Rapid Detection of the Strawberry Foliar Nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipsticks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nematode Samples
2.2. RPA Primers and Probe Design
2.3. RPA Detection
2.4. LF-RPA Assay
2.4.1. Specificity Testing
2.4.2. Sensitivity Testing
2.4.3. Testing of Plant Herbarium Materials
2.4.4. Testing of Field Samples
3. Discussion
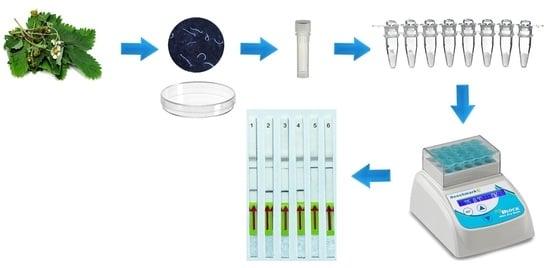
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Nematode Samples
4.2. Preparation of Nematode Crude Extract and DNA Extrication
4.3. Nematode Molecular Identification
4.4. RPA Primer and Probe Design and Testing
4.5. LF-RPA Assay
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christie, J.R. Recent observations on the strawberry dwarf nematode in Massachusetts. Plant Dis. Report. 1932, 16, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ritzema Bos, J. Zwei neue Nematodenkrankheiten der Erdbeerpflanzen. Z. Für Pflanzenkrankh. Pflanzenschutz 1891, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.W. Taxonomic status of the bud and leaf nematodes related to Alphelenchoides fragariae (Ritzema Bos, 1891). Proc. Helminth. Soc. Wash. 1952, 19, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Raski, D.J.; Allen, M.W. Spring dwarf nematode. Calif. Agric. 1948, 4, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, J.L. (Ed.) Compendium of Strawberry Diseases, 2nd ed.; APS Press: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sturhan, D. Über neue Wirtspflanzen der Blattälchen Aphelenchoides fragariae und A. ritzemabosi, mit Bemerkungen zu den Wirtspflanzenkreisen beider Nematodenarten. Anz. Schädlingskunde 1962, 35, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.R. Aphelenchoides fragariae. C.I.H. Description of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Set 5, No. 74; William Clowes & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 1975; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.E.; Ko, W.H.; Kunimoto, R.K.; Higaki, T. A foliar disease of anthurium seedlings caused by Aphelenchoides fragariae. Phytopathology 1974, 64, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.W.L.; Hill, C.F.; Sturhan, D. Further records of Aphelenchoides fragariae and A. ritzemabosi (Nematoda: Aphelenchida) from New Zealand. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2002, 31, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Son, S.; Moon, H.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y. Description of a foliar nematode, Aphelenchoides fragariae (Nematoda: Aphelenchida) with additional characteristics from Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2007, 10, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Son, S.H.; Shin, H.D.; Kim, Y.H. First report of a foliar nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae (Aphelenchidae) on Stachys riederi var. japonica, a medicinal plant, in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 2008, 24, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, L.M. Foliar nematodes: A summary of biology and control with a compilation of host range. Plant Health Prog. 2011, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Agudelo, P.; Gerard, P. A protocol for assessing resistance to Aphelenchoides fragariae in hosta cultivars. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.A.; Sher, S.A.; French, A.M. Distribution of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in California; Division of Plant Industry, Department of Food and Agriculture: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1973; 324p. [Google Scholar]
- Handoo, Z.; Kantor, M.; Carta, L. Taxonomy and identification of principal foliar nematode species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus). Plants 2020, 9, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.J. Aphelenchida, Longidoridae and Trichodoridae: Their Systematics and Bionomics; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1993; 352p. [Google Scholar]
- The California Strawberry Commission (CSC) & the California Minor Crops Council (CMCC). A Pest Management Strategic Plan for Strawberry Production in California. Available online: https://ipmdata.ipmcenters.org/documents/pmsps/CASTRAWBERRY.PDF (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Strawberry Registration & Certification Program. Available online: https://www.cdfa.ca.gov/plant/pe/nsc/nursery/strawberry.html (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Franklin, M.T. Aphelenchoides and related genera. In Plant Nematology; Southey, J.F., Ed.; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1978; pp. 172–187. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahori, H.; Tsuda, K.; Kanzaki, N.; Izui, K.; Futai, K. PCR-RFLP and sequencing analysis of DNA of Bursaphelenchus nematodes related to pine wilt disease. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1998, 21, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- McCuiston, J.L.; Hudson, L.C.; Subbotin, S.A.; Davis, E.L.; Warfield, C.Y. Conventional and PCR detection of Aphelenchoides fragariae in diverse ornamental host plant species. J. Nematol. 2007, 39, 343–355. [Google Scholar]
- Rybarczyk-Mydłowska, K.; Mooyman, P.; van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Vervoort, M.; Veenhuizen, P.; van Doorn, J.; Dees, R.; Karssen, G.; Bakker, J.; et al. Small subunit ribosomal DNA-based phylogenetic analysis of foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) and their quantitative detection in complex DNA backgrounds. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chałańska, A.; Bogumił, A.; Winiszewska, G.; Kowalewska, K.; Malewski, T. Morphological and molecular characteristics of foliar nematode attacking silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) in Poland. Helminthologia 2017, 54, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; van der Wurff, A.; van den Elsen, S.; van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; Karegar, A.; Mooijman, P.; van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Vervoort, M.T.; Quist, C.W.; Karssen, G.; Decraemer, W.; Opperman, C.H.; et al. Disparate gain and loss of parasitic abilities among nematode lineages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Monge, A.; Janssen, T.; Fang, Y.; Couvreur, M.; Karssen, G.; Bert, W. mtCOI successfully diagnoses the four main plant-parasitic Aphelenchoides species (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and supports a multiple origin of plant-parasitism in this paraphyletic genus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiwanti, S.R.; Miftakhurohmah. Molecular detection and identification of the foliar nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae on Andrographis paniculata in Indonesia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2022, 51, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.K.; Perry, R.N.; Burrows, P.R.; Hooper, D.J. Differentiation of species and populations of Aphelenchoides and of Ditylenchus angustus using a fragment of ribosomal DNA. J. Nematol. 1994, 26, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Liao, C.; Liang, L.; Yi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, G. Recent advances in recombinase polymerase amplification: Principle, advantages, disadvantages and applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1019071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotin, S.A.; Burbridge, J. Sensitive, accurate and rapid detection of the northern root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne hapla, using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification assays. Plants 2021, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, R.; Peng, H.; Jiang, R.; Shao, H.D.; Ge, J.J.; Peng, D.L. Rapid diagnosis and visual detection of potato cyst nematode (Globodera rostochiensis) using recombinase polymerase amplification combination with lateral flow assay method (RPA-LFA). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotin, S.A. On the reliability of recombinase polymerase amplification—Lateral flow assay using ITS rRNA gene primers and probe as a new detection method of the golden potato cyst nematode, Globodera rostochiensis. Russ. J. Nematol. 2023, 31, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, J.R. A description of Aphelenchoides besseyi n. sp., the summer dwarf nematode of strawberries, with comments on the identity of Aphelenchoides subtenuis (Cobb, 1929) and Aphelenchoides hodsoni Goodey, 1935. Proceeding Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1942, 9, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, M.T. Two species of Aphelenchoides associated with strawberry bud disease in Britain. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1950, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, S.; Brekke, K. Yield loss in strawberries caused by Aphelenchoides blastophthorus. (Abstract). Nematology 2000, 2, 759. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, E.; Ruthes, A.C.; Reinhard, E.; Dahlin, P. First morphological and molecular report of Aphelenchoides blastophthorus on strawberry plants in Switzerland. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2851–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.J.; Subbotin, S.A.; Álvarez-Ortega, S.; Desaeger, J.; Brito, J.A.; Xavier, K.; Freitas, L.G.; Vau, S.; Inserra, R.N. Morphological and molecular identification of two Florida populations of foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) isolated from strawberry with the description of Aphelenchoides pseudogoodeyi sp. n. (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and notes on their bionomics. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2825–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.J.; Subbotin, S.A.; Desaeger, J.A.; Dahlin, P.; Vau, S.; Inserra, R.N. Morphological and molecular analysis of two mycophagous nematodes, Aphelenchoides bicaudatus and A. rutgersi (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from Florida strawberry. J. Nematol. 2024, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Subbotin, S.A.; Oliveira, C.J.; Alvarez-Ortega, S.; Desaeger, J.; Crow, W.; Overstreet, C.; Leany, R.; Vau, S.; Inserra, R.N. The taxonomic status of Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942 (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) populations from the Southeastern USA, and description of Aphelenchoides pseudobesseyi sp. n. Nematology 2021, 23, 381–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Li, H. Aphelenchoides smolae n. sp. (Tylenchina: Aphelenchoididae) found in Lilium orientalis imported into China from The Netherlands. Nematology 2020, 22, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeno, J.L.; Jensen, H.J. A foliar nematode disease of western sword-fern, Polystichum munitum. Plant Dis. Report. 1962, 46, 699–701. [Google Scholar]
- Chitambar, J.J.; Westerdahl, B.B.; Subbotin, S.A. Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in California Agriculture. In Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Sustainable Agriculture of North America: Vol.1—Canada, Mexico and Western USA; Subbotin, S.A., Chitambar, J.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 131–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Niu, F.; Luo, Z.; Yu, L.; Yu, C.; Dai, Y.; et al. CRISPR/Cas12a coupled with Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for sensitive and specific detection of Aphelenchoides besseyi. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 912959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, S.M. Plant Nematology: An Agricultural Training Aid; Nema Aid Publications: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1980; 195p. [Google Scholar]
- De Ley, P.; Felix, M.A.; Frisse, L.M.; Nadler, S.A.; Sternberg, P.W.; Thomas, W.K. Molecular and morphological characterisation of two reproductively isolated species with mirror image anatomy (Nematoda: Cephalobidae). Nematology 1999, 2, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, S.A.; Reid, A.; Driver, F.; Curran, J. Application of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods to identification of entomopathogenic nematodes. In COST 812 Biotechnology: Genetics of Entomopathogenic Nematode–Bacterium Complexes; Burnell, A.M., Ehlers, R.U., Masson, J.P., Eds.; Proceedings of Symposium & Workshop, St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, Co.: Kildare, Ireland; Luxembourg, 1994; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Species | Locations | Plants | Materials * | Sample Codes | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphelenchoides fragariae | USA, California, Marin County, Point Reyes National Seashore | Polystichum munitum | ND, PD, Ex | CD3774 | S.A. Subbotin |
| A. fragariae | USA, California, Mendocino County | P. munitum | ND, Ex | CD4001 | S.A. Subbotin |
| A. fragariae | USA, Connecticut, Windsor | Salvia sp. | ND, Ex | CD3787 | J.A. LaMondia |
| A. fragariae | USA, Washington, Clallam County, Storm King Ranger Station | Unidentified plant | ND; Ex | CD3764 | S.A. Subbotin |
| A. fragariae | Russia, Moscow, Main Botanical Garden of the RAS | Pteris sp. | ND, PD | CA30, CA38, CA53, CD3796 | V.N. Chizhov |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Anemone hupehensis | ND, PD | CD386, CD3797 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Lantana camara | ND | CD388 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | USA, California | Oryza sativa | ND, Ext | CD754 | S.A. Subbotin |
| A. fragariae | Germany | Primula denticulata | PD | CD3804 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany | Lagarosiphon cordofanus | PD | CD3806 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | New Zealand | Ptisana salicina | PD | CD3808 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | New Zealand | Polystichum sp. | PD | CD3809 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Polypodium californica | PD | CD3794 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Lantana sp. | PD | CD3795 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Anemone × hybrida | PD | CD3799 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | USA, North Carolina | Heuchera sp. | PD | CD3798 | J.L. McCuiston |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Mimulus moschatus | PD | CD3800 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany | Matteuccia orientalis | PD | CD3801 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, München | Osmunda regalis | PD | CD3810 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | New Zealand | Todea barbara | PD | CD3811 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Penstemon campanulatus | PD | CD3934 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Lithospermum arvense | PD | CD3944 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | New Zealand | Blechnum sp. | PD | CD3950 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Solidago glomerata | PD | CD3946 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Tellima grandiflora | PD | CD3947 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Bergenia sp. | PD | CD3948 | D. Sturhan |
| A. fragariae | Germany, Münster | Ligularia sp. | PD | CD3949 | D. Sturhan |
| A. besseyi | USA, Florida | Fragaria × ananassa | ND | CD2415 | C. Oliveira |
| A. oryzae | USA, Louisiana, Morehouse Parish, Mer Rouge | Oryza sativa | ND | CD2471 | C. Overstreet |
| A. oryzae | Russia, Krasnodar | O. sativa | ND | CD3790 | V.N. Chizhov |
| A. pseudobesseyi | USA, Florida, Sumter County, Sumterville | Dryopteris erythrosora | ND | CD2704 | W. Crow |
| A. pseudobesseyi | USA, North Carolina, Jackson County, Cullowhee | Soil sample | ND | CD3097 | C. Oliveira |
| A. pseudobesseyi | USA, Florida, Alachua County, Gainesville | Echinacea sp. | ND | CD2491, CD3702 | W. Crow |
| A. ritzemabosi | USA, California, Mendocino County | Helleborus sp. | ND | CD1366 | S.A. Subbotin |
| A. smolae | USA, Oregon, Bonanza | Fragaria × ananassa | ND | CD3775 | S.A. Subbotin |
| Aphelenchoides sp. | USA, California, San Diego County | Grasses | ND | CD1300 | S.A. Subbotin |
| Aphelenchus sp. | USA, California, Tehama County | Fragaria × ananassa | ND | CD3788b | S.A. Subbotin |
| Cryptaphelenchus sp. | Tomsk region, Malinovka | Abies sibirica | ND | CD3657 | A. Ryss |
| Bursaphelenchus cocophilus | Mexico, Guerrero state | Cocos nucifera | ND | CD3548, CD3572 | I. Cide del Prado Vera |
| B. fraudulentus | Russia, Moscow, Main Botanical Garden of the RAS | Quercus robur | ND | CD2935 | A. Ryss |
| B. mucronatus | Russia, Buryatia | Abies sibirica | ND | CD3642 | A. Ryss |
| Laimaphelenchus hyrcanus | Russia, Saint Petersburg | Q. robur | ND | CD3646 | A. Ryss |
| Unidentified anguinid nematode | USA, Washington, Clallam County, Storm King Ranger Station | P. munitum | ND, Ex | CD3762 | S.A. Subbotin |
| Primer or Probe | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| AfragF2-ITS | CTT GTT TGA GAT CTT CTA GAC TA |
| AfragR1-ITS | GCG CCA CATC GGG TCA TTA TTT |
| AfragR1-ITS-biotin | [Biotin] GCG CCA CATC GGG TCA TTA TTT |
| Probe-Afrag-ITS-RPA-nfo | [FAM] TG AGT AGT TGT CTA GTT CGT GAC TAC TAA GAC TTT [THF] ATT GGT AGA GTC GCT CTA T [C3-spacer] * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subbotin, S.A. Rapid Detection of the Strawberry Foliar Nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipsticks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020844
Subbotin SA. Rapid Detection of the Strawberry Foliar Nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipsticks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020844
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubbotin, Sergei A. 2024. "Rapid Detection of the Strawberry Foliar Nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipsticks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020844
APA StyleSubbotin, S. A. (2024). Rapid Detection of the Strawberry Foliar Nematode Aphelenchoides fragariae Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipsticks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020844