In Silico Examination of Single Nucleotide Missense Mutations in NHLH2, a Gene Linked to Infertility and Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chromosomal Location, mRNA Transcripts, Protein Structure, and Identification of Variants
2.2. Predicted Effects of Variants on Protein Post-Translational Modifications
2.3. Predicted Effect of Variants on Protein Tertiary Structure and Function
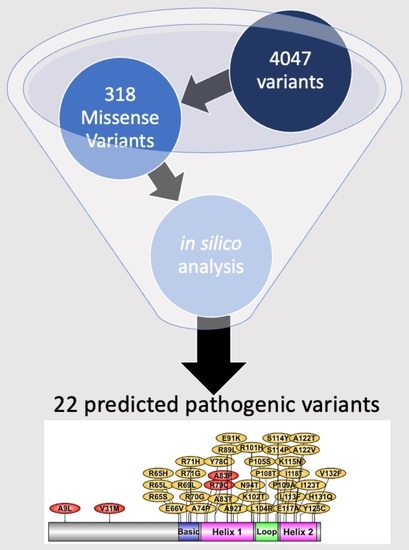
2.4. List of Most Pathogenic Variants, Predicted by In Silico Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of NHLH2 Missense SNVs for Further Study
4.2. Illustrator for Biological Sequences
4.3. Clustal Omega Phylogenetic Alignment Analysis
4.4. Nucleolar and Nuclear Localization Signal Prediction
4.5. Post-Translational Modification Prediction
4.6. Protein Structure (2D and 3D) and DNA Binding Prediction
4.7. PyMOL 3D Visualization of WT Structure
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cunningham, F.; Allen, J.E.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D988–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkowitz, S.; Garry, V.F.; Kirsch, I.R. Interlocus V-J recombination measures genomic instability in agriculture workers at risk for lymphoid malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5301–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.J.; Braun, T. NHLH2: At the intersection of obesity and fertility. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rayyan, N.; Wankhade, U.D.; Bush, K.; Good, D.J. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human nescient helix-loop-helix 2 (NHLH2) gene reduce mRNA stability and DNA binding. Gene 2013, 512, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Kim, E.; Amit, M.; Bochner, R.; Lev-Maor, G.; Ahituv, N.; Ast, G. Alternative approach to a heavy weight problem. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahituv, N.; Kavaslar, N.; Schackwitz, W.; Ustaszewska, A.; Martin, J.; Hebert, S.; Doelle, H.; Ersoy, B.; Kryukov, G.; Schmidt, S.; et al. Medical sequencing at the extremes of human body mass. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloglu, A.K.; Simsek, E.; Kocher, M.A.; Mammadova, J.; Bober, E.; Kotan, L.D.; Turan, I.; Celiloglu, C.; Gurbuz, F.; Yuksel, B.; et al. Inactivating NHLH2 variants cause idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and obesity in humans. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, U.D.; Good, D.J. Melanocortin 4 receptor is a transcriptional target of nescient helix-loop-helix-2. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 341, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.; Talbi, R.; McCarthy, E.A.; Ferrari, K.; Fergani, C.; Naule, L.; Choi, J.H.; Carroll, R.S.; Kaiser, U.B.; Aylwin, C.F.; et al. Sex-specific pubertal and metabolic regulation of Kiss1 neurons via Nhlh2. eLife 2021, 10, e69765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitts, A.; Phan, L.; Ward, M.; Holmes, J.B. The Database of Short Genetic Variation (dbSNP). The NCBI Handbook, 2nd Edition. 2013. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK174586/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN web server: A tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reva, B.; Antipin, Y.; Sander, C. Predicting the functional impact of protein mutations: Application to cancer genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. SNAP: Predict effect of non-synonymous polymorphisms on function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masica, D.L.; Douville, C.; Tokheim, C.; Bhattacharya, R.; Kim, R.; Moad, K.; Ryan, M.C.; Karchin, R. CRAVAT 4: Cancer-Related Analysis of Variants Toolkit. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e35–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnad, F.; Baucom, A.; Mukhyala, K.; Manning, G.; Zhang, Z. Assessment of computational methods for predicting the effects of missense mutations in human cancers. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.H.; Sulieman, L.; Schlueter, D.J.; Halvorson, A.; Qian, J.; Ratsimbazafy, F.; Loperena, R.; Mayo, K.; Basford, M.; Deflaux, N.; et al. The All of Us Research Program: Data quality, utility, and diversity. Patterns 2022, 3, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varterasian, M.; Lipkowitz, S.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Paterson, B.; Kirsch, I. Two new Drosophila genes related to human hematopoietic and neurogenic transcription factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1993, 4, 885–889. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.; Yan, D.; Wan, C.; Hu, B. Nucleolus and Nucleolar Stress: From Cell Fate Decision to Disease Development. Cells 2022, 11, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.L.; Vella, K.R.; Good, D.J. Energy balance pathways converging on the Nhlh2 transcription factor. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 3983–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, K.R.; Burnside, A.S.; Brennan, K.M.; Good, D.J. Expression of the hypothalamic transcription factor Nhlh2 is dependent on energy availability. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2007, 19, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, K.R.; Good, D.J. Nhlh2 is a Cold-Responsive Gene. Open Neuroendorinol. J. 2010, 3, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liang, Y.; Xu, D. Capsule network for protein post-translational modification site prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Yuchi, J.; He, F.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, J.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning based webserver for protein post-translational modification site prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W140–W146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zeng, S.; Xu, C.; Qiu, W.; Liang, Y.; Joshi, T.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning framework for general and kinase-specific phosphorylation site prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libert, S.; Pointer, K.; Bell, E.L.; Das, A.; Cohen, D.E.; Asara, J.M.; Kapur, K.; Bergmann, S.; Preisig, M.; Otowa, T.; et al. SIRT1 activates MAO-A in the brain to mediate anxiety and exploratory drive. Cell 2011, 147, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Y. GPS-PAIL: Prediction of lysine acetyltransferase-specific modification sites from protein sequences. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martin, X.; Sodaei, R.; Santpere, G. Mechanisms of Binding Specificity among bHLH Transcription Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchley, W.R.; Zhao, J. Molecular architecture of the DNA-binding region and its relationship to classification of basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.L.; Good, D.J. Nescient helix-loop-helix 2 interacts with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to regulate transcription of prohormone convertase 1/3. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.W.; Schwartz, J.H.; Freddolino, P.L.; Zhang, Y. PEPPI: Whole-proteome Protein-protein Interaction Prediction through Structure and Sequence Similarity, Functional Association, and Machine Learning. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, M.A.; Huang, F.W.; Le, E.; Good, D.J. Snord116 Post-transcriptionally Increases Nhlh2 mRNA Stability: Implications for Human Prader-Willi Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, M.; Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. News from the protein mutability landscape. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 3937–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, M.; Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. Better prediction of functional effects for sequence variants. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, H.; Douville, C.; Stenson, P.D.; Cooper, D.N.; Karchin, R. Identifying Mendelian disease genes with the variant effect scoring tool. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, C.; Masica, D.L.; Stenson, P.D.; Cooper, D.N.; Gygax, D.M.; Kim, R.; Ryan, M.; Karchin, R. Assessing the Pathogenicity of Insertion and Deletion Variants with the Variant Effect Scoring Tool (VEST-Indel). Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Ba, A.N.; Pogoutse, A.; Provart, N.; Moses, A.M. NLStradamus: A simple Hidden Markov Model for nuclear localization signal prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.S.; Troshin, P.V.; Barton, G.J. NoD: A Nucleolar localization sequence detector for eukaryotic and viral proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuffin, L.J.; Adiyaman, R.; Maghrabi, A.H.A.; Shuid, A.N.; Brackenridge, D.A.; Nealon, J.O.; Philomina, L.S. IntFOLD: An integrated web resource for high performance protein structure and function prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W408–W413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, D.B.; Buenavista, M.T.; McGuffin, L.J. The FunFOLD2 server for the prediction of protein-ligand interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W303–W307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraez, A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006, 34, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosignoli, S.; Paiardini, A. Boosting the Full Potential of PyMOL with Structural Biology Plugins. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Variant ID | Amino Acid Change | Predicted Pathogenicity |
|---|---|---|
| Rs372688621 | R65H R65L | Loss of DNA binding Loss of phosphorylation; Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1194455186 | R65S | Additional phosphorylation; Altered DNA binding |
| Rs765797948 | R69L | Loss of phosphorylation |
| Rs1262624693 | R70G | Loss of DNA binding |
| Rs1417094020 | R71H | Loss of phosphorylation |
| Rs1650933387 | R71G | Loss of phosphorylation |
| RS772525034 | A74P | Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1199787521 | Y78H | Loss of phosphorylation; Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1650932250 | Y78C | Loss of phosphorylation; Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1650931347 | E91K | Additional acetylation; Altered DNA binding |
| Rs199738358 | A92T | Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1352643678 | N94T | Not predicted to binding DNA, but model could not be predicted |
| Rs781142041 | K102T | Altered DNA binding |
| Rs757420009 | L104R | Loss of DNA binding |
| Rs1650929924 | P105S | Loss of glycosylation |
| Rs751807396 | P108T | Additional phosphorylation |
| Rs1354640857 | K115N | Loss of DNA binding |
| Rs1557829654 | R120P | Altered DNA binding |
| Rs1650928263 | R120S | Additional SUMOlaytion |
| Rs1433737875 | Y125C | Additional hydroxylation |
| Rs1230535357 | V132F | Altered DNA binding |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madsen, A.T.; Good, D.J. In Silico Examination of Single Nucleotide Missense Mutations in NHLH2, a Gene Linked to Infertility and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043193
Madsen AT, Good DJ. In Silico Examination of Single Nucleotide Missense Mutations in NHLH2, a Gene Linked to Infertility and Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043193
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadsen, Allison T., and Deborah J. Good. 2023. "In Silico Examination of Single Nucleotide Missense Mutations in NHLH2, a Gene Linked to Infertility and Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043193
APA StyleMadsen, A. T., & Good, D. J. (2023). In Silico Examination of Single Nucleotide Missense Mutations in NHLH2, a Gene Linked to Infertility and Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043193