Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. miR-21 Differential Expression in Lung Cancer Cell Lines
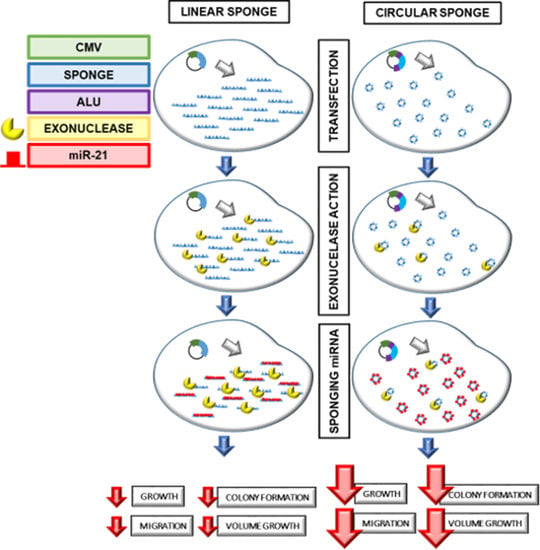
2.2. Development of a Simple and Effective miRNA Sponge Expression System
2.3. Correct Expression of Sponges In Vitro
2.4. Inhibition of Cell Growth by Circ-21
2.5. Inhibition of Cell Migration by Circ-21
2.6. Colony Formation
2.7. miR-21 Sponge Therapy Effect in 3D Tumor Spheroid Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. miR-21 Expression Levels
4.3. Sponge Design and Construction
4.4. Transfection of Cell Lines
4.5. Detection of Circ-21 Expression by RT-PCR In Vitro
4.6. Detection of Circ-21 Expression by Flow Cytometry
4.7. Microscopic Analysis
4.8. In Vitro Cell Proliferation Assay
4.9. Wound Healing Assay
4.10. Colony Formation
4.11. Multicellular Tumor Spheroids Generation
4.12. MTS Growth Volume Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; He, J.; Tian, H.; Shen, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; et al. A two-miRNA signature (miR-33a-5p and miR-128-3p) in whole blood as potential biomarker for early diagnosis of lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acunzo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA in Cancer and Cachexia—A Mini-Review. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. S1), S74–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, A.R.; Perazzoli, G.; Cabeza, L.; Mesas, C.; Quinonero, F.; Garcia-Pinel, B.; Velez, C. Novel MicroRNA Sponges to Specifically Modulate Gene Expression in Colon Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Eom, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.; Jeoung, D. The Hyaluronic Acid-HDAC3-miRNA Network in Allergic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, H.L.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.L.; Min, J.; Lu, J.R.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.Q. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Participates in the Regulation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cartilage Differentiation. Stem. Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 2139814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fededa, J.P.; Esk, C.; Mierzwa, B.; Stanyte, R.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, H.; Ebnet, K.; Yan, W.; Knoblich, J.A.; Gerlich, D.W. MicroRNA-34/449 controls mitotic spindle orientation during mammalian cortex development. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugito, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Kuranaga, Y.; Ohishi, M.; Soga, T.; Ito, Y.; Miyachi, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Hosoi, H.; Akao, Y. Cancer-Specific Energy Metabolism in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells Is Regulated by MicroRNA. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, H.; Fan, J.; Li, H.; Wen, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. MiR-320a induces diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting MafB. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 3055–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femminella, G.D.; Ferrara, N.; Rengo, G. The emerging role of microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, H.; Mu, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Ma, S. MicroRNA-365 promotes lung carcinogenesis by downregulating the USP33/SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Sun, L.C.; Ling, L.; Cong, L.H.; Lian, R. miR-143 suppresses the proliferation of NSCLC cells by inhibiting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.X.; Jiang, Y.P.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. The crosstalk between lncRNA and microRNA in cancer metastasis: Orchestrating the epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12472–12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dambal, S.; Shah, M.; Mihelich, B.; Nonn, L. The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays together. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7173–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Yue, J.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Fan, M.; Paulus, E.; Hosni-Ahmed, A.; Sims, M.; Qayyum, S.; Davidoff, A.M.; Handorf, C.R. MicroRNA-21 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by down-regulating insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP3). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25079–25087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.-f.; Wu, Z.-p.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.-s.; Hamidi, S.; Navab, R. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103698. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xin, S.; He, Z.; Che, X.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J.; Song, X. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor PDCD4 and promotes cell transformation, proliferation, and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.F.; Zhao, Y.M.; Shi, X.Y.; Xu, A.G. Serum miR-21 level: A potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14759–14763. [Google Scholar]
- Inamura, K.; Ishikawa, Y. MicroRNA in lung cancer: Novel biomarkers and potential tools for treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Hao, N.B.; Tang, B.; Guo, H.; Yong, X.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.M. microRNA inhibitors: Natural and artificial sequestration of microRNA. Cancer Lett. 2017, 407, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebert, M.S.; Neilson, J.R.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Carmell, M.A.; Rivas, F.V.; Marsden, C.G.; Thomson, J.M.; Song, J.J.; Hammond, S.M.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004, 305, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Circular RNAs as Therapeutic Agents and Targets. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hentze, M.W.; Preiss, T. Circular RNAs: Splicing’s enigma variations. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, P.; Chen, Y.G. The design and synthesis of circular RNAs. Methods 2021, 196, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.; Baird, A.M.; Brady, L.; Lim, M.; Gray, S.G.; McDermott, R.; Finn, S.P. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Human Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, I.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional sequestration of microRNA-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by circular RNA sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavenniah, A.; Luu, T.D.A.; Li, Y.P.; Lim, T.B.; Jiang, J.; Ackers-Johnson, M.; Foo, R.S. Engineered Circular RNA Sponges Act as miRNA Inhibitors to Attenuate Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, R.; Sanchez-Jimenez, E.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J.; Rama, A.R. Downregulated microRNAs in the colorectal cancer: Diagnostic and therapeutic perspectives. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallach, S.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Calabuig-Farinas, S.; Montaner, D.; Alonso, S.; Sirera, R.; Blasco, A.; Uso, M.; Guijarro, R.; Martorell, M.; et al. MicroRNA profiling associated with non-small cell lung cancer: Next generation sequencing detection, experimental validation, and prognostic value. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56143–56157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.; Spevak, C.C.; Wong, G.; Xia, W.; Gilad, E. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with protein kinase C(epsilon) promotes oncogenic signaling by the stem cell marker Nanog and the Production of microRNA-21, leading to down-regulation of the tumor suppressor protein PDCD4, anti-apoptosis, and chemotherapy resistance in breast tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26533–26546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, L.; Wei, L.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Y.; Song, X. MicroRNA-21 regulates breast cancer invasion partly by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 expression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Ma, C. Lidocaine alleviates cytotoxicity-resistance in lung cancer A549/DDP cells via down-regulation of miR-21. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 456, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mahato, R.I. miRNAs as targets for cancer treatment: Therapeutics design and delivery. Preface. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Z. Circular RNA circFADS2 is overexpressed in sepsis and suppresses LPS-induced lung cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of miR-15a-5p. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Hao, Y.; Lin, K.; Lyu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Zou, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, R.; Jin, D.; et al. Circular RNA CDR1as disrupts the p53/MDM2 complex to inhibit Gliomagenesis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Miao, Y.; Xu, T.; Sun, W.; Sang, Y.; Jia, F.; Zhang, X. Circ-EPB41L5 regulates the host gene EPB41L5 via sponging miR-19a to repress glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Yao, M. Upregulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0007534 predicts unfavorable prognosis for NSCLC and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Gene 2018, 676, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sui, X.; Zhao, H.; Cong, L.; Li, Y.; Xin, T.; Guo, M.; Hao, W. Decreased circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 predicts unfavorable prognosis in glioma and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Gene 2018, 676, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, P.; Jing, W.; Zhou, H.; Liang, C.; Tu, J. circSMAD2 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-629 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Jing, W.; Luo, P.; Qiu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Liang, C.; Yu, M.; Tu, J. The Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001445 Regulates the Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and May Serve as a Diagnostic Biomarker. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 3073467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, S.; Luo, P.; Zhou, H.; Jing, W.; Liang, C.; Tu, J. Down-regulation of hsa_circ_0001649 in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts a poor prognosis. Cancer Biomark 2018, 22, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.C.; Wong, C.W.; Liang, P.P.; Shi, M.; Cao, Y.; Rao, S.T.; Tsui, S.K.; Waye, M.M.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, W.M.; et al. Translation of the circular RNA circbeta-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tatomer, D.C.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L.; Cherry, S.; Wilusz, J.E. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 940–954.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. Molecular paleontology of transposable elements in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6569–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. circHIPK3 regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yuan, W.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Tao, J.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Lv, Q. Circular RNA circ-ITCH inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and regulating p21, PTEN expression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Lin, C.Y.; Yuan, H.Y.; Xiong, B. Overexpression of miR-21 promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2011, 33, 742–746. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Abraham, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Cole, R.N.; Boronina, T.N. Synthetic circular RNA functions as a miR-21 sponge to suppress gastric carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndodo, N.D.; Danborno, B.; Adebisi, S.S. MicroRNA-mediated sensitization of lung cancer cells to chemotherapeutics: The roles of miR-21 and miR-155. Middle East J. Med. Genet. 2018, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, Y.; Yao, Y. miRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 953. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, S.; Wedler, A.; Breuer, J.; Glass, M.; Bley, N.; Lederer, M.; Haase, J.; Misiak, C.; Fuchs, T.; Ottmann, A.; et al. Synthetic circular miR-21 RNA decoys enhance tumor suppressor expression and impair tumor growth in mice. NAR Cancer 2020, 2, zcaa014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, H.; Peng, Q.; Yang, X.; Gan, R.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Meng, Q. Downregulation of microRNA-21 expression restrains non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and migration through upregulation of programmed cell death 4. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA sponges: Progress and possibilities. RNA 2010, 16, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otaegi, G.; Pollock, A.; Sun, T. An Optimized Sponge for microRNA miR-9 Affects Spinal Motor Neuron Development in vivo. Front Neurosci. 2011, 5, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kluiver, J.; Gibcus, J.H.; Hettinga, C.; Adema, A.; Richter, M.K.; Halsema, N.; Slezak-Prochazka, I.; Ding, Y.; Kroesen, B.J.; van den Berg, A. Rapid generation of microRNA sponges for microRNA inhibition. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kluiver, J.; Slezak-Prochazka, I.; Smigielska-Czepiel, K.; Halsema, N.; Kroesen, B.J.; van den Berg, A. Generation of miRNA sponge constructs. Methods 2012, 58, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grada, A.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Prieto-Castrillo, F.; Obagi, Z.; Falanga, V. Research Techniques Made Simple: Analysis of Collective Cell Migration Using the Wound Healing Assay. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rama, A.R.; Prados, J.; Melguizo, C.; Burgos, M.; Alvarez, P.J.; Rodriguez-Serrano, F.; Ramos, J.L.; Aranega, A. Synergistic antitumoral effect of combination E gene therapy and Doxorubicin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2011, 65, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Ballesteros, A.R.; Hernandez, R.; Perazzoli, G.; Cabeza, L.; Melguizo, C.; Velez, C.; Prados, J. Specific driving of the suicide E gene by the CEA promoter enhances the effects of paclitaxel in lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 27, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rama, A.R.; Quiñonero, F.; Mesas, C.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23062963
Rama AR, Quiñonero F, Mesas C, Melguizo C, Prados J. Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(6):2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23062963
Chicago/Turabian StyleRama, Ana R., Francisco Quiñonero, Cristina Mesas, Consolación Melguizo, and Jose Prados. 2022. "Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 6: 2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23062963
APA StyleRama, A. R., Quiñonero, F., Mesas, C., Melguizo, C., & Prados, J. (2022). Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(6), 2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23062963