Linear Ubiquitination Mediates EGFR-Induced NF-κB Pathway and Tumor Development
Abstract
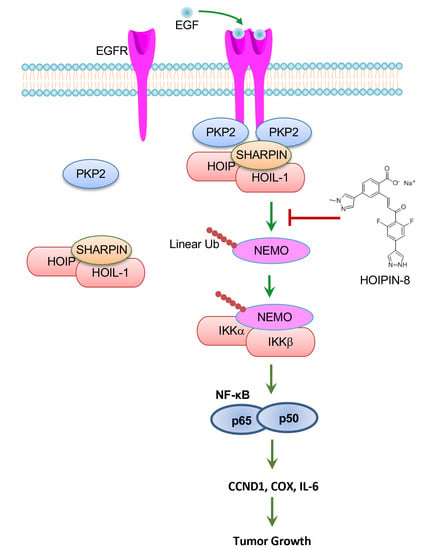
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PKP2 Is Required for EGFR-Induced NF-κB Activation
2.2. PKP2 Interacts with HOIP
2.3. PKP2 Activates NF-κB via HOIP
2.4. EGFR Activates Linear Ubiquitination and NF-κB via HOIP
2.5. Deficiency of HOIP Suppresses A431 Cell Proliferation and Tumor Development
2.6. HOIP Inhibitor Suppresses A431 Cell Proliferation and Tumor Development
2.7. HOIP Inhibitor Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Clonogenicity by Blocking EGFR-Mediated NF-κB Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Plasmids
4.4. Antibodies
4.5. Sample Preparation, Western Blotting, and Immunoprecipitation
4.6. MTT Assays
4.7. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.8. Real-Time PCR
4.9. Plasmid Transfection
4.10. Knockout by CRISPR/Cas9
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Zhang, P. EGFR-mediated autophagy in tumourigenesis and therapeutic resistance. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykosky, J.; Fenton, T.; Furnari, F.; Cavenee, W.K. Therapeutic targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancer: Successes and limitations. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6550–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shostak, K.; Chariot, A. EGFR and NF-kappaB: Partners in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, Y.; Taraborrelli, L.; Walczak, H. Linear ubiquitination in immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haas, T.L.; Emmerich, C.H.; Gerlach, B.; Schmukle, A.C.; Cordier, S.M.; Rieser, E.; Feltham, R.; Vince, J.; Warnken, U.; Wenger, T.; et al. Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, F.; Sakata, S.; Saeki, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Kirisako, T.; Kamei, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Kato, M.; Murata, S.; Yamaoka, S.; et al. Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-kappaB activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakahara, M.; Saeki, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Sakata, S.; Tanaka, K.; Nakano, H.; Iwai, K. SHARPIN is a component of the NF-kappaB-activating linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex. Nature 2011, 471, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, F.; Deribe, Y.L.; Skanland, S.S.; Stieglitz, B.; Grabbe, C.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; van Wijk, S.J.; Goswami, P.; Nagy, V.; Terzic, J.; et al. SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-kappaB activity and apoptosis. Nature 2011, 471, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, B.; Cordier, S.M.; Schmukle, A.C.; Emmerich, C.H.; Rieser, E.; Haas, T.L.; Webb, A.I.; Rickard, J.A.; Anderton, H.; Wong, W.W.; et al. Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling. Nature 2011, 471, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Berman, M.A.; Dorf, M.E. The ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2L3 regulates TNFalpha-induced linear ubiquitination. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostager, B.S.; Fox, D.K.; Whitten, D.; Wilkerson, C.G.; Eipper, B.A.; Francone, V.P.; Rothman, P.B.; Colgan, J.D. HOIL-1L interacting protein (HOIP) as an NF-kappaB regulating component of the CD40 signaling complex. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zak, D.E.; Schmitz, F.; Gold, E.S.; Diercks, A.H.; Peschon, J.J.; Valvo, J.S.; Niemisto, A.; Podolsky, I.; Fallen, S.G.; Suen, R.; et al. Systems analysis identifies an essential role for SHANK-associated RH domain-interacting protein (SHARPIN) in macrophage Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11536–11541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damgaard, R.B.; Nachbur, U.; Yabal, M.; Wong, W.W.; Fiil, B.K.; Kastirr, M.; Rieser, E.; Rickard, J.A.; Bankovacki, A.; Peschel, C.; et al. The ubiquitin ligase XIAP recruits LUBAC for NOD2 signaling in inflammation and innate immunity. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, J.; Shi, Y.; Iwai, K.; Wu, Z.H. LUBAC regulates NF-kappaB activation upon genotoxic stress by promoting linear ubiquitination of NEMO. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3741–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzfeld, M. The armadillo family of structural proteins. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1999, 186, 179–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bass-Zubek, A.E.; Godsel, L.M.; Delmar, M.; Green, K.J. Plakophilins: Multifunctional scaffolds for adhesion and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Fu, B.; Li, W.; Patil, G.; Liu, L.; Dorf, M.E.; Li, S. Comparative influenza protein interactomes identify the role of plakophilin 2 in virus restriction. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, K.; Burkart, C.; Yan, M.; Ran, D.; Weng, S.; Zhang, D.E. Plakophilin-2 promotes tumor development by enhancing ligand-dependent and -independent epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization and activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kupka, S.; De Miguel, D.; Draber, P.; Martino, L.; Surinova, S.; Rittinger, K.; Walczak, H. SPATA2-Mediated Binding of CYLD to HOIP Enables CYLD Recruitment to Signaling Complexes. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Carpenter, G. Epidermal growth factor activation of NF-kappaB is mediated through IkappaBalpha degradation and intracellular free calcium. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikawa, D.; Sato, Y.; Ohtake, F.; Komakura, K.; Hanada, K.; Sugawara, K.; Terawaki, S.; Mizukami, Y.; Phuong, H.T.; Iio, K.; et al. Molecular bases for HOIPINs-mediated inhibition of LUBAC and innate immune responses. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Bu, W.; Zhang, L.; You, M.J.; Koh, M.Y.; Cote, G.; Aldape, K.; et al. EGFR-induced and PKCepsilon monoubiquitylation-dependent NF-kappaB activation upregulates PKM2 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, D.K.; Shi, Q.; Baily, S.; Strickland, I.; Ghosh, S.; Pardee, A.B.; Iglehart, J.D. NF-kappa B activation in human breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10137–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Grabiner, B.; Zhu, Y.F.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, H.X.; You, Y.; Lang, J.Y.; Hung, M.C.; Lin, X. CARMA3 is Crucial for EGFR-Induced Activation of NF-kappa B and Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pianetti, S.; Arsura, M.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Coffey, R.J.; Sonenshein, G.E. Her-2/neu overexpression induces NF-kappaB via a PI3-kinase/Akt pathway involving calpain-mediated degradation of IkappaB-alpha that can be inhibited by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkhofer, E.C.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. Her2 activates NF-kappa B and induces invasion through the canonical pathway involving IKK alpha. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates nuclear factor-kappaB through IkappaBalpha kinase-independent but EGF receptor-kinase dependent tyrosine 42 phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, A.A.; Chatterjee, S.; Park, S.K.; Ratan, R.R.; Lefebvre, S.; Vartanian, T. The epidermal growth factor receptor engages receptor interacting protein and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B)-inducing kinase to activate NF-kappa B. Identification of a novel receptor-tyrosine kinase signalosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8865–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puliyappadamba, V.T.; Chakraborty, S.; Chauncey, S.S.; Li, L.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Mickey, B.; Noorani, S.; Shu, H.K.; Burma, S.; Boothman, D.A.; et al. Opposing effect of EGFRWT on EGFRvIII-mediated NF-kappaB activation with RIP1 as a cell death switch. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, K.; Babic, I.; Nathanson, D.; Akhavan, D.; Guo, D.; Gini, B.; Dang, J.; Zhu, S.; Yang, H.; De Jesus, J.; et al. Oncogenic EGFR signaling activates an mTORC2-NF-kappaB pathway that promotes chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowicka, A.M.; Hauselmann, I.; Borsig, L.; Bolduan, S.; Schindler, M.; Schraml, P.; Heikenwalder, M.; Moch, H. A novel pVHL-independent but NEMO-driven pathway in renal cancer promotes HIF stabilization. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3125–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Song, K.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Patil, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Hua, F.; Fu, B.; Schwamborn, J.C.; et al. Non-proteolytic ubiquitination of OTULIN regulates NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 12, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.R.; Nielsen, S.V.; Marco-Casanova, P.; Fiil, B.K.; Keusekotten, K.; Mailand, N.; Freund, S.M.; Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Komander, D. Molecular basis and regulation of OTULIN-LUBAC interaction. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, V.; Akutsu, M.; Olma, M.H.; Gomes, L.C.; Kawasaki, M.; Dikic, I. Binding of OTULIN to the PUB domain of HOIP controls NF-kappaB signaling. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Ponnusamy, S.; Chi, Y.; Xue, J.; Fahmy, B.; Fan, M.; Miranda-Carboni, G.A.; Narayanan, R.; Wu, J.; et al. ABL1-dependent OTULIN phosphorylation promotes genotoxic Wnt/beta-catenin activation to enhance drug resistance in breast cancers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Zhao, X.M.; Yoon, I.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, N.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.; Moon, H.G.; et al. Integrative analysis of mutational and transcriptional profiles reveals driver mutations of metastatic breast cancers. Cell Discov. 2016, 2, 16025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mertens, C.; Kuhn, C.; Moll, R.; Schwetlick, I.; Franke, W.W. Desmosomal plakophilin 2 as a differentiation marker in normal and malignant tissues. Differentiation 1999, 64, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.S.; Culhane, A.C.; Chan, M.W.; Venkataramu, C.R.; Ehrich, M.; Nasir, A.; Rodriguez, B.A.; Liu, J.; Yan, P.S.; Quackenbush, J.; et al. Epithelial progeny of estrogen-exposed breast progenitor cells display a cancer-like methylome. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papagerakis, S.; Shabana, A.H.; Depondt, J.; Gehanno, P.; Forest, N. Immunohistochemical localization of plakophilins (PKP1, PKP2, PKP3, and p0071) in primary oropharyngeal tumors: Correlation with clinical parameters. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.; Ayim, A.; Schmidt, A.; Jager, S.; Koch, S.; Baumann, R.; Dunne, A.A.; Moll, R. Differential expression of desmosomal plakophilins in various types of carcinomas: Correlation with cell type and differentiation. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakatsuji, H.; Takahashi, M.; Avirmed, S.; Fukawa, T.; Takemura, M.; Fukumori, T.; Kanayama, H. Up-regulation of plakophilin-2 and Down-regulation of plakophilin-3 are correlated with invasiveness in bladder cancer. Urology 2012, 79, 240.e1–240.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, C.; Carroll, E.; Ibrahim, A.F.M.; Garg, A.; Inman, G.J.; Hay, R.T.; Alpi, A.F. E3 ubiquitin ligase HOIP attenuates apoptotic cell death induced by cisplatin. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peltzer, N.; Rieser, E.; Taraborrelli, L.; Draber, P.; Darding, M.; Pernaute, B.; Shimizu, Y.; Sarr, A.; Draberova, H.; Montinaro, A.; et al. HOIP deficiency causes embryonic lethality by aberrant TNFR1-mediated endothelial cell death. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, T.; Nishikori, M.; Kogure, Y.; Arima, H.; Sasaki, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Iwai, F.; Momose, S.; Shiraishi, A.; et al. LUBAC accelerates B-cell lymphomagenesis by conferring resistance to genotoxic stress on B cells. Blood 2020, 136, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queisser, M.A.; Dada, L.A.; Deiss-Yehiely, N.; Angulo, M.; Zhou, G.; Kouri, F.M.; Knab, L.M.; Liu, J.; Stegh, A.H.; DeCamp, M.M.; et al. HOIL-1L functions as the PKCzeta ubiquitin ligase to promote lung tumor growth. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, E.J.; Diefenbacher, M.E.; Nelson, J.K.; Sancho, R.; Pucci, F.; Chakraborty, A.; Moreno, P.; Annibaldi, A.; Liccardi, G.; Encheva, V.; et al. LUBAC determines chemotherapy resistance in squamous cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Construct Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| PKP2 N109 | gtcataggttttaggaacaggggaacg | gaggattacaaggatgacgacg | Mutagenesis |
| PKP2 N251 | gctgcggctggtccctggcctgg | gaggattacaaggatgacgacg | Mutagenesis |
| PKP2 110-251 | gcactcgagatgctaaaggctggcacaactgc | gtaaagcttgctgcggctggtccctgg | Cloning: XhoI, HindIII |
| PKP2 252-348 | gcactcgagatgggcaacctcttggagaaggag | gtaaagcttgtctgcattccccagctgggag | Cloning: XhoI, HindIII |
| PKP2 110-348 | gcactcgagatgctaaaggctggcacaactgc | gtaaagcttgtctgcattccccagctgggag | Cloning: XhoI, HindIII |
| EGFR N985 | aaggtagcgctgggggtctc | gaggattacaaggatgacgacg | Mutagenesis |
| EGFR KD | gcactcgaggccaccatgatcttgaaggaaactgaattc | gtagcggccgcttcatccccctgaatgacaaggtagc | Cloning: XhoI, NotI |
| HOIP N698 | gcagcggccgcatgccgggggaggaagag | gtaatcgatctcctgggcaagcaagcg | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP N563 | gcagcggccgcatgccgggggaggaagag | gtaatcgatgccatgacgatccagccaggctc | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP N349 | gcagcggccgcatgccgggggaggaagag | gtaatcgataagatcaggttctaggcctccag | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP C298 | gcagcggccgcatggcaagtgctcatttgccctggcac | gtaatcgatcttccgcctgcgggggatac | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP C563 | gcagcggccgcatgggcaaccttgatgaagctgtggag | gtaatcgatcttccgcctgcgggggatac | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP C698 | gcagcggccgcatggagtgtgccgtgtgtggctgg | gtaatcgatcttccgcctgcgggggatac | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
| HOIP NZF1/2 | gcagcggccgcatgggaggcctagaacctgatc | gtaatcgatggcatgttgtgctggaatgg | Cloning: ClaI, NotI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, F.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Linear Ubiquitination Mediates EGFR-Induced NF-κB Pathway and Tumor Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11875. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111875
Hua F, Hao W, Wang L, Li S. Linear Ubiquitination Mediates EGFR-Induced NF-κB Pathway and Tumor Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11875. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111875
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Fang, Wenzhuo Hao, Lingyan Wang, and Shitao Li. 2021. "Linear Ubiquitination Mediates EGFR-Induced NF-κB Pathway and Tumor Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11875. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111875
APA StyleHua, F., Hao, W., Wang, L., & Li, S. (2021). Linear Ubiquitination Mediates EGFR-Induced NF-κB Pathway and Tumor Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11875. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111875