Lectin-like Transcript-1 (LLT1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Prognostic Significance and Relationship with the Tumor Immune Microenvironment
Abstract
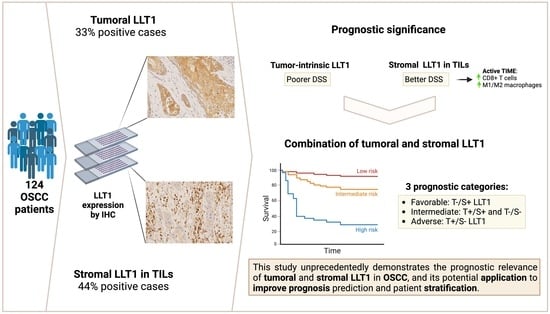
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Follow-Up
2.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis of LLT1 Expression in OSCC Tissue Specimens
2.3. Associations of LLT1 Expression with Clinicopathological Variables and Patient Survival
2.4. Relationships between Tumoral and Stromal LLT1 Expression and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Tissue Specimens
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
International Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L. Immunology and immunotherapy of head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buller, C.W.; Mathew, P.A.; Mathew, S.O. Roles of NK cell receptors 2B4 (CD244), CS1 (CD319), and LLT1 (CLEC2D) in cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: From tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, D.H.; Bronte, V. Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, F.; Stefanovic, S.; Mayer, L.; von Au, A.; Domschke, C.; Sohn, C. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in breast cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2017, 40, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.W.; Ngiow, S.F.; Ribas, A.; Smyth, M.J. Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grégoire, C.; Chasson, L.; Luci, C.; Tomasello, E.; Geissmann, F.; Vivier, E.; Walzer, T. The trafficking of natural killer cells. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 220, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.L.; Byron, K.S.; Brewster, F.E.; Purtilo, D.T. Deficient natural killer cell activity in x-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Science 1980, 210, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, J.C.; Haliotis, T.; Klein, M.; Korec, S.; Jett, J.R.; Ortaldo, J.; Heberman, R.B.; Katz, P.; Fauci, A.S. A new immunodeficiency disorder in humans involving NK cells. Nature 1980, 284, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiossone, L.; Dumas, P.Y.; Vienne, M.; Vivier, E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenart, M.; Górecka, M.; Bochenek, M.; Barreto-Duran, E.; Szczepański, A.; Gałuszka-Bulaga, A.; Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Węglarczyk, K.; Siwiec-Koźlik, A.; Korkosz, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs NK cell functions via activation of the LLT1-CD161 axis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bláha, J.; Skálová, T.; Kalousková, B.; Skořepa, O.; Cmunt, D.; Grobárová, V.; Pazicky, S.; Poláchová, E.; Abreu, C.; Stránský, J.; et al. Structure of the human NK cell NKR-P1:LLT1 receptor: Ligand complex reveals clustering in the immune synapse. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, A.; Costa, P.; Tomasello, E.; Moretta, L. IL-12-induced up-regulation of NKRP1A expression in human NK cells and consequent NKRP1A-mediated down-regulation of NK cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.O.; Chaudhary, P.; Powers, S.B.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Mathew, P.A. Overexpression of LLT1 (OCIL, CLEC2D) on prostate cancer cells inhibits NK cell-mediated killing through LLT1-NKRP1A (CD161) interaction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68650–68661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, P.; Mittelbronn, M.; Wick, W.; Meyermann, R.; Tatagiba, M.; Weller, M. Malignant glioma cells counteract antitumor immune responses through expression of lectin-like transcript-1. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3540–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrufo, A.M.; Mathew, S.O.; Chaudhary, P.; Malaer, J.D.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Mathew, P.A. Blocking LLT1 (CLEC2D, OCIL)-NKRP1A (CD161) interaction enhances natural killer cell-mediated lysis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Germain, C.; Guillaudeux, T.; Galsgaard, E.D.; Hervouet, C.; Tekaya, N.; Gallouet, A.S.; Fassy, J.; Bihl, F.; Poupon, G.; Lazzari, A.; et al. Lectin-like transcript 1 is a marker of germinal center-derived B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas dampening natural killer cell functions. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1026503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Dong, Y.; Xie, S.; Song, Y.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Ni, Y.; Ding, L. Immune checkpoint CD161/LLT1-associated immunological landscape and diagnostic value in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2024, 10, e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Begley, G.; Cecchini, M.; Eder, J.P.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Italiano, A.; Kochetkova, M.; Li, R.; et al. Developing a definition of immune exclusion in cancer: Results of a modified Delphi workshop. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanitis, E.; Dangaj, D.; Irving, M.; Coukos, G. Mechanisms regulating T-cell infiltration and activity in solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. 12), xii18–xii32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kather, J.N.; Suarez-Carmona, M.; Charoentong, P.; Weis, C.A.; Hirsch, D.; Bankhead, P.; Horning, M.; Ferber, D.; Kel, I.; Herpel, E.; et al. Topography of cancer-associated immune cells in human solid tumors. eLife 2018, 7, e36967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Irving, B.A.; Hodi, F.S. Molecular pathways: Next-generation immunotherapy--inhibiting programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6580–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Lao, I.; Shi, Y.; Luo, X.; Yan, W. Changes in the tumor immune microenvironment in resected recurrent soft tissue sarcomas. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Malaer, J.D.; Mathew, P.A. Lectin-like transcript 1 as a natural killer cell-mediated immunotherapeutic target for triple negative breast cancer and prostate cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 2019, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, J.S.; Ballas, Z.K. Natural killer cells in human health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llibre, A.; Garner, L.; Partridge, A.; Freeman, G.J.; Klenerman, P.; Willberg, C.B. Expression of lectin-like transcript-1 in human tissues. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llibre, A.; López-Macías, C.; Marafioti, T.; Mehta, H.; Partridge, A.; Kanzig, C.; Rivellese, F.; Galson, J.D.; Walker, L.J.; Milne, P.; et al. LLT1 and CD161 expression in human germinal centers promotes B cell activation and CXCR4 downregulation. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaer, J.D.; Mathew, P.A. Role of LLT1 and PCNA as natural killer cell immune evasion strategies of HCT 116 cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6613–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, V.M.; Biton, J.; Becht, E.; Knockaert, S.; Mansuet-Lupo, A.; Cosson, E.; Damotte, D.; Alifano, M.; Validire, P.; Anjuère, F.; et al. Expression of LLT1 and its receptor CD161 in lung cancer is associated with better clinical outcome. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1423184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Juanes, J.; Fernández-Vega, I.; Lorenzo-Herrero, S.; Sordo-Bahamonde, C.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; Vivanco, B.; Galache-Osuna, C.; Vazquez-Lopez, F.; Gonzalez, S.; et al. Lectin-like transcript 1 (LLT1) expression is associated with nodal metastasis in patients with head and neck cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Canteli, M.; Hermida-Prado, F.; Sordo-Bahamonde, C.; Montoro-Jiménez, I.; Pozo-Agundo, E.; Allonca, E.; Vallina-Álvarez, A.; Álvarez-Marcos, C.; Gonzalez, S.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; et al. Lectin-Like Transcript 1 (LLT1) checkpoint: A novel independent prognostic factor in HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiossone, L.; Vivier, E. Bringing natural killer cells to the clinic. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braud, V.M.; Meghraoui-Kheddar, A.; Elaldi, R.; Petti, L.; Germain, C.; Anjuère, F. LLT1-CD161 interaction in cancer: Promises and challenges. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.B.; Cao, W.; Avery, D.T.; Tangye, S.G.; Liu, Y.J.; Houchins, J.P.; Lanier, L.L. Functional consequences of interactions between human NKR-P1A and its ligand LLT1 expressed on activated dendritic cells and B cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6508–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, W.; Ruschpler, P.; Wobus, M.; Drossler, K. Differentially induced expression of C-type lectins in activated lymphocytes. J. Cell Biochem. Suppl. 2001, 81 (Suppl. 36), 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, C.; Meier, A.; Jensen, T.; Knapnougel, P.; Poupon, G.; Lazzari, A.; Neisig, A.; Håkansson, K.; Dong, T.; Wagtmann, N.; et al. Induction of lectin-like transcript 1 (LLT1) protein cell surface expression by pathogens and interferon-γ contributes to modulate immune responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37964–37975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalan, P.; Bijzet, J.; Huitema, M.G.; Kroesen, B.J.; Brouwer, E.; Boots, A.M. Expression of lectin-like transcript 1, the ligand for CD161, in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, S.; Hundrieser, J.; Pokoyski, C.; Kollrich, S.; Borns, K.; Blasczyk, R.; Poehnert, D.; Klempnauer, J.; Schwinzer, R. The c.503T>C polymorphism in the human KLRB1 gene alters ligand binding and inhibitory potential of CD161 molecules. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llibre, A.; Klenerman, P.; Willberg, C.B. Multi-functional lectin-like transcript-1: A new player in human immune regulation. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 177, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satkunanathan, S.; Kumar, N.; Bajorek, M.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Culley, F.J. Respiratory syncytial virus infection, TLR3 ligands and pro-inflammatory cytokines induce CD161 ligand LLT1 expression on the respiratory epithelium. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambard, N.D.; Mathew, S.O.; Mathew, P.A. LLT1-mediated activation of IFN-gamma production in human natural killer cells involves ERK signalling pathway. Scand. J. Immunol. 2010, 71, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, J.R.; Wilson, C.B. Regulation of interfero-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv. Immunol. 2007, 96, 41–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, M.A.; Schreiber, R.D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 571–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydiatt, W.M.; Patel, S.G.; Ridge, J.A.; O’Sullivan, B.; Shah, J.P. Staging head and neck cancers. In AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Switzerland, IL, USA, 2017; pp. 55–181. [Google Scholar]
- de Vicente, J.C.; Peña, I.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Rodríguez-Santamarta, T.; Lequerica-Fernández, P.; Suárez-Fernández, L.; Allonca, E.; García-Pedrero, J.M. Phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 correlatiowith p21 expression and inverse association with tumor size in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2017, 39, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vicente, J.C.; Rodríguez-Santamarta, T.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Allonca, E.; García-Pedrero, J.M. PD-L1 expression in tumor cells is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | No. Cases | Tumoral LLT1-Positive Expression (%) | p | Stromal LLT1-Positive Expression (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||||
| <65 years | 76 | 23 (30) | 0.40 # | 35 (46) | 0.63 # |
| ≥65 years | 48 | 18 (37) | 20 (42) | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Men | 81 | 27 (33) | 0.93 # | 33 (41) | 0.26 # |
| Women | 43 | 14 (33) | 22 (51) | ||
| Tobacco use | |||||
| Smoker | 83 | 26 (31) | 0.55 # | 38 (46) | 0.64 # |
| Non-smoker | 41 | 15 (37) | 17 (42) | ||
| Alcohol use | |||||
| Drinker | 68 | 22 (32) | 0.85 # | 27 (40) | 0.25 # |
| Non-drinker | 56 | 19 (34) | 28 (50) | ||
| Tumor status | |||||
| pT1 | 27 | 8 (30) | 0.91 * | 9 (33) | 0.18 * |
| pT2 | 54 | 17 (32) | 28 (52) | ||
| pT3 | 16 | 6 (38) | 9 (56) | ||
| pT4 | 27 | 10 (37) | 9 (33) | ||
| Nodal status | |||||
| pN0 | 76 | 24 (32). | 0.38 * | 35 (46) | 0.33 * |
| pN1 | 25 | 11 (44). | 8 (32) | ||
| pN2 | 23 | 6(26) | 12 (52) | ||
| Clinical stage | |||||
| Stage I | 20 | 6 (30) | 0.85 * | 7 (35) | 0.19 * |
| Stage II | 32 | 9 (28) | 19 (59) | ||
| Stage III | 26 | 9 (35) | 9 (35) | ||
| Stage IV | 46 | 17 (37) | 20 (44) | ||
| WHO histopathological grade | |||||
| G1 | 79 | 24 (30) | 0.40 # | 34 (43) | 0.69 # |
| G2–G3 | 45 | 17 (38) | 21 (47) | ||
| Follow-up | |||||
| Alive | 52 | 16 (31) | 0.59 * | 27 (52) | 0.24 * |
| Dead by the disease | 53 | 20 (38) | 19 (36) | ||
| Censored | 19 | 5 (26) | 9 (47) |
| Factor (Mean, SD) | Tumoral LLT1 Expression | p * | Stromal LLT1 Expression | p * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | |||
| Stroma-infiltrating CD4+ | 46.17 (49.57) | 70.52 (95.65) | 0.08 | 53.12 (77.60) | 57.34 (55.04) | 0.42 |
| Tumor-infiltrating CD4+ | 5.41 (11.84) | 7.51 (13.45) | 0.11 | 4.66 (10.40) | 7.82 (14.27) | 0.08 |
| Stroma-infiltrating CD8+ | 148.09 (154.81) | 240.89 (274.72) | 0.03 | 172.91 (201.49) | 188.43 (207.50) | 0.49 |
| Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ | 41.25 (59.29) | 62.45 (51.50) | 0.003 | 34.93 (46.72) | 64.53 (64.94) | 0.005 |
| Stroma-infiltrating CD20+ | 33.68 (62.80) | 60.57 (104.09) | 0.08 | 37.68 (73.34) | 49.25 (85.52) | 0.09 |
| Tumor-infiltrating CD20+ | 1.31 (3.11) | 2.32 (3.76) | 0.002 | 1.34 (3.12) | 2.01 (3.62) | 0.35 |
| Stroma-infiltrating CD68+ | 111.48 (69.95) | 148.35 (101.46) | 0.03 | 111.27 (72.73) | 139.15 (91.03) | 0.11 |
| Tumor-infiltrating CD68+ | 42.17 (37.92) | 70.94 (52.43) | 0.001 | 37.36 (36.68) | 68.65 (48.93) | <0.0001 |
| Stroma-infiltrating CD163+ | 162.78 (95.35) | 179.53 (102.48) | 0.48 | 166.63 (91.06) | 172.34 (105.40) | 0.92 |
| Tumor-infiltrating CD163+ | 25.20 (22.61) | 43.66 (36.33) | 0.002 | 24.59 (27.25) | 39.66 (29.13) | 0.001 |
| Type of TIME | Tumoral LLT1 Expression | p | Stromal LLT1 Expression | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | |||
| Type I (PD-L1+/CD8+ high) | 5 (40%) | 8 (62%) | 3 (23%) | 10 (77%) | ||
| Type II (PD-L1−/CD8+ low) | 31 (80%) | 8 (21%) | 0.018 | 24 (62%) | 15 (39%) | 0.06 |
| Type III (PD-L1+/CD8+ low) | 5 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (80%) | 1 (20%) | ||
| Type IV (PD-L1−/CD8+ high) | 41 (64%) | 23 (36%) | 37 (58%) | 27 (42%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Vicente, J.C.; Lequerica-Fernández, P.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Rodríguez-Santamarta, T.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Prieto-Fernández, L.; Corte-Torres, D.; Vallina, A.; Domínguez-Iglesias, F.; Álvarez-Teijeiro, S.; et al. Lectin-like Transcript-1 (LLT1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Prognostic Significance and Relationship with the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084314
de Vicente JC, Lequerica-Fernández P, Rodrigo JP, Rodríguez-Santamarta T, Blanco-Lorenzo V, Prieto-Fernández L, Corte-Torres D, Vallina A, Domínguez-Iglesias F, Álvarez-Teijeiro S, et al. Lectin-like Transcript-1 (LLT1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Prognostic Significance and Relationship with the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084314
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Vicente, Juan C., Paloma Lequerica-Fernández, Juan P. Rodrigo, Tania Rodríguez-Santamarta, Verónica Blanco-Lorenzo, Llara Prieto-Fernández, Daniela Corte-Torres, Aitana Vallina, Francisco Domínguez-Iglesias, Saúl Álvarez-Teijeiro, and et al. 2024. "Lectin-like Transcript-1 (LLT1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Prognostic Significance and Relationship with the Tumor Immune Microenvironment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084314
APA Stylede Vicente, J. C., Lequerica-Fernández, P., Rodrigo, J. P., Rodríguez-Santamarta, T., Blanco-Lorenzo, V., Prieto-Fernández, L., Corte-Torres, D., Vallina, A., Domínguez-Iglesias, F., Álvarez-Teijeiro, S., & García-Pedrero, J. M. (2024). Lectin-like Transcript-1 (LLT1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Prognostic Significance and Relationship with the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084314