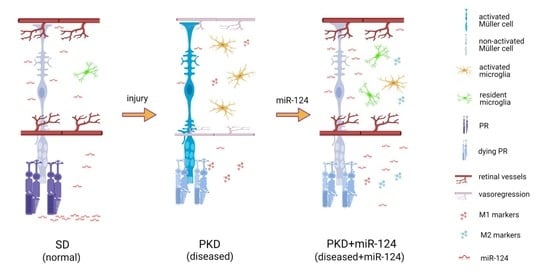
MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. miR-124 Normalizes Müller Glial Activation in the PKD Retina
2.2. miR-124 Decreases the Activation State of Microglia in PKD Retinae
2.3. miR-124 Alleviates Vasoregression of the PKD Retina
2.4. miR-124 Improves Retinal Function in Neurodegeneration
2.5. miR-124 Inhibits the Migratory Capability of Microglia
2.6. miR-124 Modulates the Polarization of Microglia to an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype
2.7. miR-124 Downregulates the Transcription Factors C/EBP-α/PU.1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rat and Intravitreal Injection
4.2. Retinal Digest Preparation and Quantitative Morphometry
4.3. miRNA In Situ Hybridization (ISH) and Fluorecent Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Primary Culture of Rat Microglia
4.5. Cell Line Cultivation and Transfection
4.6. Analysis of mRNA and miRNA Expression
4.7. Whole Mount Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Transwell Migration Assay
4.11. Wound Healing Assay
4.12. Live Cell Imaging and Time Lapse Analysis
4.13. Electroretinography (ERG)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Arg1 | Arginase-1 |
| BMDMs | Bone marrow-derived macrophages |
| BSYS | Bu Shen Yi Sui capsule |
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 |
| CCL3 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 |
| CD74 | Major histocompatibility complex, class II invariant chain |
| C/EBP-α | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| ERG | Electroretinography GCL ganglion cell layer |
| Flot1 | Flottilin-1 |
| Gapdh | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GS | Glutamine synthetase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| ILM | Inner limiting membrane |
| INL | Inner nuclear layer |
| IPL | Inner plexiform layer |
| MHC-II | Major histocompatibility complex class II molecule |
| miR-124 | MicroRNA-124 |
| miR-inh | MicroRNA-124 inhibitor |
| NVU | Neurovascular unit |
| OLM | Outer limiting membrane |
| ONL | Outer nuclear layer |
| OPL | Outer plexiform layer |
| PD | Photo-oxidative damage |
| PKD | Polycystic kidney disease |
| PU.1 | Protein binding U box |
| SCI | Spinal cord injury |
| SD | Sprague Dawley |
| Spi1 | Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (gene name of PU.1) |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TNFR | TNF receptor |
References
- Hammes, H.P.; Feng, Y.; Pfister, F.; Brownlee, M. Diabetic retinopathy: Targeting vasoregression. Diabetes 2011, 60, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlstetter, M.; Scholz, R.; Rutar, M.; Wong, W.T.; Provis, J.M.; Langmann, T. Retinal microglia: Just bystander or target for therapy? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 45, 30–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecino, E.; Rodriguez, F.D.; Ruzafa, N.; Pereiro, X.; Sharma, S.C. Glia-neuron interactions in the mammalian retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 51, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, K.; Akhtar-Schaefer, I.; Langmann, T. Microglia in Retinal Degeneration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellver-Landete, V.; Bretheau, F.; Mailhot, B.; Vallieres, N.; Lessard, M.; Janelle, M.E.; Vernoux, N.; Tremblay, M.E.; Fuehrmann, T.; Shoichet, M.S.; et al. Microglia are an essential component of the neuroprotective scar that forms after spinal cord injury. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Shyamasundar, S.; Patnala, R.; Karthikeyan, A.; Arumugam, T.V.; Ling, E.A.; Dheen, S.T. Recent progress in therapeutic strategies for microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neuropathologies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Garton, T.; Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Microglia/Macrophage Polarization After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.T.; Wu, W.F.; Deng, Y.H.; Ge, J.W. Modulators of microglia activation and polarization in ischemic stroke (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, K.; Zu, H.B. Microglial polarization: Novel therapeutic mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroba, A.I.; Valverde, A.M. Modulation of microglia in the retina: New insights into diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lull, M.E.; Block, M.L. Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, A.R.; Hoffmann, S.; Brown, N.; Cedzich, A.; Meruvu, S.; Podlich, D.; Feng, Y.; Konecke, V.; de Vries, U.; Hammes, H.P.; et al. A truncated polycystin-2 protein causes polycystic kidney disease and retinal degeneration in transgenic rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoder, B.K. Role of primary cilia in the pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Stock, O.; Pfister, F.; Tanimoto, N.; Seeliger, M.W.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Hoffmann, S.; Wolburg, H.; Gretz, N.; et al. Vasoregression linked to neuronal damage in the rat with defect of polycystin-2. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, L.J.; Sheng, K.C.; Jian, P.; Taylor, A.; Her, Z.; Herring, B.L.; Chow, A.; Leo, Y.S.; Hickey, M.J.; Morand, E.F.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor receptor CD74 mediates alphavirus-induced arthritis and myositis in murine models of alphavirus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2724–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Benedek, G.; Meza-Romero, R.; Andrew, S.; Leng, L.; Burrows, G.G.; Bourdette, D.; Offner, H.; Bucala, R.; Vandenbark, A.A. Partial MHC class II constructs inhibit MIF/CD74 binding and downstream effects. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Hu, J.; Schlotterer, A.; Wang, J.; Kolibabka, M.; Awwad, K.; Dietrich, N.; Breitschopf, K.; Wohlfart, P.; Kannt, A.; et al. Protective effect of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition in Retinal Vasculopathy associated with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7857–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, D.J.; Stow, J.L.; Mallett, A.J. Ciliopathies and the Kidney: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis 2021, 77, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, A.M.; Naeini, M.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Diseases. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karali, M.; Persico, M.; Mutarelli, M.; Carissimo, A.; Pizzo, M.; Singh Marwah, V.; Ambrosio, C.; Pinelli, M.; Carrella, D.; Ferrari, S.; et al. High-resolution analysis of the human retina miRNome reveals isomiR variations and novel microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanuki, R.; Onishi, A.; Koike, C.; Muramatsu, R.; Watanabe, S.; Muranishi, Y.; Irie, S.; Uneo, S.; Koyasu, T.; Matsui, R.; et al. miR-124a is required for hippocampal axogenesis and retinal cone survival through Lhx2 suppression. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamachi, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Uto, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Saegusa, J.; Kawano, S. MicroRNA-124 inhibits the progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louw, A.M.; Kolar, M.K.; Novikova, L.N.; Kingham, P.J.; Wiberg, M.; Kjems, J.; Novikov, L.N. Chitosan polyplex mediated delivery of miRNA-124 reduces activation of microglial cells in vitro and in rat models of spinal cord injury. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu-Tan, J.A.; Rutar, M.; Saxena, K.; Aggio-Bruce, R.; Essex, R.W.; Valter, K.; Jiao, H.; Fernando, N.; Wooff, Y.; Madigan, M.C.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Dysregulation is Associated With Retinal Inflammation and Photoreceptor Death in the Degenerating Retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 4094–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarev, E.D.; Veremeyko, T.; Barteneva, N.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Weiner, H.L. MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-alpha-PU.1 pathway. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, H. Parainflammation, chronic inflammation, and age-related macular degeneration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Xie, X.; Yuan, L.; Guo, J.; Xi, S.; Gao, J.; Lin, X.; et al. Microrna-124 targets flotillin-1 to regulate proliferation and migration in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, D. Muller glial cell reprogramming and retina regeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogler, S.; Pannicke, T.; Hollborn, M.; Grosche, A.; Busch, S.; Hoffmann, S.; Wiedemann, P.; Reichenbach, A.; Hammes, H.P.; Bringmann, A. Muller cell reactivity in response to photoreceptor degeneration in rats with defective polycystin-2. PLoS ONE 2014, 8, e61631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, R.; Liu, L. Down-Regulation of miRNA-128 Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Following Spinal Cord Injury via Activation of P38. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamzei Taj, S.; Kho, W.; Riou, A.; Wiedermann, D.; Hoehn, M. MiRNA-124 induces neuroprotection and functional improvement after focal cerebral ischemia. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, A.; Bringmann, A. Glia of the human retina. Glia 2020, 68, 768–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wong, W.T. Microglia-Muller cell interactions in the retina. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.M.; Gibbons, H.M.; Oldfield, R.L.; Bergin, P.M.; Mee, E.W.; Faull, R.L.; Dragunow, M. The transcription factor PU.1 is critical for viability and function of human brain microglia. Glia 2013, 61, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.R.; Gibbons, H.; MacGibbon, G.A.; Sirimanne, E.; Saura, J.; Gluckman, P.D.; Dragunow, M. PU.1 expression in microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 104, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenova, A.A.; Herbinet, M.; Gupta, I.; Machlovi, S.I.; Bowles, K.R.; Marcora, E.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s-associated PU.1 expression levels regulate microglial inflammatory response. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 148, 105217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Smith, A.M.; Smyth, L.C.; Jansson, D.; Scotter, E.L.; Swanson, M.E.V.; Aalderink, M.; Coppieters, N.; Narayan, P.; Handley, R.; et al. PU.1 regulates Alzheimer’s disease-associated genes in primary human microglia. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Liu, K.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J. Transcriptional mechanism of IRF8 and PU.1 governs microglial activation in neurodegenerative condition. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juhas, U.; Ryba-Stanislawowska, M.; Szargiej, P.; Mysliwska, J. Different pathways of macrophage activation and polarization. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T.; Natoli, G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerian, L.; Ghorbani, S.; Talebi, F.; Noorbakhsh, F. MicroRNA-150 targets PU.1 and regulates macrophage differentiation and function in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.; Gao, Y.F.; Ji, J.; Sun, Y.Q.; Li, J.L.; Qi, F.; Zhang, N.; Jin, L.Y.; Xue, B.; Yang, T.; et al. Bu Shen Yi Sui Capsule Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Demyelination by Promoting Microglia toward M2 Polarization, Which Correlates with Changes in miR-124 and miR-155 in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 5521503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremona, M.L.; Matthies, H.J.; Pau, K.; Bowton, E.; Speed, N.; Lute, B.J.; Anderson, M.; Sen, N.; Robertson, S.D.; Vaughan, R.A.; et al. Flotillin-1 is essential for PKC-triggered endocytosis and membrane microdomain localization of DAT. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, L.; Gong, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Li, J. Flotillin-1 promotes tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor signaling and activation of NF-kappaB in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 995–1005.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Toomre, D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legler, D.F.; Micheau, O.; Doucey, M.A.; Tschopp, J.; Bron, C. Recruitment of TNF receptor 1 to lipid rafts is essential for TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Immunity 2003, 18, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonnino, S.; Aureli, M.; Grassi, S.; Mauri, L.; Prioni, S.; Prinetti, A. Lipid rafts in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, Z.; Lin, X.; Yu, C.; Shi, T.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Song, L. Knockdown of FLOT1 impairs cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in breast cancer through upregulation of FOXO3a. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3089–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, A.; Otto, G.P.; Riento, K.; Hams, E.; Fallon, P.G.; Nichols, B.J. Flotillin microdomains interact with the cortical cytoskeleton to control uropod formation and neutrophil recruitment. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Xu, G.; Ni, Y. Expression of CCL2 and its receptor in activation and migration of microglia and monocytes induced by photoreceptor apoptosis. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rutar, M.; Natoli, R.; Valter, K.; Provis, J.M. Early focal expression of the chemokine Ccl2 by Muller cells during exposure to damage-inducing bright continuous light. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammes, H.P.; Martin, S.; Federlin, K.; Geisen, K.; Brownlee, M. Aminoguanidine treatment inhibits the development of experimental diabetic retinopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11555–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Bierhaus, A.; Bugert, P.; Dietrich, N.; Feng, Y.; Vom Hagen, F.; Nawroth, P.; Brownlee, M.; Hammes, H.P. Effect of R-(+)-alpha-lipoic acid on experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Abramsson, A.; Betsholtz, C. Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, N.; Hammes, H.P. Retinal digest preparation: A method to study diabetic retinopathy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 933, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, F.; Feng, Y.; vom Hagen, F.; Hoffmann, S.; Molema, G.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Shani, M.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P. Pericyte migration: A novel mechanism of pericyte loss in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, P.Y.; Su, D.F.; Liu, X. miRNA-124 in Immune System and Immune Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutescu, R.M.; Skosyrski, S.; Kociok, N.; Semkova, I.; Mergler, S.; Atorf, J.; Joussen, A.M.; Strauss, O.; Kremers, J. Multifocal ERG recordings under visual control of the stimulated fundus in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Gene Name | Reference Number * |
|---|---|
| Arg1 | Rn00567522_m1 |
| CCL2 | Rn00580555_m1 |
| CCL3 | Rn01464736_g1 |
| CD74 | Rn00565062_m1 |
| Cebp-α | Rn00560963_s1 |
| IL-1ß | Rn00580432_m1 |
| IL-10 | Rn00563409_m1 |
| IFN-γ | Rn00594078_m1 |
| Gapdh | Rn99999916_s1 |
| MHC-II | Rn01428452_m1 |
| Spi1/PU.1 | Rn01513815_m1 |
| TGF-ß1 | Rn00572010_m1 |
| TNF-α | Rn01525859_g1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Schlotterer, A.; Kurowski, L.; Hoffmann, S.; Hammad, S.; Dooley, S.; Buchholz, M.; Hu, J.; Fleming, I.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011068
Chen Y, Lin J, Schlotterer A, Kurowski L, Hoffmann S, Hammad S, Dooley S, Buchholz M, Hu J, Fleming I, et al. MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):11068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011068
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ying, Jihong Lin, Andrea Schlotterer, Luke Kurowski, Sigrid Hoffmann, Seddik Hammad, Steven Dooley, Malte Buchholz, Jiong Hu, Ingrid Fleming, and et al. 2021. "MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 11068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011068
APA StyleChen, Y., Lin, J., Schlotterer, A., Kurowski, L., Hoffmann, S., Hammad, S., Dooley, S., Buchholz, M., Hu, J., Fleming, I., & Hammes, H. -P. (2021). MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 11068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011068