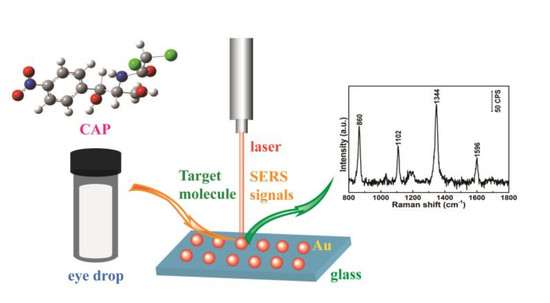
Quantitative and Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Colloidal Au NPs and CAP Solution
2.3. SERS Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Colloidal Au NPs
3.2. SERS Activities of Colloidal Au NPs
3.3. Quantitative Detection of CAP by SERS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yunis, A.A.; Arimura, G.K.; Isildar, M. DNA damage induced by chloramphenicol and its nitroso derivative: Damage in intact cells. Am. J. Hematol. 1987, 24, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isildar, M.; Jimenez, J.J.; Arimura, G.K.; Yunis, A.A. DNA damage in intact cells induced by bacterial metabolites of chloramphenicol. Am. J. Hematol. 1988, 28, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanekamp, J.C.; Bast, A. Antibiotics exposure and health risks: Chloramphenicol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shao, B.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y. Occurrence of chloramphenicol-resistance genes as environmental pollutants from swine feedlots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengov, A.; Flajs, V.C.; Zadnik, T.; Marinšek, J.; Pogačnik, M. Distribution of chloramphenicol residues in lactating cows following an external application. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, H.; Malekinejad, H.; Razavirouhani, S.M.; Pajouhi, M.R.; Mahmoudi, R.; Haghnazari, A. Chloramphenicol residues in chicken liver, kidney and muscle: A comparison among the antibacterial residues monitoring methods of Four Plate Test, ELISA and HPLC. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous determination of metronidazole, chloramphenicol and 10 sulfonamide residues in honey by LC–MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosough, M.; Mashhadiabbas, E.H. Fast HPLC-DAD quantification procedure for selected sulfonamids, metronidazole and chloramphenicol in wastewaters using second-order calibration based on MCR-ALS. Talanta 2013, 113, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Song, G.; Hu, Y. Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite Used as Cleanup Material to Detect Chloramphenicol in Milk by GC-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.J.; Yang, L.P.; Zhuang, H.; Wu, H.Z.; Zhang, J.H. Engineered “hot” core-shell nanostructures for patterned detection of chloramphenicol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 78, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.J.; Liu, L.; Shi, C.A.; Zhang, X.; Lv, M.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Xu, H.J. Study of surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity of DNA-directed self-assembled gold nanoparticle dimers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 211604–211608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhan, H.R.; Cheng, F.S.; Tang, C.Y.; Mei, J.; Hui, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lau, W.M. “Zero-transfer” production of large-scale, flexible nanostructured film at water surface for surface enhancement Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 211604–211607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, E.J.; Weber, M.L.; Stranahan, S.M.; Willets, K.A. Super-Resolution SERS Imaging beyond the Single-Molecule Limit: An Isotope-Edited Approach. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5103–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.G.; Yan, W.J.; Ma, W.; Kuang, H.; Wu, X.L.; Liu, L.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.B.; Xu, C.L. SERS encoded silver pyramids for attomolar detection of multiplexed disease biomarkers. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, K.; Wang, Y.; Kneipp, H.; Perelman, L.T.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Single Molecule Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Emory, S.R. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Góes, R.E.; Muller, M.; Fabris, J.L. Spectroscopic Detection of Glyphosate in Water Assisted by Laser-Ablated Silver Nanoparticles. Sensors 2017, 17, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.T.; Lin, K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.H. Graphene-Ag Hybrids on Laser-Textured Si Surface for SERS Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.Z.; Fang, J.H.; Mu, R.W.; Li, Y.L. Preparation of Au Core-Ag Shell Nanoparticles Film and Its SERS Activity Study. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2006, 22, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.L.; Yang, Z.B.; You, H.J.; Tian, C.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Fang, J.X. Gold mesoparticles with precisely controlled surface topographies for single-particle surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 5567–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Han, X.X.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.M.; Tang, B.; Ji, W.; Ruan, W.D.; Xu, W.Q.; Zhao, B.; Ozaki, Y. Site-specific deposition of Ag nanoparticles on ZnO nanorod arrays via galvanic reduction and their SERS applications. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Luo, L.B.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Zapien, J.A.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, S.T. ZnO/Au Composite Nanoarrays As Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, A.; Virga, A.; Angelini, A.; Ricci, A.; Descrovi, E.; Cocuzza, M.; Giorgis, F. Metal-elastomer nanostructures for tunable SERS and easy microfluidic integration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4404–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaia, Y.C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lin, Y.W.; Wu, T.M. Silver nanoparticles in multiwalled carbon nanotube-Nafion for surface-enhanced Raman scattering chemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.Y.; Teng, H.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.L.; Liu, L.M.; Xu, H.J. Low-cost Au nanoparticle-decorated cicada wing as sensitive and recyclable substrates for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, H.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H. Quantitative and Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Sensors 2017, 17, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122962
Ding Y, Zhang X, Yin H, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Liu L, Wu Z, Xu H. Quantitative and Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122962
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yufeng, Xin Zhang, Hongjun Yin, Qingyun Meng, Yongmei Zhao, Luo Liu, Zhenglong Wu, and Haijun Xu. 2017. "Quantitative and Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122962
APA StyleDing, Y., Zhang, X., Yin, H., Meng, Q., Zhao, Y., Liu, L., Wu, Z., & Xu, H. (2017). Quantitative and Sensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Sensors, 17(12), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122962