Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration
Abstract
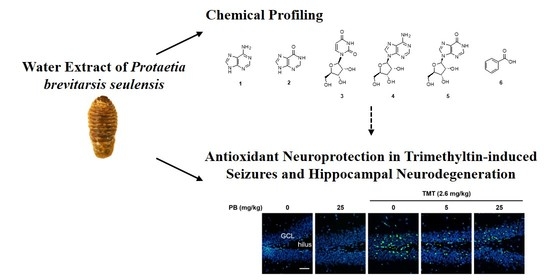
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphological Identification and Genetic Analysis
2.2. The PBWE Ameliorated TMT-Induced Neurotoxicity in Hippocampal Cultured Neurons
2.3. The PBWE Alleviated TMT-Induced Seizures in the In Vivo Model
2.4. Pretreatment with the PBWE Attenuated Hippocampal Neurodegeneration in TMT-Treated Mice
2.5. The PBWE Scavenged Free Radicals in the 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picryl-Hydrazyl-Hydrate (DPPH) Assay, and Pretreatment with the PBWE Reduced the Protein Expression of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2(Nrf2) in the In Vivo Model
2.6. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Chemical Profile of the PBWE and Antioxidative Activity of Isolated Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Medicinal Materials: PB Larvae
4.2. Morphological Identification and DNA Barcoding of PB Larvae
4.3. Extraction
4.4. Primary Hippocampal Cell Culture and Treatment with the PBWE
4.5. Cytotoxicity Examination
4.6. Animal Models, Drug Treatments, and Seizure Scoring
4.7. FJC Staining
4.8. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Isolation of the PBWE Components
4.11. UPLC Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TMT | Trimethyltin |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PB | Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis |
| PBWE | PB larvae water extract |
| COI | Cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 |
| DIV | Days in vitro |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| FJC | Fluoro-Jade C |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| PDA | Photodiode array |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| UPLC | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
| SE | Standard error of mean |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| NAC | N-acetyl cysteine |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
References
- Tsunashima, K.; Sadamatsu, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kato, N.; Sperk, G. Trimethyltin intoxication induces marked changes in neuropeptide expression in the rat hippocampus. Synapse 1998, 29, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yang, M.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.C.; Jung, C.; Shin, T.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C. Trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration: A mechanism-based review. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 125, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, R.; Krämer, G.; Thümler, R.; Bohl, J.; Gutmann, L.; Hopf, H.C. Acute trimethyltin limbic-cerebellar syndrome. Neurology 1987, 37, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, N.; Akaike, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kanai, H.; Masui, A.; Sadamatsu, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; McEwen, B.S.; Kato, N. Trimethyltin syndrome as a hippocampal degeneration model: Temporal changes and neurochemical features of seizure susceptibility and learning impairment. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Imai, H.; Minabe, Y.; Sawa, A.; Kato, N. Beneficial effects of FK506 for experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 56, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geloso, M.C.; Corvino, V.; Michetti, F. Trimethyltin-induced hippocampal degeneration as a tool to investigate neurodegenerative processes. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.J.; Suh, S.K.; Lim, Y.K.; Jhoo, W.K.; Hjelle, O.P.; Ottersen, O.P.; Shin, C.Y.; Ko, K.H.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, D.S.; et al. Ascorbate attenuates trimethyltin-induced oxidative burden and neuronal degeneration in the rat hippocampus by maintaining glutathione homeostasis. Neuroscience 2005, 133, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuto, M.; Higuchi, K.; Sugiyama, C.; Yoneyama, M.; Kuramoto, N.; Nagashima, R.; Kawada, K.; Ogita, K. Endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids prevent trimethyltin from causing neuronal degeneration of the mouse brain in vivo: Involvement of oxidative stress pathways. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 110, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. Defining Dictionary for Medicinal Herbs [Korean, ‘Hanyak Giwon Sajeon’]. Available online: http://boncho.kiom.re.kr/codex/ (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Kim, M.A.; Lee, H.A.; Park, H.C. A taxonomic study of immature stage in three species of the genus Protaetia Burmeister (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea, Cetoniidae) from Korea. Entomol. Res. 2003, 33, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.; Youn, K.; Kim, M.; Yun, E.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Jeong, W.S.; Jun, M. Fatty Acid Composition and Volatile Constituents of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 18, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, I.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.A.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Na, M. Quinoxaline-, dopamine-, and amino acid-derived metabolites from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, H.J. (Eds.) Donguibogam; Publishing Company of Donguibogam: Hadong, Gyeongnam, Korea, 2005; Volume 1610, p. 1042. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, W.; Kim, M.A.; Hwang, J.S.; Na, M.; Bae, J.S. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombosis by indole alkaloids isolated from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis (Kolbe). J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-C.; Li, H.-B.; Cheng, K.-W.; Chen, F. A systematic survey of antioxidant activity of 30 Chinese medicinal plants using the ferric reducing antioxidant power assay. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yang, M.; Kim, J.; Son, Y.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Ahn, W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C.; Shin, T.; et al. Involvement of BDNF/ERK signaling in spontaneous recovery from trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity in mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 121, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.; Takayama, C.; Hayashi, A.; Joo, H.G.; Shin, T.; et al. Possible involvement of galectin-3 in microglial activation in the hippocampus with trimethyltin treatment. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yang, M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C.; Wang, H.; Shin, T.; Moon, C. Possible role of the glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway in trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, A.A.; Wagner, C.M.; Nair, M.G. Nitrogenous compounds characterized in the deterrent skin extract of migratory adult sea lamprey from the Great Lakes region. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Lu, X.M.; Zhu, T.J.; Fang, Y.C.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W. GPR12 selections of the metabolites from an endophytic Streptomyces sp. associated with Cistanches deserticola. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Hussein, D.R.; Badr, J.M.; Youssef, D.T. Nucleoside constituents of the Egyptian tunicate Eudistoma laysani. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2007, 13, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Terakita, A.; Matsunaga, H.; Ueda, T.; Eguchi, T.; Echigoya, M.; Umemoto, K.; Godo, M. Investigation of intermolecular interaction in molecular complex of tryptamine and benzoic acid by solid-state 2D NMR. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2004, 52, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.H.; Cha, J.M.; Moon, B.C.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, S.; Choi, G. Mantidis Oötheca (mantis egg case) original species identification via morphological analysis and DNA barcoding. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 252, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Im, H.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Han, Y.S.; Kim, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the whiter-spotted flower chafer, Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, W.J.; Cha, J.M.; Yang, S.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C. Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs. Insects 2019, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortemps, E.; Amand, G.; Bomboir, A.; Lauwerys, R.; Laterre, E.C. Trimethyltin poisoning. Report of two cases. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1978, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Ang, M.J.; Moon, B.C.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, G.; Lim, H.S.; Kang, S.; Jeon, M.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C.; et al. Protective Effects of Scolopendra Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Hippocampal Neurodegeneration and Seizures in Mice. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Yang, M.; Son, Y.; Jang, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Im, H.I.; Shin, T.; et al. Glial activation with concurrent up-regulation of inflammatory mediators in trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Sugiyama, C.; Higuchi, K.; Yoneyama, M.; Yoneda, Y. Regeneration of granule neurons after lesioning of hippocampal dentate gyrus: Evaluation using adult mice treated with trimethyltin chloride as a model. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 82, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumià, J.; Marmol, F.; Sanchez, J.; Giménez-Crouseilles, J.; Carreño, M.; Bargalló, N.; Boget, T.; Pintor, L.; Setoain, X.; Donaire, A.; et al. Oxidative stress markers in the neocortex of drug-resistant epilepsy patients submitted to epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 107, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.; Ramalingam, K.; Kumar, R.V. Oxidative stress in patients with epilepsy is independent of antiepileptic drugs. Seizure 2012, 21, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huong, N.Q.; Nakamura, Y.; Kuramoto, N.; Yoneyama, M.; Nagashima, R.; Shiba, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hasebe, S.; Ogita, K. Indomethacin ameliorates trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in vivo by attenuating oxidative stress in the dentate gyrus of mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Pei, L.; Chu, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; et al. Lycopene protects against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vomund, S.; Schäfer, A.; Parnham, M.J.; Brüne, B.; von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the Master Regulator of Anti-Oxidative Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, E.J.; Nam, Y.; Tu, T.H.; Lim, Y.K.; Wie, M.B.; Kim, D.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, H.C. Protein kinase Cδ mediates trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in mice in vivo via inhibition of glutathione defense mechanism. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, E.M.; Myung, N.Y.; Jung, H.A.; Kim, S.J. The ameliorative effect of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae in HFD-induced obese mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Seo, M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, I.-W.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, J.-S.; Kim, M.-A. Inhibitory Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis Ethanol Extract on Neuroinflammation in LPS-stimulated BV-2 Microglia. J. Life Sci. 2019, 29, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparova, Z.; Stara, V.; Janega, P.; Navarova, J.; Sedlackova, N.; Mach, M.; Ujhazy, E. Pyridoindole antioxidant-induced preservation of rat hippocampal pyramidal cell number linked with reduction of oxidative stress yet without influence on cognitive deterioration in Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2014, 35, 454–462. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, S.M.; Barone, S. The neurotoxicant trimethyltin induces apoptosis via caspase activation, p38 protein kinase, and oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 147, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallorini, M.; Petzel, C.; Bolay, C.; Hiller, K.A.; Cataldi, A.; Buchalla, W.; Krifka, S.; Schweikl, H. Activation of the Nrf2-regulated antioxidant cell response inhibits HEMA-induced oxidative stress and supports cell viability. Biomaterials 2015, 56, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisiya, M.; Zabetta, C.D.C.; Bellarosa, C.; Tiribelli, C. Bilirubin mediated oxidative stress involves antioxidant response activation via Nrf2 pathway. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.J.; Kang, D.G.; Jung, C.; Sohn, H.Y. Anti-Thrombotic, Anti-Oxidant and Haemolysis Activities of Six Edible Insect Species. Foods 2020, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinesh, S.; Shikha, G.; Gangwar, B.; Nidhi, S.; Dileep, S. Biological activities of purine analogues: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Innov. 2012, 1, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, Z.; Kekesi, K.A.; Juhasz, G.; Barna, J.; Heja, L.; Lakatos, R.; Dobolyi, A. Non-adenosine nucleoside inosine, guanosine and uridine as promising antiepileptic drugs: A summary of current literature. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 14, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, Z.; Kekesi, K.A.; Dobolyi, A.; Lakatos, R.; Juhász, G. Absence epileptic activity changing effects of non-adenosine nucleoside inosine, guanosine and uridine in Wistar Albino Glaxo Rijswijk rats. Neuroscience 2015, 300, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Kulovich, S.; Alice, L.Y.; Qiao, C.-N.; Nyhan, W.L. The effectiveness of benzoate in the management of seizures in nonketotic hyperglycinemia. AMA Am. J. Dis. Child 1986, 140, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.; Varshavsky, L.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Grossman, S. The antioxidant activity of aqueous spinach extract: Chemical identification of active fractions. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Shtarkman, I.N.; Smirnova, V.S.; Chernikov, A.V.; Bruskov, V.I. Guanosine and inosine display antioxidant activity, protect DNA in vitro from oxidative damage induced by reactive oxygen species, and serve as radioprotectors in mice. Radiat Res. 2006, 165, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, T.R.; Salinas, E.S.S.; Alencar, S.M.; D’arce, M.A.B.R.; Camargo, A.C.d.; Vieira, T.M.F.d.S. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of wild and cultivated murtilla (Ugni molinae Turcz.). Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, J.; Chen, H.M.; Yang, J.X.; Jin, J.Q.; Jiang, K.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Murphy, R.W.; Zhang, Y.P. Universal COI primers for DNA barcoding amphibians. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.; Wang, H.; Shin, T.; Moon, C. Neurotoxicity of methotrexate to hippocampal cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Nishiyama, N.; Shuto, M.; Sugiyama, C.; Kawada, K.; Seko, K.; Nagashima, R.; Ogita, K. In vivo depletion of endogenous glutathione facilitates trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the dentate gyrus of mice by enhancing oxidative stress. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmued, L.C.; Stowers, C.C.; Scallet, A.C.; Xu, L. Fluoro-Jade C results in ultra high resolution and contrast labeling of degenerating neurons. Brain Res. 2005, 1035, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Moore, J.; Yu, L. High-throughput relative DPPH radical scavenging capacity assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7429–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C. Enhanced expression of immediate-early genes in mouse hippocampus after trimethyltin treatment. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Seo, Y.H.; Song, J.H.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Ang, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C.; Lee, J.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020679
Lee S, Seo YH, Song JH, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Moon BC, Ang MJ, Kim SH, Moon C, Lee J, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020679
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sueun, Young Hye Seo, Jun Ho Song, Wook Jin Kim, Ji Hye Lee, Byeong Cheol Moon, Mary Jasmin Ang, Sung Ho Kim, Changjong Moon, Jun Lee, and et al. 2021. "Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020679
APA StyleLee, S., Seo, Y. H., Song, J. H., Kim, W. J., Lee, J. H., Moon, B. C., Ang, M. J., Kim, S. H., Moon, C., Lee, J., & Kim, J. S. (2021). Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020679