Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
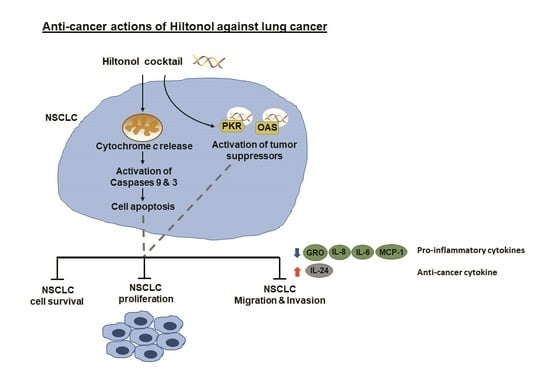
2.1. Hiltonol+++ (Hiltonol+Anti-IL6+JAK2+STAT3 Inhibitors) Cocktail Effectively Killed Lung Cancer Cells
2.2. Hiltonol+++ Suppressed Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation through Intrinsic Apoptosis
2.3. Hiltonol+++ Suppressed the Metastatic Potential of Lung Cancer Cells
2.4. Hiltonol Suppressed Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines but Upregulated Anticancer IL-24 in Lung Cancer Cells
2.5. Knockdown of PKR and/or OAS Abrogated Hiltonol-Mediated Killing of NSCLC Cells
2.6. In Silico Analysis Showed Interaction between Hiltonol and PKR/OAS
2.7. Tumor-Suppressors, PKR, OAS, and IL-24 Were Repressed in Advanced Stages of Primary Lung Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Tissue Samples
5.2. Cell Lines and Reagents
5.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
5.4. Treatment of Lung Cancer Cells with Hiltonol and polyI:C, and Combinations with Anti-IL6, Stattic, and AG490
5.5. Cell Viability Assay
5.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
5.7. TCGA Database Analysis
5.8. Computational Prediction of Hiltonol Binding Sites in PKR and OAS
5.9. siRNA-Knockdown of PKR and OAS in NSCLC Cells
5.10. Cellular Apoptosis Assay
5.11. Caspase-9 and -3 Assays
5.12. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
5.13. ELISA
5.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Abbreviations
| 7-AAD | 7-aminoactinomycin |
| AD | adenocarcinomas |
| ANOVA | two-way analysis of variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CTB | CellTiter Blue |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry 2 |
| LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylathiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| OAS | 2′5′ oligoadenylate synthetase |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| PKR | protein kinase R |
| polyI:C | polyinosinic-polycytidilic acid |
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| SCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
References
- Lu, T.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Yin, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q. Trends in the incidence, treatment, and survival of patients with lung cancer in the last four decades. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, D.K.; Miller, R.A.; Pence, K.A.; Kim, M.P. Small cell and non small cell lung cancer form metastasis on cellular 4D lung model. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, W.H.; Zhu, X.G.; Ho, S.W.T.; Chang, S.C.; Ding, J.L. Combinatorial treatment with polyI:C and anti-IL6 enhances apoptosis and suppresses metastasis of lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32884–32904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagato, T.; Lee, Y.-R.; Harabuchi, Y.; Celis, E. Combinatorial Immunotherapy of Polyinosinic–Polycytidylic Acid and Blockade of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Induce Effective CD8 T-cell Responses against Established Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caskey, M.; Lefebvre, F.; Filali-Mouhim, A.; Cameron, M.J.; Goulet, J.-P.; Haddad, E.K.; Breton, G.; Trumpfheller, C.; Pollak, S.; Shimeliovich, I.; et al. Synthetic double-stranded RNA induces innate immune responses similar to a live viral vaccine in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, M.S.; Gad, H.H.; Andersen, L.L.; Hornung, V.; Julkunen, I.; Sarkar, S.N.; Hartmann, R. Structural and functional analysis reveals that human OASL binds dsRNA to enhance RIG-I signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5236–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barber, G.N.; Tomita, J.; Hovanessian, A.G.; Meurs, E.; Katze, M.G. Functional expression and characterization of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA activated P68 protein kinase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10356–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katze, M.G.; Wambach, M.; Wong, M.L.; Garfinkel, M.; Meurs, E.; Chong, K.; Williams, B.R.; Hovanessian, A.G.; Barber, G.N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5497–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, M.A.; Levy, B.H.; Ondra, S.; Kende, M.; Scherokman, B.; Brown, D.; Mena, H.; Martin, N.; Schwab, K.; Donovan, D.; et al. Long-term Treatment of Malignant Gliomas with Intramuscularly Administered Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid Stabilized with Polylysine and Carboxymethylcellulose: An Open Pilot Study. Neurosurgery 1996, 38, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiane, S.H.; Martin, E.; Edith, J.; Tamara, R.; Klara, T.R.; Christine, T.; Salazar, A.M.; Uberla, K.; Nieto, K.; Kleinschmidt, J.; et al. Synthetic Double-Stranded RNAs Are Adjuvants for the Induction of T Helper 1 and Humoral Immune Responses to Human Papillomavirus in Rhesus Macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Fuentes, S.; Salgado-Aguayo, A.; Pertuz Belloso, S.; Gorocica Rosete, P.; Alvarado-Vásquez, N.; Aquino-Jarquin, G. Role of Chemokines in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Angiogenesis and Inflammation. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J. Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 promotes lung cancer-induced bone resorptive lesions in vivo. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caetano, M.S.; Zhang, H.; Cumpian, A.M.; Gong, L.; Unver, N.; Ostrin, E.J.; Daliri, S.; Chang, S.H.; Ochoa, C.E.; Hanash, S.; et al. IL6 Blockade Reprograms the Lung Tumor Microenvironment to Limit the Development and Progression of K-ras-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Jin, J.; Shanker, M.; Lauderdale, J.; Bates, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.D.; Archibald, S.J.; Hubin, T.J.; Ramesh, R. IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 Signaling Axis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, L.; de Jesus, D.; Brannigan, O.; Richiez-Paredes, M.; Huaman, J.; Alvarado, G.; Riker, L.; Mendez, G.; Dejoie, J.; Sauane, M. Mechanism of Action and Applications of Interleukin 24 in Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, A.M.; Erlich, R.B.; Mark, A.; Bhardwaj, N.; Herberman, R.B. Therapeutic In Situ Autovaccination against Solid Cancers with Intratumoral Poly-ICLC: Case Report, Hypothesis, and Clinical Trial. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balachandran, S.; Kim, C.N.; Yeh, W.-C.; Mak, T.W.; Bhalla, K.; Barber, G.N. Activation of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR, induces apoptosis through FADD-mediated death signaling. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6888–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, L.-C.; Mo Park, J.; Zhang, K.; Luo, J.-L.; Maeda, S.; Kaufman, R.J.; Eckmann, L.; Guiney, D.G.; Karin, M. The protein kinase PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of Toll-like receptor 4. Nature 2004, 428, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullan, P.B.; Hosey, A.M.; Buckley, N.E.; Quinn, J.E.; Kennedy, R.D.; Johnston, P.G.; Harkin, D.P. The 2,5 oligoadenylate synthetase/RNaseL pathway is a novel effector of BRCA1- and interferon-γ-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5492–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodsell, D.S.; Sanner, M.F.; Olson, A.J.; Forli, S. The AutoDock suite at 30. Protein Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Imamura, T.; Hiasa, Y. Roles of protein kinase R in cancer: Potential as a therapeutic target. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. dsRNA-activation of TLR3 and RLR signaling: Gene induction-dependent and independent effects. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. MAYO Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, G.; Jin, G.; Guo, J.; Bumgarner, R.; Katze, M.G.; Sen, G.C. A Comprehensive View of Regulation of Gene Expression by Double-stranded RNA-mediated Cell Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30178–30182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galabru, J.; Katze, M.G.; Robert, N.; Hovanessian, A.G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 178, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Hung, C.S.; Su, C.Y.; Hsu, W.; Ding, J.L. Human FBXL8 is a novel E3 ligase which promotes BRCA metastasis by stimulating pro-tumorigenic cytokines and inhibiting tumor suppressors. Cancers 2020, 7, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.-C.; Zhang, B.-X.; Su, E.C.-Y.; Wu, W.-C.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Salazar, A.M.; Lin, Y.-K.; Ding, J.L. Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041626
Chang S-C, Zhang B-X, Su EC-Y, Wu W-C, Hsieh T-H, Salazar AM, Lin Y-K, Ding JL. Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041626
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Shu-Chun, Bo-Xiang Zhang, Emily Chia-Yu Su, Wei-Ciao Wu, Tsung-Han Hsieh, Andres M. Salazar, Yen-Kuang Lin, and Jeak Ling Ding. 2021. "Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041626
APA StyleChang, S. -C., Zhang, B. -X., Su, E. C. -Y., Wu, W. -C., Hsieh, T. -H., Salazar, A. M., Lin, Y. -K., & Ding, J. L. (2021). Hiltonol Cocktail Kills Lung Cancer Cells by Activating Cancer-Suppressors, PKR/OAS, and Restraining the Tumor Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041626