Investigating the Endo-Lysosomal System in Major Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Lewy Body Disease: Evidence for SORL1 as a Cross-Disease Gene
Abstract
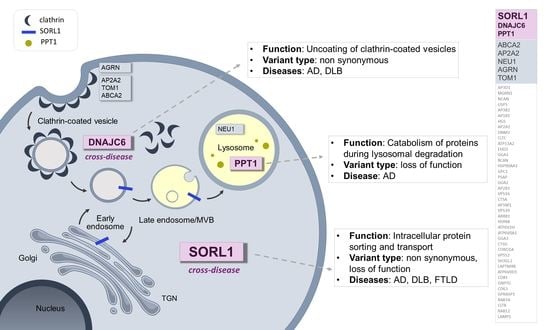
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Previously Reported Disease-Associated Variants and Predicted Null Variants
2.2. Association Analyses of the Endo-Lysosomal Pathway Genes Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Other Neurological Disorders
2.3. Multiple Variant Carriers in the Endo-Lysosomal Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Gene Selection
4.3. Genetic Analyses
4.4. Variant Annotation, Filtering and Bioinformatics
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathological Aspects of Alzheimer Disease, Parkinson Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Neurodegener Dis. 2008, 5, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Estrada, L.D. Protein Misfolding and Neurodegeneration. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brion, J.P. Neurofibrillary Tangles and Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 40, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Domingo-Sàbat, M.; Ariza, A. Molecular Pathology of Lewy Body Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 724–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.A. Review: Neuropathology of Non-Tau Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2019, 45, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathological Assessment of the Alzheimer Spectrum. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1229–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M. NEURODEGENERATION. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: The Prion Concept in Relation to Assembled Aβ, Tau, and A-Synuclein. Science 2015, 349, 1255555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, L.; Bali, J.; Barr, M.M.; Court, F.A.; Krämer-Albers, E.M.; Picou, F.; Raposo, G.; van der Vos, K.E.; van Niel, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15482–15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Schapira, A.H.; Gardiner, C.; Sargent, I.L.; Wood, M.J.; Cooper, J.M. Lysosomal Dysfunction Increases Exosome-Mediated Alpha-Synuclein Release and Transmission. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.B.; Dammer, E.B.; Ren, R.J.; Wang, G. The Endosomal-Lysosomal System: From Acidification and Cargo Sorting to Neurodegeneration. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Yu, W.H.; Kumar, A.; Lee, S.; Mohan, P.S.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Wolfe, D.M.; Martinez-Vicente, M.; Massey, A.C.; Sovak, G.; et al. Lysosomal Proteolysis and Autophagy Require Presenilin 1 and are Disrupted by Alzheimer-Related PS1 Mutations. Cell 2010, 141, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casterton, R.L.; Hunt, R.J.; Fanto, M. Pathomechanism Heterogeneity in the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia Disease Spectrum: Providing Focus through the Lens of Autophagy. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2692–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, H.; Zhang, J.; Makinson, S.R.; Cahill, M.K.; Kelley, K.W.; Huang, H.Y.; Shang, Y.; Oldham, M.C.; Martens, L.H.; Gao, F.; et al. Progranulin Deficiency Promotes Circuit-Specific Synaptic Pruning by Microglia Via Complement Activation. Cell 2016, 165, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benussi, L.; Ciani, M.; Tonoli, E.; Morbin, M.; Palamara, L.; Albani, D.; Fusco, F.; Forloni, G.; Glionna, M.; Baco, M.; et al. Loss of Exosomes in Progranulin-Associated Frontotemporal Dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 40, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Damiano, J.; Franceschetti, S.; Carpenter, S.; Canafoglia, L.; Morbin, M.; Rossi, G.; Pareyson, D.; Mole, S.E.; Staropoli, J.F.; et al. Strikingly Different Clinicopathological Phenotypes Determined by Progranulin-Mutation Dosage. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Rourke, J.G.; Bogdanik, L.; Yáñez, A.; Lall, D.; Wolf, A.J.; Muhammad, A.K.; Ho, R.; Carmona, S.; Vit, J.P.; Zarrow, J.; et al. C9orf72 is Required for Proper Macrophage and Microglial Function in Mice. Science 2016, 351, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hwang, R.D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J. NDST3 Deacetylates A-Tubulin and Suppresses V-ATPase Assembly and Lysosomal Acidification. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Casey, A.E.; Sargeant, T.J.; Mäkinen, V.P. Genetic Variation within Endolysosomal System is Associated with Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2018, 141, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Hernandez, D.G.; Nalls, M.A.; Rohrer, J.D.; Ramasamy, A.; Kwok, J.B.; Dobson-Stone, C.; Brooks, W.S.; Schofield, P.R.; Halliday, G.M.; et al. Frontotemporal Dementia and its Subtypes: A Genome-Wide Association Study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, A.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Diez-Fairen, M.; Quinn, J.P.; Billingsley, K.J. Genetic Risk Profiling in Parkinson’s Disease and Utilizing Genetics to Gain Insight into Disease-Related Biological Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longobardi, A.; Benussi, L.; Nicsanu, R.; Bellini, S.; Ferrari, C.; Saraceno, C.; Zanardini, R.; Catania, M.; Di Fede, G.; Squitti, R.; et al. Plasma Extracellular Vesicle Size and Concentration are Altered in Alzheimer’s Disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies, and Frontotemporal Dementia. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 667369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglayan, S.; Bauerfeind, A.; Schmidt, V.; Carlo, A.S.; Prabakaran, T.; Hübner, N.; Willnow, T.E. Identification of Alzheimer Disease Risk Genotype that Predicts Efficiency of SORL1 Expression in the Brain. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogaeva, E.; Meng, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Kawarai, T.; Zou, F.; Katayama, T.; Baldwin, C.T.; Cheng, R.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. The Neuronal Sortilin-Related Receptor SORL1 is Genetically Associated with Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardarajan, B.N.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cheng, R.; Bohm, C.; Ghani, M.; Reitz, C.; Reyes-Dumeyer, D.; Shen, Y.; Rogaeva, E.; et al. Coding Mutations in SORL1 and Alzheimer Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olgiati, S.; Quadri, M.; Fang, M.; Rood, J.P.; Saute, J.A.; Chien, H.F.; Bouwkamp, C.G.; Graafland, J.; Minneboo, M.; Breedveld, G.J.; et al. DNAJC6 Mutations Associated with Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guennec, K.; Tubeuf, H.; Hannequin, D.; Wallon, D.; Quenez, O.; Rousseau, S.; Richard, A.C.; Deleuze, J.F.; Boland, A.; Frebourg, T.; et al. Biallelic Loss of Function of SORL1 in an Early Onset Alzheimer’s Disease Patient. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, S.; Takagi-Niidome, S.; Liao, F.; Carlo, A.S.; Schmidt, V.; Burgert, T.; Kitago, Y.; Füchtbauer, E.M.; Füchtbauer, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; et al. Lysosomal Sorting of Amyloid-Β by the SORLA Receptor is Impaired by a Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 223ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, C.; Hannequin, D.; Coutant, S.; Rovelet-Lecrux, A.; Wallon, D.; Rousseau, S.; Legallic, S.; Paquet, C.; Bombois, S.; Pariente, J.; et al. High Frequency of Potentially Pathogenic SORL1 Mutations in Autosomal Dominant Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, J.; Van den Bossche, T.; van der Zee, J.; Engelborghs, S.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Lladó, A.; Graff, C.; Thonberg, H.; Pastor, P.; Ortega-Cubero, S.; et al. A Comprehensive Study of the Genetic Impact of Rare Variants in SORL1 in European Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, S.L.; Das, A.K.; Yi, W.; Lu, J.Y.; Wisniewski, K.E. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis due to Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase Deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 1999, 66, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diggelen, O.P.; Thobois, S.; Tilikete, C.; Zabot, M.T.; Keulemans, J.L.; van Bunderen, P.A.; Taschner, P.E.; Losekoot, M.; Voznyi, Y.V. Adult Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis with Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase Deficiency: First Adult-Onset Patients of a Childhood Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.T.; Liao, Y.C.; Lee, W.J.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L. SORL1 Gene, Plasma Biomarkers, and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease for the Han Chinese Population in Taiwan. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciani, M.; Bonvicini, C.; Scassellati, C.; Carrara, M.; Maj, C.; Fostinelli, S.; Binetti, G.; Ghidoni, R.; Benussi, L. The Missing Heritability of Sporadic Frontotemporal Dementia: New Insights from Rare Variants in Neurodegenerative Candidate Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiromerisiou, G.; Bourinaris, T.; Houlden, H.; Lewis, P.A.; Senkevich, K.; Hammer, M.; Federoff, M.; Khan, A.; Spanaki, C.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; et al. SORL1 Mutation in a Greek Family with Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gialluisi, A.; Reccia, M.G.; Modugno, N.; Nutile, T.; Lombardi, A.; Di Giovannantonio, L.G.; Pietracupa, S.; Ruggiero, D.; Scala, S.; Gambardella, S.; et al. Identification of Sixteen Novel Candidate Genes for Late Onset Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener 2021, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köroğlu, Ç.; Baysal, L.; Cetinkaya, M.; Karasoy, H.; Tolun, A. DNAJC6 is Responsible for Juvenile Parkinsonism with Phenotypic Variability. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladeokin, A.C.; Akiyama, T.; Kimura, A.; Kimura, Y.; Takahashi-Jitsuki, A.; Nakamura, H.; Makihara, H.; Masukawa, D.; Nakabayashi, J.; Hirano, H.; et al. Network-Guided Analysis of Hippocampal Proteome Identifies Novel Proteins that Colocalize with Aβ in a Mice Model of Early-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Modeste, E.; Dammer, E.; Merino, P.; Taylor, G.; Duong, D.M.; Deng, Q.; Holler, C.J.; Gearing, M.; Dickson, D.; et al. Network Analysis of the Progranulin-Deficient Mouse Brain Proteome Reveals Pathogenic Mechanisms Shared in Human Frontotemporal Dementia Caused by GRN Mutations. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathews, P.M.; Levy, E. Exosome Production is Key to Neuronal Endosomal Pathway Integrity in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Telpoukhovskaia, M.A.; Bahr, B.A.; Chen, X.; Gan, L. Endo-Lysosomal Dysfunction: A Converging Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Tuck, E.; Stubbs, V.; van der Lee, S.J.; Aalfs, C.; van Spaendonk, R.; Scheltens, P.; Hardy, J.; Holstege, H.; Livesey, F.J. SORL1 Deficiency in Human Excitatory Neurons Causes APP-Dependent Defects in the Endolysosome-Autophagy Network. Cell. Rep. 2021, 35, 109259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Becerra, C.H.; Yi, W.; Lu, J.Y.; Siakotos, A.N.; Wisniewski, K.E.; Hofmann, S.L. Molecular genetics of palmitoyl-protein thioesterase deficiency in the U.S. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 102, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benussi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; Pegoiani, E.; Moretti, D.V.; Zanetti, O.; Binetti, G. Progranulin Leu271LeufsX10 is One of the most Common FTLD and CBS Associated Mutations Worldwide. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Park, M. Palmitoylation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, D.; Charbonnier, C.; Nicolas, G. SORL1 Genetic Variants and Alzheimer Disease Risk: A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Sequencing Data. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.M.; Schmidt, V.; Spoelgen, R.; Gliemann, J.; Behlke, J.; Galatis, D.; McKinstry, W.J.; Parker, M.W.; Masters, C.L.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. Molecular Dissection of the Interaction between Amyloid Precursor Protein and its Neuronal Trafficking Receptor SorLA/LR11. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 2618–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Kuzuya, A.; Tanigawa, K.; Araki, M.; Kawai, R.; Ma, B.; Sasakura, Y.; Maesako, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; et al. Fibronectin Type III Domain-Containing Protein 5 Interacts with APP and Decreases Amyloid Β Production in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, E.; Greene, L.E. Multiple Roles of Auxilin and hsc70 in Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Traffic 2007, 8, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yim, Y.I.; Sun, T.; Wu, L.G.; Raimondi, A.; De Camilli, P.; Eisenberg, E.; Greene, L.E. Endocytosis and Clathrin-Uncoating Defects at Synapses of Auxilin Knockout Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4412–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edvardson, S.; Cinnamon, Y.; Ta-Shma, A.; Shaag, A.; Yim, Y.I.; Zenvirt, S.; Jalas, C.; Lesage, S.; Brice, A.; Taraboulos, A.; et al. A Deleterious Mutation in DNAJC6 Encoding the Neuronal-Specific Clathrin-Uncoating Co-Chaperone Auxilin, is Associated with Juvenile Parkinsonism. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beilina, A.; Bonet-Ponce, L.; Kumaran, R.; Kordich, J.J.; Ishida, M.; Mamais, A.; Kaganovich, A.; Saez-Atienzar, S.; Gershlick, D.C.; Roosen, D.A.; et al. The Parkinson’s Disease Protein LRRK2 Interacts with the GARP Complex to Promote Retrograde Transport to the Trans-Golgi Network. Cell. Rep. 2020, 31, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarouchlioti, C.; Parfitt, D.A.; Li, W.; Gittings, L.M.; Cheetham, M.E. DNAJ Proteins in Neurodegeneration: Essential and Protective Factors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alabi, S.B.; Crews, C.M. Major Advances in Targeted Protein Degradation: PROTACs, LYTACs, and MADTACs. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ouyang, L. Targeting Lysosomal Degradation Pathways: New Strategies and Techniques for Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3493–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of Primary Progressive Aphasia and its Variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Fourth Consensus Report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group Under the Auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rascovsky, K.; Hodges, J.R.; Knopman, D.; Mendez, M.F.; Kramer, J.H.; Neuhaus, J.; van Swieten, J.C.; Seelaar, H.; Dopper, E.G.; Onyike, C.U.; et al. Sensitivity of Revised Diagnostic Criteria for the Behavioural Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain 2011, 134, 2456–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–947. [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A.; Myers, R.H.; Connor, L.; Cupples, L.A.; Growdon, J.H. Segregation Analysis Reveals Evidence of a Major Gene for Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1991, 48, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Fostinelli, S.; Ciani, M.; Zanardini, R.; Zanetti, O.; Binetti, G.; Ghidoni, R.; Benussi, L. The Heritability of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Validation of Pedigree Classification Criteria in a Northern Italy Cohort. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.S.; Farmer, J.M.; Wood, E.M.; Johnson, J.K.; Boxer, A.; Neuhaus, J.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; Wilhelmsen, K.C.; Lee, V.M.; Grossman, M.; et al. Comparison of Family Histories in FTLD Subtypes and Related Tauopathies. Neurology 2005, 65, 1817–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacace, R.; Heeman, B.; Van Mossevelde, S.; De Roeck, A.; Hoogmartens, J.; De Rijk, P.; Gossye, H.; De Vos, K.; De Coster, W.; Strazisar, M.; et al. Loss of DPP6 in Neurodegenerative Dementia: A Genetic Player in the Dysfunction of Neuronal Excitability. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolders, S.; Philtjens, S.; Crosiers, D.; Sieben, A.; Hens, E.; Heeman, B.; Van Mossevelde, S.; Pals, P.; Asselbergh, B.; Dos Santos Dias, R.; et al. Contribution of Rare Homozygous and Compound Heterozygous VPS13C Missense Mutations to Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rheenen, W.; Pulit, S.L.; Dekker, A.M.; Al Khleifat, A.; Brands, W.J.; Iacoangeli, A.; Kenna, K.P.; Kavak, E.; Kooyman, M.; McLaughlin, R.L.; et al. Project MinE: Study Design and Pilot Analyses of a Large-Scale Whole-Genome Sequencing Study in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Spek, R.A.A.; van Rheenen, W.; Pulit, S.L.; Kenna, K.P.; van den Berg, L.H.; Veldink, J.H.; Project MinE ALS Sequencing Consortium. The Project MinE Databrowser: Bringing Large-Scale Whole-Genome Sequencing in ALS to Researchers and the Public. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. Front. Degener 2019, 20, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing Next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reumers, J.; De Rijk, P.; Zhao, H.; Liekens, A.; Smeets, D.; Cleary, J.; Van Loo, P.; Van Den Bossche, M.; Catthoor, K.; Sabbe, B.; et al. Optimized Filtering Reduces the Error Rate in Detecting Genomic Variants by Short-Read Sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 30, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witvliet, D.K.; Strokach, A.; Giraldo-Forero, A.F.; Teyra, J.; Colak, R.; Kim, P.M. ELASPIC Web-Server: Proteome-Wide Structure-Based Prediction of Mutation Effects on Protein Stability and Binding Affinity. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, M.; Chang, H.Y.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Kandasaamy, S.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Qureshi, M.; Raj, S.; et al. The InterPro Protein Families and Domains Database: 20 Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D344–D354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P.; Casadio, R. I-Mutant2.0: Predicting Stability Changes upon Mutation from the Protein Sequence or Structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W306–W310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Randall, A.; Baldi, P. Prediction of Protein Stability Changes for Single-Site Mutations using Support Vector Machines. Proteins 2006, 62, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Emond, M.J.; Bamshad, M.J.; Barnes, K.C.; Rieder, M.J.; Nickerson, D.A.; NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project—ESP Lung Project Team; Christiani, D.C.; Wurfel, M.M.; Lin, X. Optimal Unified Approach for Rare-Variant Association Testing with Application to Small-Sample Case-Control Whole-Exome Sequencing Studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Fuchsberger, C.; Kim, S.; Scott, L. An Efficient Resampling Method for Calibrating Single and Gene-Based Rare Variant Association Analysis in Case-Control Studies. Biostatistics 2016, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| AD (n = 282) | DLB (n = 114) | FTLD (n = 301) | CTRL (n = 251) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (% Female) | 61.3 | 43.9 | 46.8 | 47.4 | 0.0005 1 |
| Age, years | 67.0 ± 9.8 | 75.2 ± 7.6 | 67.2 ± 10.1 | 62.0 ± 9.4 | <0.0001 2 |
| Age at disease onset, years | 65.0 ± 9.6 | 72.5 ± 8.2 | 64.4 ± 10.4 | - | <0.0001 2 |
| Gene | AA Change | Variant Type | dbSNP | ∆∆G Mu-Pro and I-Mutant | Diagnostic Group (Number of Carriers) | Previously Identified Diseases | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORL1 | p.N1246K | non synonymous | rs1699102 | −0.39288546 | −1.30 | AD (1) | AD [22,23] |
| p.N371T | non synonymous | rs150609294 | −1.2548181 | −0.66 | AD (1); FTLD (1) | AD [24] | |
| p.D2065V | non synonymous | rs140327834 | −0.28006864 | −0.57 | AD (4); DLB (2); FTLD (6) | AD [24] | |
| DNAJC6 | p.M133L | non synonymous | rs61757223 | n.a. | n.a. | AD (1); DLB (1) | PD [25] |
| Gene | AA Change | Variant Type | dbSNP | Diagnostic Group (Number of Carriers) | Previously Associated Diseases (LOF Mechanism) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPT1 | p.R48X | LOF | - | AD (1) | NCL [30,31] |
| SORL1 | p.R985X | LOF | rs372188860 | AD (1) | AD [26,27,28,29] |
| p.R1207X | LOF | rs774626685 | AD (1) |
| Gene | Function * | AA Change | Variant Type | Diagnostic Group | Disease Onset | Family History | Association with Neurodegenerative Diseases in the Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORL1 | Intracellular protein sorting/transport | N1246K | non synonymous | AD | 72 | F | AD—Genetic and molecular studies in humans [22,23,24,32] FTLD—Genetic studies in humans [33] PD—Genetic studies in humans [34] |
| N371T | non synonymous | AD | 53 | U | |||
| FTLD (bvFTD) | 72 | U | |||||
| D2065V | non synonymous | AD | 60 | F | |||
| AD | 61 | F | |||||
| AD | 50 | AS | |||||
| AD | 66 | F | |||||
| DLB | 74 | AS | |||||
| DLB | 68 | AS | |||||
| FTLD (bvFTD) | 63 | AS | |||||
| FTLD (bvFTD) | 75 | F | |||||
| FTLD | 62 | U | |||||
| FTLD (PPA) | 68 | F | |||||
| FTLD (bvFTD) | 76 | F | |||||
| FTLD (PPA) | 71 | AS | |||||
| R985X | LOF | AD | 46 | F | |||
| R1207X | LOF | AD | 68 | U | |||
| DNAJC6 | Uncoating of clathrin-coated vesicles | M133L | non synonymous | AD | 65 | U | PD—Genetic studies in humans [25,35,36] |
| DLB | 67 | U | |||||
| PPT1 | Catabolism of lipid-modified proteins during lysosomal degradation | R48X | LOF | AD | 61 | F | AD—Molecular studies in animal models [37] FTLD—Molecular studies in animal models [38] |
| Gene | Variant | gnomAD_NFE | CADD | Poly Phen2 | ∆∆GMu-Pro and I-Mutant | Diagnostic Group | p Value | MAP | p Value Fdr | p Value Bonf. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORL1 | p.D2065V | 0.00416 a | 28.5 | D | −0.28 | −0.57 | AD + DLB + FTLD | 0.031 | <0.001 | 0.611 | 1 |
| DLB | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.618 | 1 | |||||||
| FTLD | 0.021 | 0.004 | 0.656 | 1 | |||||||
| AGRN | p.V554M | 0.0065 a | 25.8 | D | −0.52 | 0.03 | DLB | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.618 | 1 |
| NEU1 | p.R397W | 0.00004617 b | 26.8 | D | −0.95 | −0.76 | DLB | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.618 | 1 |
| TOM1 | p.V67A | 0.00007169 b | 26.5 | D | −1.165 | −2.26 | DLB | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.618 | 1 |
| ABCA2 | p.H1449P | 0 c | 24.3 | D | n.a. | n.a. | DLB | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.618 | 1 |
| Gene | Diagnostic Group | Number of Variants | Number of Carriers | p Value Burden | p Value Skato | p Value Skat | p Value Fdr | p Value Bonf. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORL1 | AD + DLB + FTLD | 26 | 40 | 0.127 | 0.076 | 0.038 | 0.961 | 1 |
| FTLD | 19 | 26 | 0.025 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.481 | 0.963 | |
| DNAJC6 | DLB | 2 | 2 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.776 | 1 |
| NEU1 | DLB | 1 | 2 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.776 | 1 |
| AP2A2 | AD + DLB + FTLD | 7 | 18 | 0.037 | 0.058 | 0.392 | 0.522 | 1 |
| AD | 4 | 8 | 0.043 | 0.090 | 0.364 | 0.622 | 1 | |
| FTLD | 5 | 9 | 0.022 | 0.080 | 0.374 | 0.481 | 0.858 |
| Patient | Diagnostic Group | FTLD Subtype | Disease Onset | FH | Sex | Study Group | Variants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FTLD | PPA | 68 | F | M | Belgium | SORL1 p.D2065V a | GGA3 p.K99R a | - |
| 2 | AD | - | 68 | U | M | Belgium | SORL1 p.R1207X b | SORL1 p.D140N b | - |
| 3 | AD | - | 65 | U | M | Belgium | DNAJC6 p.M133L b | AGRN p.A897V a | - |
| 4 | AD | - | 61 | F | F | Belgium | PPT1p.R48X b | GNPTG p.R66Q b | - |
| 5 | FTLD | PPA | 57 | F (low) * | F | Italy | SORL1 p.S1167Y b | ABCA2 p.H1449P c | GPC1 p.R90W b |
| 6 | FTLD | PPA | 63 | AS | F | Italy | SORL1 p.R729W b | CTSA p.P330A b | GGA3 p.P235L b |
| 7 | FTLD | bvFTD | 82 | F (low) * | M | Italy | SORL1 V2097I a | ABCA2 S1378F b | - |
| 8 | FTLD | - | 66 | F | M | Belgium | SORL1 p.S636T a | VPS39 p.V473M b | |
| 9 | FTLD | - | 49 | AS | F | Belgium | VPS52 p.Y508C b | VPS52 p.R578W b | - |
| 10 | FTLD | bvFTD + IBM | 70 | F | M | Belgium | AGRN p.R956H b | CD81 p.G129R b | HGS p.L525V b |
| 11 | FTLD | PPA | 50 | F | M | Italy | ABCA2 p.H1449P c | ATP6V0D1 c.C817-2A c | - |
| 12 | FTLD | bvFTD | 59 | F (medium) * | M | Italy | ABCA2 p.H1449P c | GGA2 p.L83I b | - |
| 13 | FTLD | PPA | 60 | F (high) * | M | Italy | AGRN p.V1691M b | ATP6V0D1 c.C817-2A c | - |
| 14 | FTLD | PPA | 54 | F (high) * | M | Italy | DNM2 p.R318W b | ATP6V0D1 c.C817-2A c | - |
| 15 | DLB | - | 70 | F | M | Italy | GGA2 p.S39W c | GGA3 p.P40R b | - |
| 16 | FTLD | bvFTD | 65 | F | M | Belgium | GGA2 p.R105G b | VPS39 p.F573L b | - |
| 17 | FTLD | bvFTD | 39 | AS | F | Belgium | GNPTG p.R186W c | MGRN1 p.P67L c | - |
| 18 | DLB | - | 78 | F | M | Belgium | NEU1 p.R397W b | TOM1 p.V67A b | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benussi, L.; Longobardi, A.; Kocoglu, C.; Carrara, M.; Bellini, S.; Ferrari, C.; Nicsanu, R.; Saraceno, C.; Bonvicini, C.; Fostinelli, S.; et al. Investigating the Endo-Lysosomal System in Major Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Lewy Body Disease: Evidence for SORL1 as a Cross-Disease Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413633
Benussi L, Longobardi A, Kocoglu C, Carrara M, Bellini S, Ferrari C, Nicsanu R, Saraceno C, Bonvicini C, Fostinelli S, et al. Investigating the Endo-Lysosomal System in Major Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Lewy Body Disease: Evidence for SORL1 as a Cross-Disease Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(24):13633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413633
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenussi, Luisa, Antonio Longobardi, Cemile Kocoglu, Matteo Carrara, Sonia Bellini, Clarissa Ferrari, Roland Nicsanu, Claudia Saraceno, Cristian Bonvicini, Silvia Fostinelli, and et al. 2021. "Investigating the Endo-Lysosomal System in Major Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Lewy Body Disease: Evidence for SORL1 as a Cross-Disease Gene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 24: 13633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413633
APA StyleBenussi, L., Longobardi, A., Kocoglu, C., Carrara, M., Bellini, S., Ferrari, C., Nicsanu, R., Saraceno, C., Bonvicini, C., Fostinelli, S., Zanardini, R., Catania, M., Moisse, M., Van Damme, P., Di Fede, G., Binetti, G., Van Broeckhoven, C., van der Zee, J., & Ghidoni, R. (2021). Investigating the Endo-Lysosomal System in Major Neurocognitive Disorders Due to Alzheimer’s Disease, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Lewy Body Disease: Evidence for SORL1 as a Cross-Disease Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24), 13633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413633