor and Catalytic Domains of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6777–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denninger, J.W.; Schelvis, J.P.M.; Brandish, P.E.; Zhao, Y.; Babcock, G.T.; Marletta, M.A. Interaction of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase with YC-1: Kinetic and Resonance Raman Studies. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 4191–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisburger, S.P.; Thomas, W.C.; Watkins, M.B.; Ando, N. X-Ray Scattering Studies of Protein Structural Dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7615–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, E.D.; Bepler, T.; Berger, B.; Davis, J.H. CryoDRGN: Reconstruction of Heterogeneous Cryo-EM Structures Using Neural Networks. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wittenborn, E.C.; Marletta, M.A. Structural Perspectives on the Mechanism of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115439
Wittenborn EC, Marletta MA. Structural Perspectives on the Mechanism of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115439
Chicago/Turabian StyleWittenborn, Elizabeth C., and Michael A. Marletta. 2021. "Structural Perspectives on the Mechanism of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115439
APA StyleWittenborn, E. C., & Marletta, M. A. (2021). Structural Perspectives on the Mechanism of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115439