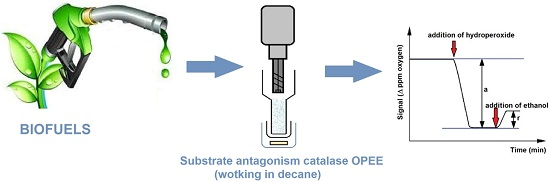
Bioethanol in Biofuels Checked by an Amperometric Organic Phase Enzyme Electrode (OPEE) Working in “Substrate Antagonism” Format
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Biosensors
1.2. Organic Phase Biosensors
1.3. Biofuels
1.4. Aim of the Research
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Samples
3. Methods
Biosensor Fabrication and Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Choice of the Solvent
4.2. Analytical Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guilbault, G.G. Analytical Uses of Immobilized Enzymes; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Tomassetti, M. Bioinstrumentation: Research, Developments and Applications; Wise, D.L., Ed.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson, B. Enzyme Thermistor Devices. In Biosensors Principles and Applications; Blum, L.J., Coulet, P.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- Guilbault, G. Enzymatic Methods of Analysis. In International Series of Monographs in Analytical Chemistry; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, J.H.T.; Guilbault, G.G. Analytical Applications of Piezoelectric Crystal Biosensors. In Biosensor Principles and Applications; Blum, L.J., Coulet, P.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 107–138. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Tomassetti, M. Tossicologia Degli Alimenti; Capuano, A., Dugo, G., Restani, P., Eds.; UTET: Torino, Italy, 1999; pp. 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Mulchandani, A. Principles of Enzyme Biosensors. In Enzyme and Microbial Biosensors, Volume 6 of the Series Methods in Biotechnology; Mulchandani, A., Rogers, K.R., Eds.; Humana Press: New York City, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Coulet, P.R. What is a Biosensor? In Biosensor Principles and Application; Blum, L.J., Coulet, P.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Blankert, B.; Viré, J.C.; Kauffmann, J.M. Biosensors in drug discovery and drug analysis. Anal. Lett. 2005, 38, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Hall, G.F.; Downs, M.E.A.; Turner, A.P.F. Organic phase enzyme electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 249, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibanov, A.M. Enzymes that work in organic solvents. Chem. Tech. 1986, 16, 354–359. [Google Scholar]
- Kim Rogers, R. Biosensors for environmental applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mionetto, N.; Marti, L.; Marty, J.L.; Karube, I. Biosensor and Organic Solvents: A New Approach for the Detection of Insecticides. In Workshop on Biosensors and Biological Techniques in Enviromental Analysis, September; ESPCI: Paris, France, 1994; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wheals, A.E.; Basso, L.C.; Alves, D.M.G.; Amorim, H.V. Fuel ethanol after 25 years. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, C.E. Ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass: Technology, economics, and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 1994, 50, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iob, A.; Buenafe, R.; Abbas, N.M. Determination of oxygenates in gasoline by FTIR. Fuel 1998, 77, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, U.A. Biotecnologia—Tecnologia das Fermentações; Lima, U.A., Aquarone, E., Borzani, W., Eds.; Edgard Blücher: São Paulo, Brazil, 1975; pp. 48–69. [Google Scholar]
- Delbianco, A.; Sposini, M. Alba o tramonto nell’orizzonte del bioetanolo? Fuel Altern. 2001, 4, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Portrait, E. The potential of liquid biofuels in France. Renew. Energy 1999, 16, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.R.; Goldemberg, J. The alcohol program. Energy Policy 1999, 27, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Tomassetti, M. Relazioni Scientifiche Della Scuola Sui Sensori Elettrochimici; Mascini, M., Campanella, L., Eds.; La Goliardica: Roma, Italy, 1985; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Tomassetti, M. Sensors in pharmaceutical analysis. Sel. Electrode Rev. 1989, 11, 69–110. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Favero, G.; Fortuney, A.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. An enzyme sensor for quality control of olive oil directly operating in n-Hexane Solution. Life Chem. Rep. 1994, 11, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Giancola, D.; Gregori, E.; Tomassetti, M. Determination of hydroperoxides in nonaqueous solvents or mixed solvents, using a biosensor with two antagonist enzymes operating in parallel. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 95, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; De Santis, G.; Favero, G.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. Two OPEEs (organic phase enzyme electrodes) used to check the percentage water content in hydrofobic foods and drugs. Analyst 2001, 126, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, L.; Martini, U.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. A new enzyme sensor able to determine the hydrogen peroxide directly in chloroform. Analusis 1996, 24, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Fortuney, A.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. Tyrosinase biosensor response as a function of physical properties of organic solvents. Talanta 1994, 41, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Favero, G.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. Enzymatic immobilisation in kappa-carrageenan gel suitable for organic phase enzyme electrode (OPEE) assembly. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 1999, 7, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Martini, U.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. The effect of organic solvent properties on a catalase enzyme sensor for monitoring hydrogen peroxide in nonaqueous solutions. Electroanalysis 1996, 8, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, M.; Martini, E.; Campanella, L. New immunosensors operating in organic phase (OPIEs) for analysis of triazinic pesticides in olive oil. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Tomassetti, M.; Campanella, L. Determination of traces of several pesticides in sunflower oil using organic phase immuno electrodes (OPIEs). Talanta 2015, 132, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, L.; Spuri Capesciotti, G.; Russo, M.V.; Tomassetti, M. Study of the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme catalase on organic hydroperoxides in non-polar organic solvent. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2008, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Spuri Capesciotti, G.; Gatta, T.; Tomassetti, M. An innovative organic phase enzyme electrode (OPEE) for the determination of ethanol in leadless petrols. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 147, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Gladyshew, P.P.; Goryaev, M.I. Peroxidation of n-paraffins by extracts of Aspergillus Niger Izvestiya Akad. Nauk Kazakhskai SSR Seriya Klimicheskaya 1975, 25, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Favero, G.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. The effect of organic solvent properties on the response of a tyrosinase enzyme sensor. Talanta 1994, 41, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Favero, G.; Sammartino, M.P.; Tomassetti, M. OPEEs—What Are They? In Abstract Book, Proceedings of the 2nd Italian Workshop on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors, Rome, Italy, 18–19 March 1999; Pillotton, R., Mazzei, F., Botrè, F., Eds.;
- Adeyoju, O.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Smyth, M.R. Determination of kinetic parameters for the inhibitory effects of organic sulphides on an amperometric peroxide biosensor in non-aqueous media. Talanta 1994, 41, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Merola, G.; Tomassetti, M.; Campanella, L. Agent orange herbicides, organophosphate and triazinic pesticides analysis in olive oil and industrial oil mill waste effluents using new organic phase immunosensors. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwuoha, E.I.; Smyth, M.R.; Lyons, M.E.G. Solvent effects on the reactivities of an amperometric glucose sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 390, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuoha, E.I.; Smyth, M.R.; Lyons, M.E.G. Organic phase enzyme electrodes: Kinetics and analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997, 12, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.S.; Klibanov, A.M. Are water-immiscibility and apolarity of the solvent relevant to enzyme efficiency? Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 41, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dordick, J.S. Enzymatic catalysis in monophasic organic solvents. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1989, 11, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanca, S.E.; Popescu, I.C. Phenols monitoring and Hill coefficient evaluation using tyrosinase-based amperometric biosensors. Bioelectrochemical 2004, 64, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyoju, O.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Smyth, M.R. Kinetic characterization of the effects of organic solvents on the performance of a peroxidase-modified electrode in detecting peroxides, thiourea and ethylenethiourea. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyoju, O.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Smyth, M.R. Kinetic-study of the inhibitory effects of methyl isothiocyanate on aperoxidase-modified platinum-electrode in nonaqueous media. Anal. Lett. 1994, 27, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Dong, S. Ampetometric biosensor for tyrosinase inhibitors in a pure organic phase. Analyst 1996, 121, 1979–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Hydroperoxide Used as Substrate | t-Butylhydroperoxide |
|---|---|
| Equation of calibration curve to ethanol | Y = 143.0 (±4.8)X + 8.0 (±1.1) |
| Linearity range (mM) | 4.2 × 10−2 − 3.7 × 10−1 |
| Limit of detection (LOD) (mM) | 0.02 |
| Pooled SD | ≤8 |
| Relative Standard Deviation % (RSD%) (n ≥ 5) | 1.2 |
| Hydroperoxide Used for Ethanol Measurements | Biosensor Lifetime (Days) | Mean Response Time vs. Ethanol (n ≥ 5) (min) | Mean Response Time vs. Hydroperoxide (n ≥ 5) (min) | Total Response Time (n ≥ 5) (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tert-butyl-hydroperoxide | ≥7 | 10 (±5) | 5 (±3) | 15 (±8) |
| Measure | Ethanol Concentration (M) | Ethanol Concentration as (g/L) d = 790 (g/L) MW = 46.07 | Ethanol Concentration as (v/v)% | t-Test: Two Sided, ν A = ν B = 3 − 1 = 2, p = 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal value of Ethanol in biofuel (sample A) after being diluted 150 times by volume | 1.14 × 10−2 | 5.25 × 10−1 | 6.6 × 10−2 | t exp. | t critic | Result of the test | |
| Found ethanol in biofuel (A) (diluted 150 times by volume), using biosensor | 1 | 9.27 × 10−3 | 4.27 × 10−1 | 5.41 × 10−2 | −4.210 | 4.303 | Not significant |
| 2 | 1.05 × 10−2 | 4.84 × 10−1 | 6.12 × 10−2 | ||||
| 3 | 9.94 × 10−3 | 4.58 × 10−1 | 5.80 × 10−2 | ||||
| Mean | 9.90 × 10−3 | 4.56 × 10−1 | 5.78 × 10−2 | ||||
| SD | 6.16 × 10−4 | 2.84 × 10−2 | 3.59 × 10−3 | ||||
| RSD% | 6.22 | 6.22 | 6.22 | ||||
| Nominal value of Ethanol in biofuel (sample B) after being diluted 150 times by volume | 1.14 × 10−2 | 5.25 × 10−1 | 6.6 × 10−2 | t exp. | t critic | Result of the test | |
| Found ethanol in biofuel (A) (diluted 150 times by volume), using biosensor | 1 | 9.59 × 10−3 | 4.42 × 10−1 | 5.59 × 10−2 | −3.723 | 4.303 | Not significant |
| 2 | 9.73 × 10−3 | 4.48 × 10−1 | 5.67 × 10−2 | ||||
| 3 | 1.08 × 10−2 | 4.96 × 10−1 | 6.27 × 10−2 | ||||
| Mean | 1.00 × 10−2 | 4.62 × 10−1 | 5.85 × 10−2 | ||||
| SD | 6.39 × 10−4 | 2.94 × 10−2 | 3.73 × 10−3 | ||||
| RSD% | 6.37 | 6.37 | 6.37 | ||||
| Ethanol Concentration Determined after 150 Times Dilution by Volume (M) (n = 5); RSD% ≤ 5 | Ethanol Concentration Added (M) | Total Ethanol Concentration Found (M) (n = 5); RSD% ≤ 5 | Recovery % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal value after dilution (M) | 1.00 × 10−2 | 0.50 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 10−2 | 80.0 |
| Nominal value after dilution (M) | 1.00 × 10−2 | 0.50 × 10−2 | 1.42 × 10−2 | 94.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomassetti, M.; Spuri Capesciotti, G.; Angeloni, R.; Martini, E.; Campanella, L. Bioethanol in Biofuels Checked by an Amperometric Organic Phase Enzyme Electrode (OPEE) Working in “Substrate Antagonism” Format. Sensors 2016, 16, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091355
Tomassetti M, Spuri Capesciotti G, Angeloni R, Martini E, Campanella L. Bioethanol in Biofuels Checked by an Amperometric Organic Phase Enzyme Electrode (OPEE) Working in “Substrate Antagonism” Format. Sensors. 2016; 16(9):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091355
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomassetti, Mauro, Gabriele Spuri Capesciotti, Riccardo Angeloni, Elisabetta Martini, and Luigi Campanella. 2016. "Bioethanol in Biofuels Checked by an Amperometric Organic Phase Enzyme Electrode (OPEE) Working in “Substrate Antagonism” Format" Sensors 16, no. 9: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091355
APA StyleTomassetti, M., Spuri Capesciotti, G., Angeloni, R., Martini, E., & Campanella, L. (2016). Bioethanol in Biofuels Checked by an Amperometric Organic Phase Enzyme Electrode (OPEE) Working in “Substrate Antagonism” Format. Sensors, 16(9), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091355