Comparison of Thermal Detector Arrays for Off-Axis THz Holography and Real-Time THz Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Figures of Merit
| Detector Type | LWIR-Bolometer | LWIR-Bolometer | THz Bolometer | Pyroelectric Camera |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Devitech IR-032 | XENICS Gobi 640 | NEC IRV-T0831 | Spiricon Pyrocam III HR |
| Identification | Cam1 | Cam2 | Cam3 | Cam4 |
| Detector material | VOx | a-Si | SiN | LiTaO3 |
| Designated operation range | 8–14 μm (22–37 THz) | 8–14 μm (22–37 THz) | (43–300 μm) 1–7 THz | 1.06–3000 μm 0.1–300 THz |
| Pixel size (μm) | NA | NA | NA | 75 |
| Pixel pitch (μm) | 25 | 17 | 23.5 | 80 |
| Number of pixels | 640 × 480 | 640 × 480 | 320 × 240 | 160 × 160 |
| Detector size (mm2) | 16.0 × 12.0 | 10.9 × 8.2 | 7.5 × 5.6 | 12.8 × 12.8 |
| NEP () | NA | NA | <0.1 @ 4 THz | 12.8 |
| NETD (mK) | 50 | 50 | NA | NA |
| Sensitivity | NA | NA | NA | 96 nW/pix |
| D* () | 3.05 × 107 | 4.49 × 107 | 2.35 × 107 | 5.86 × 107 |
| ADC (bit) | 14 | 16 | 14 | 16 |
| Frame rate (fps) | 50 | 50 | 30 | 50 |
3. Experimental
3.1. Thermal Array Detectors
3.2. THz Laser Source
3.3. Experimental Set-Up


3.3.1. Camera Response
3.3.2. Interference Fringe Contrast
3.3.3. Real-Time Holography
4. Results and Discussion
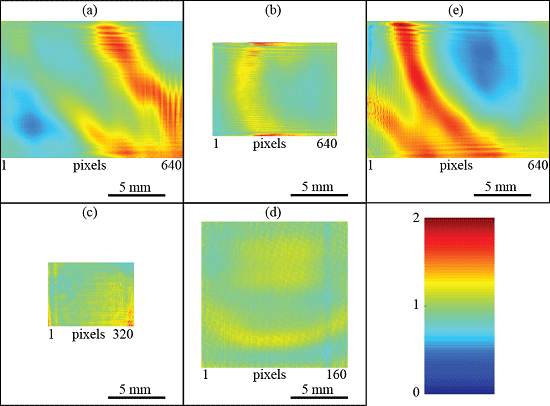
4.1. Beam Profiling
| Detector Type | LWIR-Bolometer | LWIR-Bolometer | THz Bolometer | Pyroelectric Camera |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identification | Cam1 | Cam2 | Cam3 | Cam4 |
| SNRref for beam profile at λ = 118.8 μm | 60 | 80 | 60 | 3 |
| SNRref for beam profile at λ = 393.6 μm | 10 | 7 | 15 | 3 |
| SNRref for interference fringes at λ = 118.8 μm | 85 (70) | 50 | 60 (40) | 0.5 |
4.2. Camera Response

4.3. Interference Fringe Pattern



4.4. Real Time Off-Axis Holography
| Identification | Cam1 | Cam2 | Cam3 | Cam4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR for 40 ms integration time and 10 mW THz power | 136 | 80 | 96 | 0.8 |
| Integration time for SNR = 4 and 10 mW THz power | 0.035 ms | 0.100 ms | 0.069 ms | 1000 ms |
| THz power for SNR = 4 and 40 ms integration time | 0.29 mW | 0.50 mW | 0.42 mW | 50 mW |
| λ = 118.8 μm | 90° | 90° | 90° | 22° |
| λ = 96.5 μm | 75° | 90° | 90° | 18° |


5. Conclusions/Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruse, P.W. Uncooled Thermal Imaging: Arrays, Systems, and Applications; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Datskos, P.G.; Lavrik, N.V.; Rajic, S. Performance of uncooled microcantilever thermal detectors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choporova, Y.Y.; Knyazev, B.A.; Mitkov, M.S. Classical holography in the terahertz range: Recording and reconstruction techniques. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, B.A.; Dem’yanenko, A.A.; Esaev, D.G. Terahertz imaging with a 160 × 120 pixel microbolometer 90-fps camera. In Proceedings of the Joint 32nd International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and 15th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics, Cardiff, UK, 2–9 September 2007; pp. 354–355.
- Behnken, B.N.; Karunasiri, G.; Chamberlin, D.R.; Robrish, P.R.; Faist, J. Real-time imaging using a 2.8 THz quantum cascade laser and uncooled infrared micrometer camera. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnken, B.N.; Lowe, M.; Karunasiri, G.; Chamberlain, D.; Robrish, P.; Faist, J. Detection of 3.4 THz radiation from a quantum cascade laser using a microbolometer infrared camera. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2007, 6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.M.; Hu, Q. Real-time, continuous-wave terahertz imaging by use of a microbolometer focal-plane array. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2563–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, N. Uncooled bolometer-type terahertz focal plane array and camera for real-time imaging. C. R. Phys. 2010, 11, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dem‘yanenko, M.A.; Esaev, D.G.; Ovsyuk, V.N.; Fomin, B.I.; Aseev, A.L.; Knyazev, B.A.; Kulipanov, G.N.; Vinokurov, N.A. Microbolometer detector arrays for the infrared and terahertz ranges. J. Opt. Technol. 2009, 76, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, U. Bolometers; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, D.; Marchese, L.; Terroux, M.; Oulachgar, H.; Genereux, F.; Doucet, M.; Mercier, L.; Tremblay, B.; Alain, C.; Beaupre, P.; et al. Review of terahertz technology development at ino. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 922–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, N.; Kurashina, S.; Miyoshi, M.; Doi, K.; Ishi, T.; Sudou, T.; Morimoto, T.; Goto, H.; Sasaki, T. Microbolometer terahertz focal plane array and camera with improved sensitivity in the sub-terahertz region. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oden, J.; Meilhan, J.; Lalanne-Dera, J.; Roux, J.F.; Garet, F.; Coutaz, J.L.; Simoens, F. Imaging of broadband terahertz beams using an array of antenna-coupled microbolometers operating at room temperature. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 4817–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoens, F.; Meilhan, J.; Gidon, S.; Lasfargues, G.; Dera, J.L.; Ouvrier-Buffet, J.L.; Pocas, S.; Rabaud, W.; Guellec, F.; Dupont, B.; et al. Antenna-coupled microbolometer based uncooled 2d array and camera for 2D real-time terahertz imaging. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2013, 8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Vicario, C.; Hauri, C.P. High-performing nonlinear visualization of terahertz radiation on a silicon charge-coupled device. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, M.; Hauri, C.P. Demonstration of a low-frequency three-dimensional terahertz bullet with extreme brightness. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizov, F.F.; Reva, V.P.; Golenkov, A.G.; Zabudsky, V.V. Uncooled detectors challenges for THz/sub-THz arrays imaging. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklaus, F.; Decharat, A.; Jansson, C.; Stemme, G. Performance model for uncooled infrared bolometer arrays and performance predictions of bolometers operating at atmospheric pressure. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2008, 51, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, P.K.; Hack, E. Phase Estimation in Optical Interferometry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Hack, E.; Zolliker, P. Terahertz holography for imaging amplitude and phase objects. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 16079–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picart, P.; Leval, J. General theoretical formulation of image formation in digital fresnel holography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2008, 25, 1744–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hack, E.; Valzania, L.; Gäumann, G.; Shalaby, M.; Hauri, C.P.; Zolliker, P. Comparison of Thermal Detector Arrays for Off-Axis THz Holography and Real-Time THz Imaging. Sensors 2016, 16, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020221
Hack E, Valzania L, Gäumann G, Shalaby M, Hauri CP, Zolliker P. Comparison of Thermal Detector Arrays for Off-Axis THz Holography and Real-Time THz Imaging. Sensors. 2016; 16(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleHack, Erwin, Lorenzo Valzania, Gregory Gäumann, Mostafa Shalaby, Christoph P. Hauri, and Peter Zolliker. 2016. "Comparison of Thermal Detector Arrays for Off-Axis THz Holography and Real-Time THz Imaging" Sensors 16, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020221
APA StyleHack, E., Valzania, L., Gäumann, G., Shalaby, M., Hauri, C. P., & Zolliker, P. (2016). Comparison of Thermal Detector Arrays for Off-Axis THz Holography and Real-Time THz Imaging. Sensors, 16(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020221