The Exon Junction Complex Core Represses Cancer-Specific Mature mRNA Re-splicing: A Potential Key Role in Terminating Splicing
Abstract
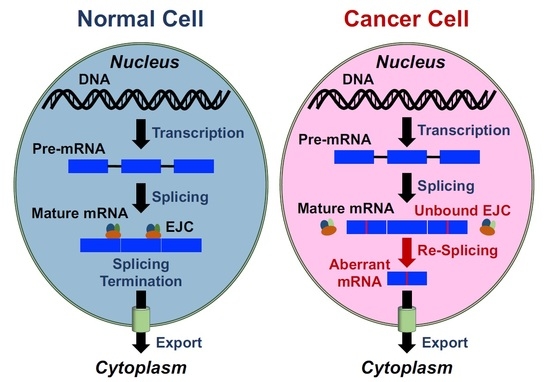
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Re-Splicing of mRNA Is Enhanced by EIF4A3 Knock-Down
2.2. The EJC Core Factors Were Identified as Repressors of mRNA Re-splicing
2.3. The EJC Core Represses mRNA Re-splicing in Normal Cells
2.4. mRNA Re-Splicing Is Not Due to Repression of EJC-mediated NMD
2.5. mRNA Re-Splicing Is Not Due to Repression of EJC-Mediated mRNA Export
2.6. RBM8A Expression Is Relevant to Cancer-specific mRNA Re-splicing Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and siRNA-Mediated Knock-Down
4.2. Establishment of Stable MCF-7 Cell Lines and Induction of RBM8A
4.3. RT–PCR and RT–qPCR Analyses
4.4. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.5. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2011, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, S.; Georgomanolis, T.; Zirkel, A.; Diermeier, S.; O’Reilly, D.; Murphy, S.; Langst, G.; Cook, P.R.; Papantonis, A. Splicing of many human genes involves sites embedded within introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibley, C.R.; Emmett, W.; Blazquez, L.; Faro, A.; Haberman, N.; Briese, M.; Trabzuni, D.; Ryten, M.; Weale, M.E.; Hardy, J.; et al. Recursive splicing in long vertebrate genes. Nature 2015, 521, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parra, M.K.; Tan, J.S.; Mohandas, N.; Conboy, J.G. Intrasplicing coordinates alternative first exons with alternative splicing in the protein 4.1R gene. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Kameyama, T.; Ohe, K.; Tsukahara, T.; Mayeda, A. Nested introns in an intron: Evidence of multi-step splicing in a large intron of the human dystrophin pre-mRNA. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gazzoli, I.; Pulyakhina, I.; Verwey, N.E.; Ariyurek, Y.; Laros, J.F.; t Hoen, P.A.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Non-sequential and multi-step splicing of the dystrophin transcript. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bortoli, F.; Espinosa, S.; Zhao, R. DEAH-box RNA helicases in pre-mRNA splicing. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 46, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, J.P. Aberrant and alternative splicing in cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7647–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kameyama, T.; Suzuki, H.; Mayeda, A. Re-splicing of mature mRNA in cancer cells promotes activation of distant weak alternative splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, H.H.; Huang, C.S.; Weng, P.L.; Yeh, T.H. TSG∆154-1054 splice variant increases TSG101 oncogenicity by inhibiting its E3-ligase-mediated proteasomal degradation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8240–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.H.; Kameyama, T.; Mayeda, A.; Yeh, T.H. Cancer-specifically re-spliced TSG101 mRNA promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraiuolo, R.M.; Manthey, K.C.; Stanton, M.J.; Triplett, A.A.; Wagner, K.U. The multifaceted roles of the tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG101) in normal development and disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Hir, H.; Sauliere, J.; Wang, Z. The exon junction complex as a node of post-transcriptional networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlautmann, L.P.; Gehring, N.H. A day in the life of the exon junction complex. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyret-Lalle, C.; Duriez, C.; Van Kerckhove, J.; Gilbert, C.; Wang, Q.; Puisieux, A. p53 induction prevents accumulation of aberrant transcripts in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 486–488. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Ross, T.M.; Chu, X.J.; Bartkovitz, D.; Podlaski, F.; Janson, C.; et al. Discovery of RG7388, a potent and selective p53-MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5979–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, N.H.; Lamprinaki, S.; Hentze, M.W.; Kulozik, A.E. The hierarchy of exon-junction complex assembly by the spliceosome explains key features of mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Steitz, J.A. Classification of gas5 as a multi-small-nucleolar-RNA (snoRNA) host gene and a member of the 5’-terminal oligopyrimidine gene family reveals common features of snoRNA host genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6897–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tani, H.; Torimura, M.; Akimitsu, N. The RNA degradation pathway regulates the function of GAS5 a non-coding RNA in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Kucukural, A.; Cenik, C.; Leszyk, J.D.; Shaffer, S.A.; Weng, Z.; Moore, M.J. The cellular EJC interactome reveals higher-order mRNP structure and an EJC-SR protein nexus. Cell 2012, 151, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metkar, M.; Ozadam, H.; Lajoie, B.R.; Imakaev, M.; Mirny, L.A.; Dekker, J.; Moore, M.J. Higher-order organization principles of pre-translational mRNPs. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehm, V.; Britto-Borges, T.; Steckelberg, A.L.; Singh, K.K.; Gerbracht, J.V.; Gueney, E.; Blazquez, L.; Altmuller, J.; Dieterich, C.; Gehring, N.H. Exon junction complexes suppress spurious splice sites to safeguard transcriptome integrity. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blazquez, L.; Emmett, W.; Faraway, R.; Pineda, J.M.B.; Bajew, S.; Gohr, A.; Haberman, N.; Sibley, C.R.; Bradley, R.K.; Irimia, M.; et al. Exon junction complex shapes the transcriptome by repressing recursive splicing. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulière, J.; Murigneux, V.; Wang, Z.; Marquenet, E.; Barbosa, I.; Le Tonquèze, O.; Audic, Y.; Paillard, L.; Roest Crollius, H.; Le Hir, H. CLIP-seq of eIF4AIII reveals transcriptome-wide mapping of the human exon junction complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowarz, E.; Loscher, D.; Marschalek, R. Optimized sleeping beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, L.; Chuah, M.K.; Belay, E.; Jerchow, B.; Manoj, N.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Grzela, D.P.; Schmitt, A.; Becker, K.; Matrai, J.; et al. Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive sleeping beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, E.; Lane, D. Immunoblotting. In Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual; Harlow, E., Lane, D., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 471–510. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otani, Y.; Fujita, K.-i.; Kameyama, T.; Mayeda, A. The Exon Junction Complex Core Represses Cancer-Specific Mature mRNA Re-splicing: A Potential Key Role in Terminating Splicing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126519
Otani Y, Fujita K-i, Kameyama T, Mayeda A. The Exon Junction Complex Core Represses Cancer-Specific Mature mRNA Re-splicing: A Potential Key Role in Terminating Splicing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126519
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtani, Yuta, Ken-ichi Fujita, Toshiki Kameyama, and Akila Mayeda. 2021. "The Exon Junction Complex Core Represses Cancer-Specific Mature mRNA Re-splicing: A Potential Key Role in Terminating Splicing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126519
APA StyleOtani, Y., Fujita, K. -i., Kameyama, T., & Mayeda, A. (2021). The Exon Junction Complex Core Represses Cancer-Specific Mature mRNA Re-splicing: A Potential Key Role in Terminating Splicing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126519