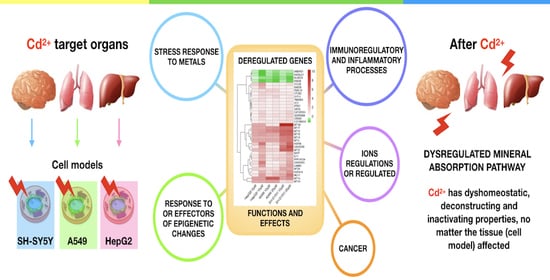
Is Cadmium Toxicity Tissue-Specific? Toxicogenomics Studies Reveal Common and Specific Pathways in Pulmonary, Hepatic, and Neuronal Cell Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Deregulated Pathways in Pulmonary (A549), Hepatic (HepG2) and Neuronal (SH-SY5Y) Cell Models Exposed to Cadmium
2.2. Cadmium Regulates a Group of Genes in Common in HepG2, A549 and SH-SY5Y
2.3. The Two by Two Comparison in the Different Cell Models Reveals Specific Patterns of Expression
2.4. Metallothioneins and Heat Shock Proteins Are the Forefront Defense and Response against Cadmium
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Microarray Expression Profiling
4.3. Immunochemical Analysis of Metallothioneins and Heat Shock Proteins
4.3.1. Metallothioneins Extraction and Expression
4.3.2. Heat Shock Proteins Extraction and Expression
4.4. Determination of Gene Expression Level by Quantitative Reverse Transcription (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Statistical Analysis of Immunochemical and qPCR Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Substance Priority List | ATSDR. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Zhang, K.; Chai, F.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, X.; Fomba, K.W.; Zhou, G. Size Distribution and Source of Heavy Metals in Particulate Matter on the Lead and Zinc Smelting Affected Area. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Cadmium Dietary Exposure in the European Population. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C. Health Risk Assessment of Dietary Cadmium Intake: Do Current Guidelines Indicate How Much Is Safe? Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, A.; Jahnke, G. Chapter 10 - Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Foods. In Chemical Contaminants and Residues in Food, 2nd ed.; Schrenk, D., Cartus, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 209–222. ISBN 9780081006740. [Google Scholar]
- Satarug, S.; Moore, M.R. Adverse Health Effects of Chronic Exposure to Low-Level Cadmium in Foodstuffs and Cigarette Smoke. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Du, Y. Cadmium and Its Neurotoxic Effects. Oxid. Med. Cel. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoshima, K. Epidemiology of Renal Tubular Dysfunction in the Inhabitants of a Cadmium-Polluted Area in the Jinzu River Basin in Toyama Prefecture. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1987, 152, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. IJERPH 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, R.A. Cadmium Toxicity and Treatment. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziller, A.; Fraissinet-Tachet, L. Metallothionein Diversity and Distribution in the Tree of Life: A Multifunctional Protein. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, V.; Andréasson, C. Hsp70-Mediated Quality Control: Should I Stay or Should I Go? Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenzweig, R.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. The Hsp70 Chaperone Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urani, C.; Melchioretto, P.; Canevali, C.; Crosta, G.F. Cytotoxicity and Induction of Protective Mechanisms in HepG2 Cells Exposed to Cadmium. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, J.; DeGraff, W.G.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D.; Mitchell, J.B. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: Assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forcella, M.; Lau, P.; Oldani, M.; Melchioretto, P.; Bogni, A.; Gribaldo, L.; Fusi, P.; Urani, C. Neuronal Specific and Non-Specific Responses to Cadmium Possibly Involved in Neurodegeneration: A Toxicogenomics Study in a Human Neuronal Cell Model. NeuroToxicology 2020, 76, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C. The Evolving Role for Zinc and Zinc Transporters in Cadmium Tolerance and Urothelial Cancer. Stresses 2021, 1, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-K.; Thévenod, F. Cell Organelles as Targets of Mammalian Cadmium Toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1017–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.Y.; DesMarais, T.; Costa, M. Metals and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urani, C.; Melchioretto, P.; Bruschi, M.; Fabbri, M.; Sacco, M.G.; Gribaldo, L. Impact of Cadmium on Intracellular Zinc Levels in HepG2 Cells: Quantitative Evaluations and Molecular Effects. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, M.; Fabbri, M.; Melchioretto, P.; Callegaro, G.; Fusi, P.; Gribaldo, L.; Forcella, M.; Urani, C. In Vitro and Bioinformatics Mechanistic-Based Approach for Cadmium Carcinogenicity Understanding. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 65, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The Essential Metals for Humans: A Brief Overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement With The Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Qiu, R.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S. Cadmium–Zinc Exchange and Their Binary Relationship in the Structure of Zn-Related Proteins: A Mini Review. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, G.; Liu, Y.; Templeton, D.M. Interplay of Calcium and Cadmium in Mediating Cadmium Toxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 211, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kumari, V.; Ram, C.; Bharath Kumar, B.S.; Verma, S. Impact of Oral Cadmium Intoxication on Levels of Different Essential Trace Elements and Oxidative Stress Measures in Mice: A Response to Dose. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5401–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M. Whole Genome Analysis and MicroRNAs Regulation in HepG2 Cells Exposed to Cadmium. ALTEX 2012, 29, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Luo, S.; Akinyemiju, T.; Hwang, S.; Wei, Q. Variants in SNAI1, AMDHD1 and CUBN in Vitamin D Pathway Genes Are Associated with Breast Cancer Risk: A Large-Scale Analysis of 14 GWASs in the DRIVE Study. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2160–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Kiel, D.P.; Kraft, P. The Genetics of Vitamin D. Bone 2019, 126, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Shinjo, K.; Kondo, Y.; Shen, L.; Toyota, M.; Suzuki, H.; Gao, W.; An, B.; Fujii, M.; Murakami, H.; et al. Epigenetic Profiles Distinguish Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma from Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9073–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Polom, K.; Williams, C.; de Oliveira, F.M.S.; Guergova-Kuras, M.; Lisacek, F.; Karlsson, N.G.; Roviello, F.; Kamali-Moghaddam, M. A Targeted Proteomics Approach Reveals a Serum Protein Signature as Diagnostic Biomarker for Resectable Gastric Cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Zhuang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, C.; Liu, L.; Sun, C. Exploration of Methylation-Driven Genes for Monitoring and Prognosis of Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhuang, R.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Tan, R.; et al. Rab26 Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells through Mediating Autophagic Degradation of Phosphorylated Src. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luparello, C. Cadmium-Associated Molecular Signatures in Cancer Cell Models. Cancers 2021, 13, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urani, C.; Melchioretto, P.; Gribaldo, L. Regulation of Metallothioneins and ZnT-1 Transporter Expression in Human Hepatoma Cells HepG2 Exposed to Zinc and Cadmium. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovio, F.; Melchioretto, P.; Forcella, M.; Fusi, P.; Urani, C. Cadmium Promotes Glycolysis Upregulation and Glutamine Dependency in Human Neuronal Cells. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 149, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, M.; Manzoni, M.; Villa, A.M.; Stefanini, F.M.; Melchioretto, P.; Monti, E.; Forcella, M.; Urani, C.; Fusi, P. Cadmium Elicits Alterations in Mitochondrial Morphology and Functionality in C3H10T1/2Cl8 Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, M.; Yu, H.; Pan, Z.; Liu, L.; Geng, Q.; Pan, H.; Yan, M.; Yao, M. OTUB2 Stabilizes U2AF2 to Promote the Warburg Effect and Tumorigenesis via the AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Theranostics 2019, 9, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Guan, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; et al. GADD45B as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Stage II Colorectal Cancer. Genes 2018, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.-C.; Wu, P.-C.; Chung, I.-F.; Jiang, J.-H.; Fann, M.-J.; Kao, L.-S. Cell Death Caused by the Synergistic Effects of Zinc and Dopamine Is Mediated by a Stress Sensor Gene Gadd45b – Implication in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, Z.; Tian, K.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yu, L.; Pang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. DNA Methylation Mechanism of Intracellular Zinc Deficiency-Induced Injury in Primary Hippocampal Neurons in the Rat Brain. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Dang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ou, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. LAMB3 Promotes Tumour Progression through the AKT–FOXO3/4 Axis and Is Transcriptionally Regulated by the BRD2/Acetylated ELK4 Complex in Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4666–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Taheri, M. H19 LncRNA: Roles in Tumorigenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Dean, W.; Konfortova, G.; Kelsey, G. Identification of Novel Imprinted Genes in a Genome-Wide Screen for Maternal Methylation. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Yu, H.; Jiang, C.; Dai, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiang, J.; et al. An in Silicoanalysis of Dynamic Changes in MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Stepwise Development of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Med. Genomics 2012, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Méndez-Armenta, M.; Ríos, C. Cadmium Neurotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 23, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesauro, M.; Bruschi, M.; Filippini, T.; D’Alfonso, S.; Mazzini, L.; Corrado, L.; Consonni, M.; Vinceti, M.; Fusi, P.; Urani, C. Metal(Loid)s Role in the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Environmental, Epidemiological, and Genetic Data. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzaroba, L.; Alfieri, D.F.; Colado Simão, A.N.; Vissoci Reiche, E.M. The Role of Zinc, Copper, Manganese and Iron in Neurodegenerative Diseases. NeuroToxicology 2019, 74, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlos Rodrigo, M.A.; Jimenez Jimemez, A.M.; Haddad, Y.; Bodoor, K.; Adam, P.; Krizkova, S.; Heger, Z.; Adam, V. Metallothionein Isoforms as Double Agents – Their Roles in Carcinogenesis, Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 52, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Takano, H.; Shimada, A.; Satoh, M. Metallothionein as an Anti-Inflammatory Mediator. Mediators Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI Gene Expression and Hybridization Array Data Repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene | Description | Gene | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMDHD1 | amidohydrolase domain containing 1 | MT1B | metallothionein 1B |
| BATF | basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor | MT1E | metallothionein 1E |
| CATSPER1 | cation channel sperm associated 1 | MT1F | metallothionein 1F |
| CCL26 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 26 | MT1G | metallothionein 1G |
| CREB5 | cAMP responsive element binding protein 5 | MT1H | metallothionein 1H |
| FBXL19 | F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 19 | MT1L | metallothionein 1L, pseudogene |
| GADD45B | growth arrest and DNA damage inducible beta | MT1M | metallothionein 1M |
| GADD45G | growth arrest and DNA damage inducible gamma | MT1X | metallothionein 1X |
| HSPA1A | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 1A | MT2A | metallothionein 2A |
| HSPA6 | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 6 | OTUB2 | OTU deubiquitinase, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 2 |
| IFRD1 | interferon related developmental regulator 1 | PPP1R15A | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 15A |
| IL11 | interleukin 11 | RAB26 | RAB26, member RAS oncogene family |
| KAZALD1 | Kazal type serine peptidase inhibitor domain 1 | RAB3B | RAB3B, member RAS oncogene family |
| KLHDC9 | kelch domain containing 9 | SERPINB8 | serpin family B member 8 |
| LAMB3 | laminin subunit beta 3 | SIRT6 | sirtuin 6 |
| LOC388242 | SAGA complex associated factor 29 pseudogene | SYT11 | synaptotagmin 11 |
| MLC1 | modulator of VRAC current 1 | TMEM54 | transmembrane protein 54 |
| MT1A | metallothionein 1A | VCY | variable charge Y-linked |
| Gene | Description | A549 | HepG2 | SH-SY5Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTA2 | actin alpha 2, smooth muscle | |||
| H19 | H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript | |||
| PEG13 | paternally expressed 13 | |||
| SEPHS2 | selenophosphate synthetase 2 | |||
| ZNF57 | zinc finger protein 57 | |||
| C4BPB | complement component 4 binding protein beta | |||
| A1BG | alpha-1-B glycoprotein | |||
| CCDC142 | coiled-coil domain containing 142 | |||
| AFMID | arylformamidase | |||
| HSD17B7 | hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 7 | |||
| ITPRIPL2 | ITPRIP like 2 | |||
| SCGB3A2 | secretoglobin family 3A member 2 | |||
| AGT | angiotensinogen | |||
| FTCD | formimidoyltransferase cyclodeaminase | |||
| C1S | complement C1s | |||
| NUPR1 | nuclear protein 1, transcriptional regulator | |||
| SLC6A12 | solute carrier family 6 member 12 | |||
| PDZK1 | PDZ domain containing 1 | |||
| SOCS1 | suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 | |||
| APOH | apolipoprotein H | |||
| ABCB6 | ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 6 (Langereis blood group) | |||
| SCARA3 | scavenger receptor class A member 3 | |||
| ASS1 | argininosuccinate synthase 1 | |||
| PNPLA3 | patatin like phospholipase domain containing 3 | |||
| C1orf115 | chromosome 1 open reading frame 115 | |||
| GAL3ST1 | galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 1 | |||
| FGD6 | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 6 | |||
| DUSP6 | dual specificity phosphatase 6 | |||
| GLCCI1 | glucocorticoid induced 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forcella, M.; Lau, P.; Fabbri, M.; Fusi, P.; Oldani, M.; Melchioretto, P.; Gribaldo, L.; Urani, C. Is Cadmium Toxicity Tissue-Specific? Toxicogenomics Studies Reveal Common and Specific Pathways in Pulmonary, Hepatic, and Neuronal Cell Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031768
Forcella M, Lau P, Fabbri M, Fusi P, Oldani M, Melchioretto P, Gribaldo L, Urani C. Is Cadmium Toxicity Tissue-Specific? Toxicogenomics Studies Reveal Common and Specific Pathways in Pulmonary, Hepatic, and Neuronal Cell Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031768
Chicago/Turabian StyleForcella, Matilde, Pierre Lau, Marco Fabbri, Paola Fusi, Monica Oldani, Pasquale Melchioretto, Laura Gribaldo, and Chiara Urani. 2022. "Is Cadmium Toxicity Tissue-Specific? Toxicogenomics Studies Reveal Common and Specific Pathways in Pulmonary, Hepatic, and Neuronal Cell Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031768
APA StyleForcella, M., Lau, P., Fabbri, M., Fusi, P., Oldani, M., Melchioretto, P., Gribaldo, L., & Urani, C. (2022). Is Cadmium Toxicity Tissue-Specific? Toxicogenomics Studies Reveal Common and Specific Pathways in Pulmonary, Hepatic, and Neuronal Cell Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031768