The Anti-Tumorigenic Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in Colon Cancer: A Study in Mice and Humans
Abstract
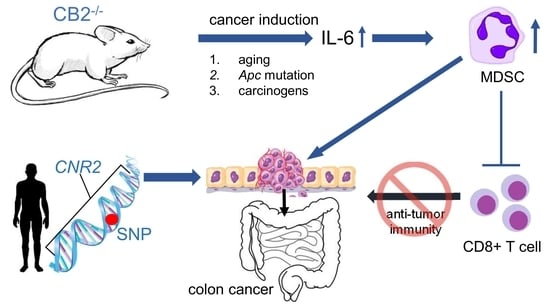
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CB2−/− Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Spontaneous Cancer
2.2. IL-6 Is Upregulated in CB2−/− Female Mice under Steady-State Conditions
2.3. CB2 Has a Protective Role against Carcinogen-Induced Colon Cancer in Female Mice
2.4. CB2 Has a Protective Role against Colon Cancer in ApcMin/+ Mice
2.5. Splenic Immunosuppressive Profile in CAC-Induced CB2−/− and ApcMin/+ CB2−/− Mice
2.6. Immunosuppressive Environment in Colon Polpys of CB2−/− Mice
2.7. Association of Polymorphisms in the CNR2 Gene with Colon Cancer Incidence in Humans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Genotyping
4.3. Serum Analysis
4.4. Histopathology
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Colonoscopies
4.7. Colon Histology
4.8. RNA Extraction and qPCR
| Primer Sequence 5′-3′ | |
| β-actin_F | GTCACCCACACTGTGCCCATC |
| β-actin_R | CCGTCAGGCAGCTCATAGCTC |
| IL-6_F | CCGGAGAGGAGACTTCACAG |
| IL-6_R | GGAAATTGGGGTAGGAAGGA |
| Arg1_F | TTGGGTGGATGCTCACACTG |
| Arg1_R | TTGCCCATGCAGATTCCC |
| IL-17_F | ACCGCAATGAAGACCCTGAT |
| IL-17_R | TCCCTCCGCATTGACACA |
| CD8_F | CCGTTGACCCGCTTTCTGT |
| CD8_R | CGGCGTCCATTTTCTTTGGAA |
4.9. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assessment in Colon Tumor Fragments
4.10. Statistical Analyses
4.11. Human Genomic Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuire, S. World Cancer Report 2014; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Przegląd Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Chumanevich, A.; Fletcher, E.; Larsen, B.; Lattwein, K.; Kaur, K.; Fayad, R. Adiponectin deficiency: Role in chronic inflammation induced colon cancer. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Robertis, M.; Massi, E.; Poeta, M.L.; Carotti, S.; Morini, S.; Cecchetelli, L.; Signori, E.; Fazio, V.M. The AOM/DSS murine model for the study of colon carcinogenesis: From pathways to diagnosis and therapy studies. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Cheng, D.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; Qi, W.; Wang, C. Preventive effect of genistein on AOM/DSS-induced colonic neoplasm by modulating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3 signaling pathway in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, A.I.; Shaker, A.; Rao, M.S.; Ciorba, M.A. Modeling colitis-associated cancer with azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2012, 67, e4100. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, R.; Piao, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, C. Quercetin Suppresses AOM/DSS-Induced Colon Carcinogenesis through Its Anti-Inflammation Effects in Mice. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9242601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, A.; Bothwell, A.L. Stat6 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in a mouse model of adenomatous polyposis by expansion of MDSCs and inhibition of cytotoxic CD8 response. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonim, M.A.; Ibba, S.V.; Tarhuni, A.F.; Errami, Y.; Luu, H.H.; Dean, M.J.; El-Bahrawy, A.H.; Wyczechowska, D.; Benslimane, I.A.; Del Valle, L. Targeting PARP-1 with metronomic therapy modulates MDSC suppressive function and enhances anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in colon cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele Orberg, E.; Fan, H.; Tam, A.J.; Dejea, C.M.; Destefano Shields, C.E.; Wu, S.; Chung, L.; Finard, B.B.; Wu, X.; Fathi, P. The myeloid immune signature of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced murine colon tumorigenesis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bab, I.; Ofek, O.; Tam, J.; Rehnelt, J.; Zimmer, A. Endocannabinoids and the regulation of bone metabolism. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: Signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackie, K. Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2006, 46, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. Handb. Exp. Pharm. 2005, 168, 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, R.; Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Targeting the endocannabinoid system as a potential anticancer approach. Drug Metab. Rev. 2018, 50, 26–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, E.; Martín-Ruiz, A.; Martín, P.; Calvo, V.; Provencio, M.; García, J.M. CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation promotes colon cancer progression via AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zou, Y.; Kong, W.; Dong, B.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, W.; Huang, Y. Cannabinoid receptor 2 as a novel target for promotion of renal cell carcinoma prognosis and progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladin, D.A.; Soliman, E.; Griffin, L.; Van Dross, R. Preclinical and clinical assessment of cannabinoids as anti-cancer agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Antitumorigenic targets of cannabinoids–current status and implications. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKallip, R.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances breast cancer growth and metastasis by suppression of the antitumor immune response. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3281–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scandiffio, R.; Geddo, F.; Cottone, E.; Querio, G.; Antoniotti, S.; Gallo, M.P.; Maffei, M.E.; Bovolin, P. Protective effects of (E)-β-Caryophyllene (BCP) in chronic inflammation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechtner, S.; Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, I.; Szlenk, C.T.; Muench, T.R.; Natesan, S.; Ahmed, S. Cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist JWH-015 inhibits interleukin-1β-induced inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and in adjuvant induced arthritis rat via glucocorticoid receptor. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapellos, T.S.; Recio, C.; Greaves, D.R.; Iqbal, A.J. Cannabinoid receptor 2 modulates neutrophil recruitment in a murine model of endotoxemia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4315412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tschöp, J.; Kasten, K.R.; Nogueiras, R.; Goetzman, H.S.; Cave, C.M.; England, L.G.; Dattilo, J.; Lentsch, A.B.; Tschöp, M.H.; Caldwell, C.C. The cannabinoid receptor 2 is critical for the host response to sepsis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, K.; Mehta, H.; Drevets, D.A.; Coggeshall, K.M. IL-6 increases B-cell IgG production in a feed-forward proinflammatory mechanism to skew hematopoiesis and elevate myeloid production. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2010, 115, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millrud, C.R.; Bergenfelz, C.; Leandersson, K. On the origin of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwong, L.N.; Dove, W.F. APC and its modifiers in colon cancer. APC Proteins 2009, 656, 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okita, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ohira, M.; Muguruma, K.; Kubo, N.; Watanabe, M.; Fukushima, W.; Hirakawa, K. Role of tumor-infiltrating CD11b+ antigen-presenting cells in the progression of gastric cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 186, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, R.; Kovalska, J.; Janda, J.; Vannucci, L.; Rajmon, R.; Horak, V. Tumor progression is associated with increasing CD11b+ cells and CCL2 in Lewis rat sarcoma. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, Q.; Jin, Y. Interleukin-17 acts as double-edged sword in anti-tumor immunity and tumorigenesis. Cytokine 2017, 89, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raber, P.L.; Thevenot, P.; Sierra, R.; Wyczechowska, D.; Halle, D.; Ramirez, M.E.; Ochoa, A.C.; Fletcher, M.; Velasco, C.; Wilk, A. Subpopulations of myeloid-derived suppressor cells impair T cell responses through independent nitric oxide-related pathways. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2853–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-E.; Paik, H.Y.; Yoon, H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, N.; Sung, M.-K. Sex-and gender-specific disparities in colorectal cancer risk. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2015, 21, 5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsak, M.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Freudenberg, J.; Ostertag, A.; Morieux, C.; Kornak, U.; Essig, J.; Erxlebe, E.; Bab, I.; Kubisch, C.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor type 2 gene is associated with human osteoporosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karsak, M.; Malkin, I.; Toliat, M.R.; Kubisch, C.; Nurnberg, P.; Zimmer, A.; Livshits, G. The cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CNR2) gene is associated with hand bone strength phenotypes in an ethnically homogeneous family sample. Hum. Genet. 2009, 126, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankman, J.L.; Cravatt, B.F. Chemical probes of endocannabinoid metabolism. Pharm. Rev. 2013, 65, 849–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raphael-Mizrahi, B.; Attar-Namdar, M.; Chourasia, M.; Cascio, M.G.; Shurki, A.; Tam, J.; Neuman, M.; Rimmerman, N.; Vogel, Z.; Shteyer, A.; et al. Osteogenic growth peptide is a potent anti-inflammatory and bone preserving hormone via cannabinoid receptor type 2. eLife 2022, 11, e65834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, Z.; Chorev, M.; Muhlrad, A.; Shteyer, A.; Namdar-Attar, M.; Casap, N.; Tartakovsky, A.; Vidson, M.; Bab, I. Structural and functional characterization of osteogenic growth peptide from human serum: Identity with rat and mouse homologs. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 2330–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bab, I.; Gavish, H.; Namdar-Attar, M.; Muhlrad, A.; Greenberg, Z.; Chen, Y.; Mansur, N.; Shteyer, A.; Chorev, M. Isolation of mitogenically active C-terminal truncated pentapeptide of osteogenic growth peptide from human plasma and culture medium of murine osteoblastic cells. J. Pept. Res. 1999, 54, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bab, I.; Gazit, D.; Chorev, M.; Muhlrad, A.; Shteyer, A.; Greenberg, Z.; Namdar, M.; Kahn, A. Histone H4-related osteogenic growth peptide (OGP): A novel circulating stimulator of osteoblastic activity. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutahara, N.M.; Weems, Y.S.; Arreguin-Arevalo, J.A.; Nett, T.M.; LaPorte, M.E.; Uchida, J.; Pang, J.; McBride, T.; Randel, R.D.; Weems, C.W. Effects of endocannabinoid 1 and 2 (CB1; CB2) receptor agonists on luteal weight, circulating progesterone, luteal mRNA for luteinizing hormone (LH) receptors, and luteal unoccupied and occupied receptors for LH in vivo in ewes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 94, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, J.; Grabiec, U.; Greither, T.; Fischer, B.; Dehghani, F. The endocannabinoid system in the human granulosa cell line KGN. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 423, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, R.M.; Marusich, J.A.; Wiley, J.L. Sex differences in cannabinoid pharmacology: A reflection of differences in the endocannabinoid system? Life Sci. 2013, 92, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, F.; Bellini, G.; Luongo, L.; Manzo, I.; Tolone, S.; Tortora, C.; Bernardo, M.E.; Grandone, A.; Conforti, A.; Docimo, L. Cannabinoid receptor 2 as antiobesity target: Inflammation, fat storage, and browning modulation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3469–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louvet, A.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Chobert, M.N.; Deveaux, V.; Pavoine, C.; Zimmer, A.; Pecker, F.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors protect against alcoholic liver disease by regulating Kupffer cell polarization in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turano, M.; Cammarota, F.; Duraturo, F.; Izzo, P.; De Rosa, M. A potential role of IL-6/IL-6R in the development and management of colon cancer. Membranes 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltgalvis, K.A.; Berger, F.G.; Pena, M.M.O.; Davis, J.M.; Muga, S.J.; Carson, J.A. Interleukin-6 and cachexia in Apc Min/+ mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R393–R401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belluco, C.; Nitti, D.; Frantz, M.; Toppan, P.; Basso, D.; Plebani, M.; Lise, M.; Jessup, J.M. Interleukin-6 blood level is associated with circulating carcinoembryonic antigen and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 7, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzler, K.L.; Hardee, J.P.; Puppa, M.J.; Narsale, A.A.; Sato, S.; Davis, J.M.; Carson, J.A. Sex differences in the relationship of IL-6 signaling to cancer cachexia progression. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puppa, M.J.; White, J.P.; Sato, S.; Cairns, M.; Baynes, J.W.; Carson, J.A. Gut barrier dysfunction in the ApcMin/+ mouse model of colon cancer cachexia. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palazuelos, J.; Davoust, N.; Julien, B.; Hatterer, E.; Aguado, T.; Mechoulam, R.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; Silva, A.; Guzman, M. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor controls myeloid progenitor trafficking: Involvement in the pathogenesis of an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13320–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staiano, R.I.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannotti, F.A.; Piscitelli, F.; Orlando, P.; Secondo, A.; Granata, F.; Lepore, M.T.; Fiorelli, A. Human lung-resident macrophages express CB1 and CB2 receptors whose activation inhibits the release of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Lanuti, M.; Catanzaro, G.; Fezza, F.; Rapino, C.; Maccarrone, M. Detailed characterization of the endocannabinoid system in human macrophages and foam cells, and anti-inflammatory role of type-2 cannabinoid receptor. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edin, S.; Wikberg, M.L.; Dahlin, A.M.; Rutegård, J.; Öberg, Å.; Oldenborg, P.-A.; Palmqvist, R. The distribution of macrophages with a M1 or M2 phenotype in relation to prognosis and the molecular characteristics of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carayon, P.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Derocq, J.-M.; Jbilo, O.; Bord, A.; Bouaboula, M.; Galiegue, S.; Mondiere, P.; Pénarier, G.; et al. Modulation and functional involvement of CB2 peripheral cannabinoid receptors during B-cell differentiation. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1998, 92, 3605–3615. [Google Scholar]
- Ziring, D.; Wei, B.; Velazquez, P.; Schrage, M.; Buckley, N.E.; Braun, J. Formation of B and T cell subsets require the cannabinoid receptor CB2. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, N.P.; Singh, B.; Price, R.L.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Cannabinoid receptor-2 (CB2) agonist ameliorates colitis in IL-10−/− mice by attenuating the activation of T cells and promoting their apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, W.; Alrafas, H.R.; Wilson, K.; Miranda, K.; Culpepper, C.; Chatzistamou, I.; Cai, G.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 prevents colitis-associated colon cancer through myeloid cell de-activation upstream of IL-22 production. Iscience 2020, 23, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, A.F.; Marcon, R.; Dutra, R.C.; Claudino, R.F.; Cola, M.; Leite, D.F.P.; Calixto, J.B. β-Caryophyllene inhibits dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through CB2 receptor activation and PPARγ pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-K.; Chou, P.-H.; Ng, S.-K.; Lin, W.-Y.; Wei, T.-T. Cannabinoids orchestrate cross-talk between cancer cells and endothelial cells in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Shi, R.; Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, A.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, K. Monoacylglycerol lipase regulates cannabinoid receptor 2-dependent macrophage activation and cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, K.D.; Davison, J.S.; Pittman, Q.J.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in health and disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1394–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Martínez, E.; Gómez, I.; Martín, P.; Sánchez, A.; Román, L.; Tejerina, E.; Bonilla, F.; Merino, A.G.; de Herreros, A.G.; Provencio, M. Cannabinoids receptor type 2, CB2, expression correlates with human colon cancer progression and predicts patient survival. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, P.; Goya, P.; Jagerovic, N. Emerging strategies targeting CB2 cannabinoid receptor: Biased agonism and allosterism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, E.; Walraed, J.; Banister, S.D.; Stove, C.P. Insights into biased signaling at cannabinoid receptors: Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 169, 113623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, M.S.; Connor, M.; Glass, M. Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor signaling and bias. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soethoudt, M.; Grether, U.; Fingerle, J.; Grim, T.W.; Fezza, F.; De Petrocellis, L.; Ullmer, C.; Rothenhäusler, B.; Perret, C.; Van Gils, N. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand profiling reveals biased signalling and off-target activity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neale, B. GWAS Analysis of the UKBiobank. Available online: http://www.nealelab.is/uk-biobank (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Berisa, T.; Pickrell, J.K. Approximately independent linkage disequilibrium blocks in human populations. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machiela, M.J.; Chanock, S.J. LDlink: A web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3555–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Milanesi, M.; Utsunomiya, A.T.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Garcia, J.F. GHap: An R package for genome-wide haplotyping. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2861–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iden, J.A.; Raphael-Mizrahi, B.; Awida, Z.; Naim, A.; Zyc, D.; Liron, T.; Kasher, M.; Livshits, G.; Vered, M.; Gabet, Y. The Anti-Tumorigenic Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in Colon Cancer: A Study in Mice and Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044060
Iden JA, Raphael-Mizrahi B, Awida Z, Naim A, Zyc D, Liron T, Kasher M, Livshits G, Vered M, Gabet Y. The Anti-Tumorigenic Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in Colon Cancer: A Study in Mice and Humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044060
Chicago/Turabian StyleIden, Jennifer Ana, Bitya Raphael-Mizrahi, Zamzam Awida, Aaron Naim, Dan Zyc, Tamar Liron, Melody Kasher, Gregory Livshits, Marilena Vered, and Yankel Gabet. 2023. "The Anti-Tumorigenic Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in Colon Cancer: A Study in Mice and Humans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044060
APA StyleIden, J. A., Raphael-Mizrahi, B., Awida, Z., Naim, A., Zyc, D., Liron, T., Kasher, M., Livshits, G., Vered, M., & Gabet, Y. (2023). The Anti-Tumorigenic Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in Colon Cancer: A Study in Mice and Humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044060