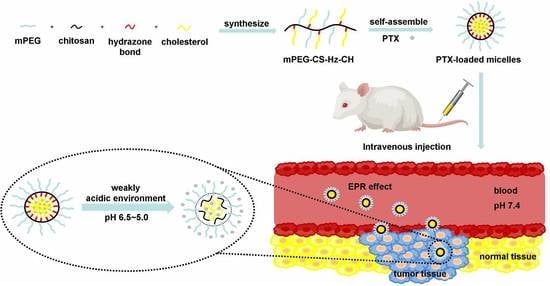
A pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micellar System Based on Chitosan Derivative for Efficient Delivery of Paclitaxel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of mPEG-CS-Hz-CH
2.2. Characterization of mPEG-CS-Hz-CH
2.2.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
2.2.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) Analysis
2.2.3. Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) Determination
2.3. Preparation of PTX-Loaded mPEG-CS-Hz-CH Micelles
2.4. Characterization of PTX-Loaded mPEG-CS-Hz-CH Micelles
2.4.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.4.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.5. Protein Adsorption
2.6. In Vitro pH-Dependent Drug Release Behavior
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.8. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Lines and Animals
3.3. Synthesis of mPEG-CS-Hz-CH
3.3.1. Synthesis of CH-CHO
3.3.2. Synthesis of mPEG-CS-NH-NH2
3.3.3. Synthesis of mPEG-CS-Hz-CH
3.4. Characterization of mPEG-CS-Hz-CH
3.5. Preparation and Characterization of PTX-Loaded mPEG-CS-Hz-CH Micelles
3.6. Protein Adsorption Test
3.7. In Vitro Release Study
3.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3.9. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy Study
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Porter, M.; Konstantopoulos, A.; Zhang, P.; Cui, H. Preclinical development of drug delivery systems for paclitaxel-based cancer chemotherapy. J. Control Release 2017, 267, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofias, A.M.; Dunne, M.; Storm, G.; Allen, C. The battle of “nano” paclitaxel. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 122, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.M.; Elsheikh, M.A.; Khalifa, A.M.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R. Current strategies for different paclitaxel-loaded Nano-delivery Systems towards therapeutic applications for ovarian carcinoma: A review article. J. Control. Release 2019, 311, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Chauhan, P.N.; Noolvi, M.N.; Chaturvedi, K.; Ganguly, K.; Shukla, S.S.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Polymeric micelles: Basic research to clinical practice. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Fei, C.; Yin, H.; Feng, Y. Stimuli-responsive polymer wormlike micelles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 89, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.; Sharma, D.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Tumor microenvironment targeted nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy and diagnosis: A review. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Kumar, A.; Tan, A.; Jin, S.; Mozhi, A.; Liang, X. pH-Sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, W.; Deng, W.; Lam, K.S. Stimuli-responsive cross-linked micelles for on-demand drug delivery against cancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamala, M.; Wilson, W.R.; Yang, M.; Palmer, B.D.; Wu, Z. Mechanisms and biomaterials in pH-responsive tumour targeted drug delivery: A review. Biomaterials 2016, 85, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonawane, S.J.; Kalhapure, R.S.; Govender, T. Hydrazone linkages in pH responsive drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Nurus Sakib, M.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications—A review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.S.; Almeida, A.; Prezotti, F.; Cury, B.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Sarmento, B. Synthesis and characterization of 3,6-O,O’-dimyristoyl chitosan micelles for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosta-Rigau, L.; Zhang, Y.; Teo, B.M.; Postma, A.; Städler, B. Cholesterol—A biological compound as a building block in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled nanoparticles of 6-O-cholesterol-modified chitosan for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, D.-D.; Cho, H.-J. Cholesterol-modified poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolate, A.; Baradia, D.; Patil, S.; Vhora, I.; Kore, G.; Misra, A. PEG—A versatile conjugating ligand for drugs and drug delivery systems. J. Control Release 2014, 192, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiri Manjili, H.; Ghasemi, P.; Malvandi, H.; Mousavi, M.S.; Attari, E.; Danafar, H. Pharmacokinetics and in vivo delivery of curcumin by copolymeric mPEG-PCL micelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 116, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Ishima, Y.; Ishida, T. Long-term storage of PEGylated liposomal oxaliplatin with improved stability and long circulation times in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Liu, S.; Shan, X.; Mao, J.; Yang, F.; Wu, X.; Qiu, L.; Chen, J. Self-assembly of pH-sensitive micelles for enhanced delivery of doxorubicin to melanoma cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2020, 59, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, M.; Liu, X. Facile synthesis of mPEG-luteolin-capped silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity to neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numpilai, T.; Witoon, T.; Chareonpanich, M.; Limtrakul, J. Impact of physicochemical properties of porous silica materials conjugated with dexamethasone via pH-responsive hydrazone bond on drug loading and release behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. Determination of the degree of N-acetylation for chitin and chitosan by various NMR spectroscopy techniques: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipser, B.; Bradford, J.J.; Hollingsworth, R.I. Cholesterol and its derivatives, are the principal steroids isolated from the leech species Hirudo medicinalis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 1998, 120, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Krajicek, M.E. Mucoadhesive polymers as platforms for peroral peptide delivery and absorption: Synthesis and evaluation of different chitosan-EDTA conjugates. J. Control Release 1998, 50, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, R.; Cao, Z.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Leong, K.W.; Wang, J. Surface charge critically affects tumor penetration and therapeutic efficacy of cancer nanomedicines. Nano Today 2016, 11, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J. Surface hydration: Principles and applications toward low-fouling/nonfouling biomaterials. Polymer 2010, 51, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmati, M.; Mozafari, M. Protein adsorption on polymers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, N.; Gong, X.; Kawashima, Y.; Cui, F.; Sun, S. Tumor-targeting micelles based on folic acid and α-tocopherol succinate conjugated hyaluronic acid for paclitaxel delivery. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Pan, J.; Liang, N.; Gong, X.; Sun, S. A pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micellar System Based on Chitosan Derivative for Efficient Delivery of Paclitaxel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136659
Han Y, Pan J, Liang N, Gong X, Sun S. A pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micellar System Based on Chitosan Derivative for Efficient Delivery of Paclitaxel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):6659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136659
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yang, Jieyi Pan, Na Liang, Xianfeng Gong, and Shaoping Sun. 2021. "A pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micellar System Based on Chitosan Derivative for Efficient Delivery of Paclitaxel" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 6659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136659
APA StyleHan, Y., Pan, J., Liang, N., Gong, X., & Sun, S. (2021). A pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micellar System Based on Chitosan Derivative for Efficient Delivery of Paclitaxel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 6659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136659