Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure and Morphology of the ZnO NRs
3.2. The Sensing Performance of ZnO NR
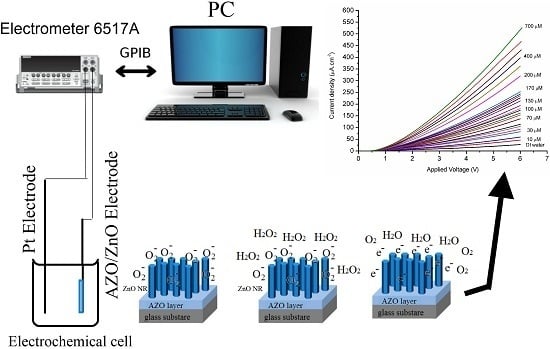
3.2.1. The I-V Response to Hydrogen Peroxide
3.2.2. Amperometric Response
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Li, G. An amperometric biosensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide released from human breast cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z. Tin oxide nanorod array-based electrochemical hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zuo, Y. Factors affecting the levels of hydrogen peroxide in rainwater. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komazaki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tana ka, S. Automated measurement system for H2O2 in the atmosphere by diffusion scrubber sampling and HPLC analysis of Ti(iv)-PAR-H2O2 complex. Analyst 2001, 126, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Gong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tian, Y. WO3 nanostructures facilitate electron transfer of enzyme: Application to detection of H2O2 with high selectivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Liu, D. Facile synthesis of copper oxide nanostructures and their application in non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, D.; Gopalakrishnan, J.B.; Krishnan, U.M.; Madanagurusamy, S.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Nanostructured ZnO thin film for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 43, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafi, A.K.M.; Wu, G.; Chen, A. A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase onto Au-modified titanium dioxide nanotube arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratoddi, I.; Macagnano, A.; Battocchio, C.; Zampetti, E.; Venditti, I.; Russo, M.V.; Bearzotti, A. Platinum nanoparticles on electrospun titania nanofibers as hydrogen sensing materials working at room temperature. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9177–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Qin, L.; Hao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Mu, F.; Yan, Z. Application of tubular tetrapod magnesium oxide in a biosensor for hydrogen peroxide. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Deng, M.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, L. Electrochemical behavior of cuprous oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites and their application in nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hardan, N.H.; Jalar, A.; Hamid, M.A.A.; Keng, L.K.; Shamsudin, R.; Majlis, B.Y. The room-temperature sensing performance of ZnO nanorods for 2-methoxyethanol solvent. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabbina, P.K.; Kaushik, A.; Pokhrel, N.; Bhansali, S.; Pala, N. Electrochemical cortisol immunosensors based on sonochemically synthesized zinc oxide 1D nanorods and 2D nanoflakes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Q.; Komori, K.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y.; Sakai, Y. Electrochemical biosensor for the detection of H2O2 from living cancer cells based on ZnO nanosheets. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 670, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Jang, N.K.; Khang, G.; Hahn, Y.-B. Fabrication of highly sensitive uric acid biosensor based on directly grown ZnO nanosheets on electrode surface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jo, S.-Y.; Sun, G.-J.; Katoch, A.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, S.S. Tailoring the surface area of ZnO nanorods for improved performance in glucose sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.X.; Xu, C.X.; Zhu, G.P.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, L.Y.; Li, X.S. Tyrosinase immobilization on ZnO nanorods for phenol detection. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Hahn, Y.-B. Wide linear-range detecting high sensitivity cholesterol biosensors based on aspect-ratio controlled ZnO nanorods grown on silver electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Saha, S.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Gupta, V.; Bhansali, S.; Singh, S.P. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Mo, C.; Xu, Y.; Cai, X.; Guo, L. A novel non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on ultralong manganite MnOOH nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayu, M.B.; Spidle, R.T.; Devkota, T.; Deb, A.K.; Delong, R.K.; Ghosh, K.C.; Wanekaya, A.K.; Chusuei, C.C. Morphology of hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanoparticles tethered to carbon nanotubes affects electrocatalytic activity for H2O2 detection. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Hu, F. Electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using metal nanoparticles: A review. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical biosensing based on noble metal nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Tu, J. Mesoporous indium oxide for nonenzymatic uric acid sensing. In International Conference on Materials, Environmental and Biological Engineering (MEBE 2015); Atlantis Press: Guilin, China, 2015; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- House, J.L.; Anderson, E.M.; Ward, W.K. Immobilization techniques to avoid enzyme loss from oxidase-based biosensors: A one-year study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2007, 1, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Sarawathi, R. A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on reduced graphene Oxide/ZnO composite modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Asif, S.A.B.; Al-Qarni, S.A.S.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Al-Sayari, S.A.; Al-Assiri, M.S. Fabrication of non-enzymatic sensor using Co doped ZnO nanoparticles as a marker of H2O2. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2014, 62, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlani, A.; Fallah, M.; Lotfi, B.; Khazraei, A.; Golsanamlou, S.; Muzart, J.; Mirza-Aghayan, M. New ZnO nanostructures as non-enzymatic glucose biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.M. ZnO nanomulberry and its significant nonenzymatic signal enhancement for protein microarray. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7728–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulgafour, H.I.; Hassan, Z.; Al-Hardan, N.; Yam, F.K. Growth of zinc oxide nanoflowers by thermal evaporation method. Phys. B 2010, 405, 2570–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, X. Electrodeposition of hierarchical ZnO nanorod-nanosheet structures and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2358–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Asiri, A.M. Fabrication of highly sensitive ethanol sensor based on doped nanostructure materials using tiny chips. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63252–63263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, S.A.; Khalil, K.M.S. Humidity sensing properties of NiO/Al2O3 nanocomposite materials. Solid State Ion. 2003, 164, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-J.; Hwang, S.W.; Whang, D. Non-enzymatic electrochemical CuO nanoflowers sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. Talanta 2010, 80, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Du, Z.; Liu, S.; Hao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on MnO2/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Talanta 2010, 82, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gu, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, M. Non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on rose-shaped FeMoO4 nanostructures produced by convenient microwave-hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 64, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-C.; Zhang, W.-D. Electrodeposition of TiO2 nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotube arrays for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Xu, Q.; Yin, L.; Hu, X. Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles for direct glucose and H2O2 detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 5803–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hardan, N.H.; Abdul Hamid, M.A.; Shamsudin, R.; Othman, N.K.; Kar Keng, L. Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods. Sensors 2016, 16, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071004
Al-Hardan NH, Abdul Hamid MA, Shamsudin R, Othman NK, Kar Keng L. Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hardan, Naif H., Muhammad Azmi Abdul Hamid, Roslinda Shamsudin, Norinsan Kamil Othman, and Lim Kar Keng. 2016. "Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods" Sensors 16, no. 7: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071004
APA StyleAl-Hardan, N. H., Abdul Hamid, M. A., Shamsudin, R., Othman, N. K., & Kar Keng, L. (2016). Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanorods. Sensors, 16(7), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071004