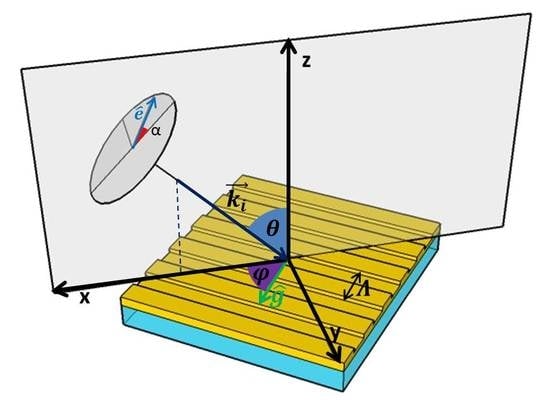
Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR) Optimization for Phase-Interrogation Biosensing in a Microfluidic Chamber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Numerical Simulations
2.2. Grating and Microfluidic System Fabrication for GC-SPR
2.3. GC-SPR Detection Setup
2.4. Sensing and Functionalization Experiments
2.5. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Theory of Phase-Interrogation for GC-SPR in Conical Mounting
3.2. Simulation Study for Grating Line Depth Contribution to SPR Response in Phase Interrogation
3.3. Polar Angles Optimization for Sensitivity Enhancement
3.4. Azimuthal Angles Optimization for Sensitivity Enhancement
3.5. GC-SPR Response Enhancement: Biotin-PEG-Thiol Functionalization and Biorecognition with Avidin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elosua, C.; Matias, I.R.; Bariain, C.; Arregui, F.J. Volatile organic compound optical fiber sensors: A review. Sensors 2006, 6, 1440–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Dinh, X.-Q.; Yu, X.; Luan, F. A Review on Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Biosensing Applications. Plasmonics 2011, 6, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligler, F.S. Perspective on optical biosensors and integrated sensor systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Fulton, A.L.; Beebe, D.J. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 2014, 507, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chung, M.T.; McHugh, W.; Nidetz, R.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.; Cornell, T.T.; Shanley, T.P.; Kurabayashi, K. Multiplex serum cytokine immunoassay using nanoplasmonic biosensor microarrays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J.; Yee, S.S.; Gauglitz, G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors: Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaran, D.R.; Gobi, K.V.; Miura, N. Recent advancements in surface plasmon resonance immunosensors for detection of small molecules of biomedical, food and environmental interest. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habauzit, D.; Chopineau, J.; Roig, B. SPR-based biosensors: A tool for biodetection of hormonal compounds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhalim, I.; Zourob, M.; Lakhtakia, A. Surface plasmon resonance for biosensing: A mini-review. Electromagnetics 2008, 28, 214–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, X.D.; Kirk, A.G.; Tabrizian, M. Towards integrated and sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensors: A review of recent progress. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, E.; Lausted, C.; Lin, T.; Yang, C.W.T.; Hood, L.; Lagally, E.T. Parallel microfluidic surface plasmon resonance imaging arrays. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhan, S.; Huang, Z.; Hong, X. Review: Advances And Applications Of Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing Instrumentation. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 574–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhan, A.R.; Jackman, J.A.; Park, J.H.; Cho, N.-J.; Kim, D.-H. Nanoplasmonic sensors for detecting circulating cancer biomarkers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Kawata, S.; Minami, S. Optical chemical sensor based on surface plasmon measurement. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofas, S.; Malmqvist, M.; Ronnberg, I.; Stenberg, E.; Liedberg, B.; Lundström, I. Bioanalysis with surface plasmon resonance. Sens. Actuators B 1991, 5, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. On the sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance sensors with spectral interrogation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 41, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.C.; Chen, S.J. A sensitivity comparison of optical biosensors based on four different surface plasmon resonance modes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostálek, J.; Homola, J.; Miler, M. Rich information format surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on array of diffraction gratings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliarik, M.; Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors: Approaching their limits? Opt. Express 2009, 17, 16505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabney, A.; Abdulhalim, I. Sensitivity-enhancement methods for surface plasmon sensors. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 571–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliarik, M.; Vala, M.; Tichý, I.; Homola, J. Compact and low-cost biosensor based on novel approach to spectroscopy of surface plasmons. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3430–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.H.; Shuler, M.L.; Kim, S.J. Design optimization of nano-grating surface plasmon resonance sensors. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 4842–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanato, F.; Lee, K.H.; Ruffato, G.; Wong, C.C. The role of polarization on surface plasmon polariton excitation on metallic gratings in the conical mounting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonato, A.; Ruffato, G.; Zacco, G.; Silvestri, D.; Natali, M.; Carli, M.; Giallongo, G.; Granozzi, G.; Morpurgo, M.; Romanato, F. Enhanced sensitivity azimuthally controlled grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance applied to the calibration of thiol-poly(ethylene oxide) grafting. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigo, L.; Gazzola, E.; Cittadini, M.; Zilio, P.; Zacco, G.; Romanato, F.; Martucci, A.; Guglielmi, M.; Brusatin, G. Short and long range surface plasmon polariton waveguides for xylene sensing. Nanotechnology 2013, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perino, M.; Pasqualotto, E.; Scaramuzza, M.; De Toni, A.; Paccagnella, A. Enhancement and control of surface plasmon resonance sensitivity using grating in conical mounting configuration. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffato, G.; Romanato, F. Grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance in conical mounting with polarization modulation. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2718–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffato, G.; Pasqualotto, E.; Sonato, A.; Zacco, G.; Silvestri, D.; Morpurgo, M.; De Toni, A.; Romanato, F. Implementation and testing of a compact and high-resolution sensing device based on grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance with polarization modulation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonato, A.; Agostini, M.; Ruffato, G.; Gazzola, E.; Liuni, D.; Greco, G.; Travagliati, M.; Cecchini, M.; Romanato, F. A surface acoustic wave (saw)-enhanced grating-coupling phase-interrogation surface plasmon resonance (spr) microfluidic biosensor. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L. Multilayer-coated diffraction gratings: Differential method of Chandezon et al. revisited: Errata. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1996, 13, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Using symmetries of grating groove profiles to reduce computation cost of the C method. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, S.J.; Bryan-Brown, G.P.; Sambles, J.R. Polarization conversion from diffraction gratings. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 6393–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffato, G.; Romanato, F. Near-field numerical analysis of surface plasmon polariton propagation on metallic gratings. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2013, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Granet, G.; Plumey, J.P.; Chandezon, J. Some topics in extending the C method to multilayer gratings of different profiles. Pure Appl. Opt. 1996, 5, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preist, T.W.; Cotter, N.P.K.; Sambles, J.R. Periodic multilayer gratings of arbitrary shape. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1995, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, B.; Ce, L.; Plumey, J.P. Coordinate transformation method as applied to asymmetric gratings with vertical facets. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1997, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, E.; Pozzato, A.; Ruffato, G.; Sovernigo, E.; Sonato, A. High-throughput fabrication and calibration of compact high-sensitivity plasmonic lab-on-chip for biosensing. Optofluid. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 3, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neviere, M.; Vincent, P.; Petit, R.; Cadilhac, M. Systematic study of resonances of holographic thin film couplers. Opt. Commun. 1973, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, E.M. Resolution and sensitivity in surface plasmon microscopy and sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herminghaus, S.; Klopfleisch, M.; Schmidt, H.J. Attenuated total reflectance as a quantum interference phenomenon. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallinet, B.; Siegfried, T.; Sigg, H.; Nordlander, P.; Martin, O.J.F. Plasmonic radiance: Probing structure at the Ångström scale with visible light. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.E.; Mack, N.H.; Malyarchuk, V.; Soares, J.A.N.T.; Lee, T.-W.; Gray, S.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A. Quantitative multispectral biosensing and 1D imaging using quasi-3D plasmonic crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17143–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.L.; Chua, M.; Mittman, H.; Choo, L.X.; Lim, H.Q.; Olivo, M. A Phase-Intensity Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borile, G.; Rossi, S.; Filippi, A.; Tregnago, C.; Capaldo, P.; Pigazzi, M.; Romanato, F. Label-free, real-time on-chip sensing of living leukemia cells via grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance. Unpublished Paper. 2018; (Unpublished, manuscript in preparation). [Google Scholar]
- Agnese, S.; Alessandro, P.; Fabio, S.; Enrico, G.; Gianluca, R.; Filippo, R. Multiplexing nanostructured plasmonic device for high throughput biosensing. In Proceedings of the 18th Italian National Conference on Photonic Technologies (Fotonica 2016), Rome, Italy, 6–8 June 2016. [Google Scholar]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossi, S.; Gazzola, E.; Capaldo, P.; Borile, G.; Romanato, F. Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR) Optimization for Phase-Interrogation Biosensing in a Microfluidic Chamber. Sensors 2018, 18, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051621
Rossi S, Gazzola E, Capaldo P, Borile G, Romanato F. Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR) Optimization for Phase-Interrogation Biosensing in a Microfluidic Chamber. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051621
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossi, Stefano, Enrico Gazzola, Pietro Capaldo, Giulia Borile, and Filippo Romanato. 2018. "Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR) Optimization for Phase-Interrogation Biosensing in a Microfluidic Chamber" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051621
APA StyleRossi, S., Gazzola, E., Capaldo, P., Borile, G., & Romanato, F. (2018). Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR) Optimization for Phase-Interrogation Biosensing in a Microfluidic Chamber. Sensors, 18(5), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051621