Prussian Blue: A Safe Pigment with Zeolitic-Like Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Insoluble Prussian Blue
3. Characteristics of Prussian Blue
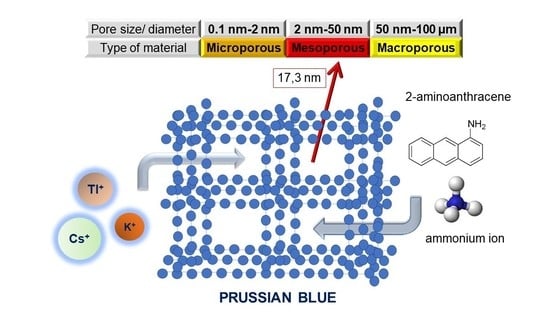
3.1. Structural Characteristics
3.2. Physicochemical Characteristics
4. Adsorption Properties of PB
4.1. Adsorption of Cesium
| Adsorbent | Synthesis | Adsorption Capacity/mg g−1 | Removal Efficiency/% | Equilibrium Time | Kinetic Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoclusters | Single-precursor | 45.87 | >99.7 | 6 h | Langmuir | [49] |
| Nanoparticles | Single precursor | 96.00 | 24 h | Langmuir | [45] | |
| Nanocomposites with graphene oxide | Anchoring the magnetic PB onto the graphene surface | 55.56 | >90.0 | 12 h | Langmuir | [46] |
| Nanoparticles with PDDA as interlayer | Single precursor | 16.20 | 91.0 | 1 h | Freundlich | [43] |
| Co-precipitation | 94.0 | 3 h | [48] | |||
| Co-precipitation | 84.7–86.7 | [44] | ||||
| Nanocomposites | Co-precipitation | 280.82 | 24 h | Temkin | [47] | |
| Nanoparticles with PEG | Hydrothermal | 274.70 | 64.8 | 1 h | [50] | |
| Microparticles | Hydrothermal | 16.30 | 97.0 | 10 min | Freundlich | [51] |
| Microgels | Ligand substitution reaction | 149.70 | 83.7 | 24 h | Langmuir | [56] |
4.2. Adsorption of Thallium
4.3. Adsorption of Cations
4.4. Adsorption of Gases
4.5. Adsorption of Molecules
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mumpton, F.A. La roca magica: Uses of natural zeolites in agriculture and industry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 96, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calderón, A.; Quiroz, H.P. Zeolites derived from natural minerals: Solid rock and volcanic ash. Mater. Today 2020, 34, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontova, E.; Daurat, M.; Long, J.; Godefroy, A.; Salles, F.; Guari, Y.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Larionova, J. Fashioning Prussian blue nanoparticles by adsorption of luminophores: Synthesis, properties, and in vitro imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, L.; Mallah, T. Nanoparticles of Prussian blue analogs and related coordination polymers: From information storage to biomedical Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 32–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, M. Prussian blue: Artists’ pigment and chemists’ sponge. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Cao, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Pan, F. Synthetic control of Prussian blue derived nano-materials for energy storage and conversion application. Mater. Today Energy 2019, 14, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, A.; Uchida, H.; Ishizaki, M.; Satoh, T.; Kaga, S.; Okamoto, S.; Ohta, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Simple synthesis of the three primary colour nanoparticle inks of Prussian blue and its analogues. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 345609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guari, Y.; Larionova, J. Prussian Blue-Type Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites. Synthesis, Devices and Applications; Guari, Y., Larionova, J., Eds.; Pan Stanford: Singapore, 2019; pp. XI–XII. [Google Scholar]
- Busquets, M.A.; Estelrich, J. Prussian blue nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface modification and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1413–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; p. 4. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/expert-committee-on-selection-and-use-of-essential-medicines/essential-medicines-lists (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Grandjean, F.; Samain, L.; Long, G.J. Characterization and utilization of Prussian blue and its pigments. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 18018–18044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacarro, G.; Taglietti, A.; Pallavicini, P. Prussian blue nanoparticles as a versatile photothermal tool. Molecules 2018, 23, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishizaki, M.; Kanaizuka, K.; Abe, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kurihara, M. Preparation of electrochromic Prussian blue nanoparticles dispersible into various solvents for realisation of printed electronics. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.J.; Ludi, A. Single-crystal study of Prussian blue-Fe4[Fe(CN)6]2 14H2O. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1972, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.J.; Schwarzenbach, D.; Petter, W.; Ludi, A. Crystal structure of Prussian blue-Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3xH2O. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 2704–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, F.; Fischer, P.; Ludi, A.; Halg, W. Neutron-diffraction study of Prussian blue, Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3xH2O-Location of water molecules and long-range magnetic order. Inorg. Chem. 1980, 19, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Suenaga, M.; Ono, K. Mössbauer study of soluble Prussian blue, insoluble Prussian blue, and Turnbull’s blue. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 3597–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Torad, N.L.K.; Chiang, Y.-D.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Yamauchi, Y. Size- and shape-controlled synthesis of Prussian blue nanoparticles by a polyvinylpyrrolidone-assisted crystallization process. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2012, 14, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pau, P.C.F.; Berg, J.O.; McMillan, W.G. Application of Stokes’s law to ions in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok-Badura, J.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Karoń, K. Hybrid-pectin-based sorbents for cesium ion removal. Molecules 2020, 13, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.rxlist.com/radiogardase-drug.htm#description (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Hornok, V.; Dékány, I. Synthesis and stabilization of Prussian blue nanoparticles and application for sensors. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, M.; Akiba, S.; Ohtani, A.; Hoshi, Y.; Ono, K.; Matsuba, M.; Togashi, T.; Kananizuka, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Proton-exchange mechanism of specific Cs+ adsorption via lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water molecules. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 16049–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Aoki, S.; Takaishi, M.; Sato, Y.; Abe, H. An XAFS study of Cs adsorption by the precipitation bands of Mn-Fe-based Prussian blue analogues spontaneously formed in agarose gel. Phys. Che. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22553–22562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Minami, K.; Noda, K.; Ishizaki, M.; Kurihara, M.; Ogawa, H.; Kawamoto, T. Unveiling Cs-adsorption mechanism of Prussian blue analogs: Cs+-percolation via vacancies to complete dehydrated state. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34808–34816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harjula, R.; Lehto, J.; Paajanen, A.; Brodkin, L.; Tusa, E. Removal of radioactive cesium from nuclear waste solutions with the transition metal hexacyanoferrate ion exchanger Cs treat. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2001, 137, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Sasano, H.; Miyajima, R.; Sazoka, A. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of cesium onto insoluble Prussian blue synthesized by an immediate precipitation reaction between Fe3+ and [Fe(CN)6]-4. Adsorption 2014, 20, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delchet, C.; Tokarev, A.; Dumail, X.; Toquer, C.; Barré, Y.; Guari, Y.; Guerin, Y.; Larionova, J.; Grandjean, A. Extraction of radioactive cesium using innovative functionalized porous materials. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5707–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, B.-S.; Lee, K.-W.; Yeom, B.; Lee, T.S. Cesium ion-exchange resin using dodecylbenzenesulfonate for binding to Prussian blue. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.J.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, K.-W.; Ogden, M.D.; Harwood, L.M.; Lee, T.S. Prussian blue decoration on polyacrylonitrile nanofibers using polydopamine for effective Cs ion removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4872–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, H.; Kang, S.-W.; Hwang, Y. Immobilization of Prussian blue nanoparticles in acrylic acid-surface functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) sponges for cesium adsorption. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 24, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, H.; Kim, H.; Oh, D.; Bae, S.; Hwang, Y. Surface modification of poly(vinyl alcohol) sponge by acrylic acid to immobilize Prussian blue for selective adsorption of aqueous cesium. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, A.K.; Hu, B.; Fugetsu, B. Prussian blue caged in alginate/calcium beads as adsorbents for removal of cesium ions from contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258–259, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandal, N.; Mittal, G.; Bhatnagar, A.; Pathak, D.P.; Singh, A.K. Preparation, characterization, and in vivo pharmaco scintigraphy evaluation of an intestinal release delivery system of Prussian blue for decorporation of cesium and thallium. J. Drug Delivery 2017, 2017, 4875784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Fugetsu, B.; Yu, H.; Abe, Y. Prussian blue caged in spongiform adsorbents using diatomite and carbon nanotubes for elimination of cesium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darder, M.; González-Alfaro, Y.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Silicate-based multi-functional nanostructured materials with magnetite and Prussian blue: Application to cesium uptake. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 35415–35421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-R.; Chang, Y.-R.; Liu, X.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kitajima, A.; Parajuli, D.; Takasaki, M.; Yoshino, K.; Chen, M.-L.; et al. Prussian blue (PB) granules for cesium (Cs) removal from drinking water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 143, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Kim, S.-H.; Rethinasabapathy, M.; Haldorai, Y.; Lee, G.-W.; Choe, S.R.; Jang, S.-C.; Kang, S.-M.; Han, Y.-K.; Roh, C.; et al. Porous·3D Prussian blue/cellulose aerogel as a decorporation agent for removal of ingested cesium from the gastrointestinal tract. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eun, S.; Hong, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, S.; Jung, J.; Ryu, J. Prussian blue-embedded carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibril membranes for removing radioactive cesium from aqueous solution. Carbohyd. Pol. 2020, 235, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Sato, Y.; Aoki, S.; Takaishi, M. In situ XRF analysis of Cs adsorption by the precipitation bands of Prussian blue analogues formed in agarose gels. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hodges, C.S.; Kumar Misha, P.; Young Yoon, J.; Hunter, T.N.; Lee, J.; Harbottle, D. Bio-inspired preparation of clay-hexacyanoferrate composite hydrogels as super adsorbents for Cs+. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33173–33185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, S. Magnetic separation of cesium ion using Prussian blue modified magnetite. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, Y.; Namiki, T.; Ishii, Y.; Koido, S.; Nagase, Y.; Tsubota, A.; Tada, N.; Kitamoto, Y. Inorganic-organic magnetic nanocomposites for use in preventive medicine: A rapid and reliable elimination system for cesium. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammawong, C.; Opaprakasit, P.; Tangboriboonrat, P.; Sreearunothai, P. Prussian blue coated magnetic nanoparticles for removal of cesium from contaminated environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhai, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H. In situ controllable synthesis of magnetic Prussian blue/graphene oxide nanocomposites for removal of radioactive cesium in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 332–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, D.S. Magnetic Prussian blue nanocomposites for effective cesium removal from aqueous solution. Ind. Eng. Chem Res. 2016, 55, 3852–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-C.; Hong, S.-B.; Yang, H.-M.; Lee, K.-W.; Moon, J.-K.; Seo, B.-K.; Huh, Y.S.; Roh, C. Removal of radioactive cesium using Prussian blue magnetic nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.-M.; Jang, S.-C.; Hong, S.B.; Le, K.-W.; Roh, C.; Huh, Y.S.; Seo, B.-K. Prussian blue functionalized magnetic nanoclusters for the removal of radioactive cesium from water. J. Alloys Comp. 2016, 657, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xu, J.; Kung, L.; Hua, D. Cesium removal from human blood by poly(ethylene glycol)-decorated Prussian blue magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Plus Chem. 2017, 82, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Ma, X.; Du, X.; Gao, F.; Hao, X.; Tang, B.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Electroactive magnetic microparticles for the selective elimination of cesium ions in the wastewater. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hao, X.G.; Wang, Z.D.; Guan, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.I.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, S.B. Separation of low concentrations of cesium ion from wastewater by electrochemically switched ion Exchange method: Experimental adsorption kinetic analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, T.; Tanaka, M.; Honjo, M.; Fukunaga, Y.; Okamura, T.; Ohba, M. Direct synthesis of Prussian blue nanoparticles in liposomes incorporating natural ion channels for Cs+ adsorption and particle size control. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.-X.; Hu, M.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Q.; Xu, L.; Jiang, D.-M.; Jiang, J.-S. Three-dimensional hierarchical Prussian blue composed of ultrathin nanosheets: Enhanced hetero-catalytic and adsorption properties. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17568–17571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard, O.; Laceby, J.P.; Lepage, H.; Onda, Y.; Cerdan, O.; Ayrault, S. Radiocesium transfer from hillslopes to the Pacific Ocean after the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident: A review. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 148, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Hua, D.; Wu, N. Prussian blue analogue functionalized magnetic microgels with ionized chitosan for the cleaning of cesium-contaminated clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promote iron catalysts. Acta Phys. Chim. USSR 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; An, X.; Li, H. Continuous separation and recovery of caesium by electromagnetic coupling regeneration process with an electroactive magnetic Fe3O4@cupric hexacyanoferrate. J. App. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, P.J.; Yongsheng, Y.; Progar, J.J.; Brownell, C.R.; Sadrieh, N.; May, J.C.; Leutzinger, E.; Place, D.A.; Duffy, E.P.; Houn, F.; et al. Quantitative determination of cesium binding to ferric hexacyanoferrate: Prussian blue. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, S.; Vipin, A.K.; Kumashiro, T.; Takiguchi, S.; Fugetsu, B.; Sakata, I. Stabilization of Prussian blue using copper sulfate for eliminating radioactive cesium from a high pH solution and seawater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Arzate, S.; Santamaría, A. Tallium toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 99, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hou, X.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Y.M.; You, J.; Xu, L. Adsorptive removal of trace thallium (I) from wastewater: A review and new perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, S.; Zengin, A.; Akbulut, Y.; Sahan, T. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with aminated polymer brush as a novel material for effective removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Faustino, P.J.; Progar, J.J.; Brownell, C.R.; Sadrieh, N.; May, J.C.; Leutzinger, E.; Place, D.A.; Duffy, E.P.; Xu, L.X.; et al. Quantitative determination of thallium binding to ferric hexacyanoferrate: Prussian blue. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 353, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faustino, P.J.; Brown, A.; Lowry, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Dumbar, K.R.; Mohammad, A. Quantitative evaluation of the thallium binding of soluble and insoluble Prussian blue hexacyanoferrate analogs: A scientific comparison based on their critical quality attributes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangvanich, T.; Sukwarotwat, V.; Wiacek, R.J.; Grudzien, R.M.; Fryxell, G.E.; Addleman, R.S.; Timchalk, C.; Yantsee, W. Selective capture of cesium and thallium from natural waters and simulated wastes with copper ferrocyanide functionalized mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, T.; Taulemesse, J.M.; Dauvergne, A.; Chaunut, T.; Testa, F.; Guibal, E. Thallium (I) sorption using Prussian blue immobilized in alginate capsules. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 99, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafakhah, S.; Guo, L.; Sriramulu, D.; Huang, S.; Saeedikhani, M.; Yang, H.Y. Efficient sodium-ion intercalation into the freestanding Prussian blue/graphene aerogel anode in a hybrid capacitive deionization system. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5989–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uogintė, I.; Lujanienė, G.; Mažeika, K. Study of Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solutions using magnetic Prussian blue nano-sorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, C.C.; Scarpa, R.C.; Huang, X.; Moir, R.D.; Jones, W.D.; Fairli, D.P.; Tanzi, R.E.; Bush, A.I. Characterization of copper interactions with Alzheimer amyloid β peptides. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, S.S.; Long, J.R. Hydrogen storage in the dehydrated Prussian blue analogues M3[Co(CN)6]2 (M ) Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6506–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thallapally, P.K.; Motkuri, R.K.; Fernández, C.A.; McGrail, B.P.; Behrooz, G.S. Prussian blue analogues for CO2 and SO2 capture and separation applications. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 4909–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadas, F.; El-Faki, H.; Deniz, E.; Yavuz, C.T.; Aparicio, S.; Atilhan, M. CO2 adsorption studies on Prussian blue analogues. Microporous Macroporous Mater. 2012, 162, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Parajuli, D.; Nakamura, T.; Minami, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Hakuta, Y.; Ohkoshi, S.; Kawamoto, T. Historical pigment exhibiting ammonia gas capture beyond standard adsorbents with adsorption sites of two kinds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6376–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, D.; Noguchi, H.; Takahashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Kawamoto, T. Prospective application of copper hexacyanoferrate for capturing dissolved ammonia. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6708–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Jiang, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Ishizaki, M.; Asai, M.; Kurihara, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Parajuli, D. Interpretation of the role of composition on the inclusion efficiency of monovalent cations into cobalt hexacyanoferrate. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 5950–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Minami, K.; Noda, K.; Sakurai, K.; Kawamoto, T. Trace ammonia removal from air selective adsorbents reusable with water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15115–15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.S.; Long, J.R. The role of vacancies in the hydrogen storage properties of Prussian blue analogues. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autie-Castro, G.; Autie, M.; Reguera, E.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Jiménez-López, A.; Santamaría-González, J. Adsorption and separation of propane and propylene by porous hexacyanometallates. App. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjema, L.; Mamontova, E.; Long, J.; Larionova, J.; Guari, Y.; Trens, P. Prussian blue analogues for the separation of hydrocarbons in humid conditions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 7598–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontova, E.; Long, J.; Ferreira, R.; Botas, A.M.P.; Salles, F.; Guari, Y.; Carlos, L.A.; Larionova, J. Making Prussian blue analogues nanoparticles luminescent: Effect of the luminophore confinement over the properties. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7097–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estelrich, J.; Busquets, M.A. Prussian Blue: A Safe Pigment with Zeolitic-Like Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020780
Estelrich J, Busquets MA. Prussian Blue: A Safe Pigment with Zeolitic-Like Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020780
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstelrich, Joan, and Maria Antònia Busquets. 2021. "Prussian Blue: A Safe Pigment with Zeolitic-Like Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020780
APA StyleEstelrich, J., & Busquets, M. A. (2021). Prussian Blue: A Safe Pigment with Zeolitic-Like Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020780