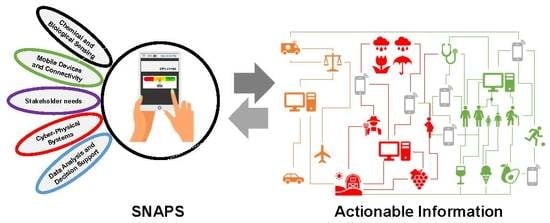
SNAPS: Sensor Analytics Point Solutions for Detection and Decision Support Systems
Abstract
:1. Overview
2. Sensor Engineering
Point of Need Sensing and Smartphones
3. Sensor-Analytics Point Solutions (SNAPS)
SNAPS Hardware and Software
4. Auto-Actuation and Partial Levels of Autonomy for Low-Risk Automation
5. Coupling Sensor Transduction with Data Analytics for Decision Support
6. Proof of Concept SNAPS
7. Challenges and Opportunities
From SNAPS to PEAS
8. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J. Glucose Biosensors: 40 Years of Advances and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Anzai, J.-I. Recent Progress in Lectin-Based Biosensors. Materials 2015, 8, 8590–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors based on Graphene Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 76, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Bashir, R. Electrical/electrochemical impedance for rapid detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolo, A.G. Plasmonics for future biosensors. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, F.W.; Yarman, A.; Bachmann, T.; Hirsch, T.; Kubick, S.; Renneberg, R.; Schumacher, S.; Wollenberger, U.; Teller, C.; Bier, F.F. Future of biosensors: A personal view. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 140, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Feng, Y.; Pan, G.; Liu, L. Advances in molecularly imprinting technology for bioanalytical applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L. Biosensors and bioelectrochemistry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 117–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. Nanosensors: A review of recent research. Sens. Rev. 2009, 29, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Mujawar, M.A. Point of Care Sensing Devices: Better Care for Everyone. Sensors 2018, 18, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K. Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Recent Advances and Trends. Biosensors 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidic, J.; Vizzini, P.; Manzano, M.; Kavanaugh, D.; RamaRao, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Radonic, V.; Knezevic, N.; Giouroudi, I.; Gadjanski, I. Point-of-Need DNA Testing for Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Sensors 2019, 19, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Chung, T.H.; Hassibi, B.; Murray, R.M. On a stochastic sensor selection algorithm with applications in sensor scheduling and sensor coverage. Automatica 2006, 42, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidenreich, A.; Barraza, G.; Jayachandran, K.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Precision Agriculture Application for Sustainable Nitrogen Management of Justicia brandegeana Using Optical Sensor Technology. Agriculture 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarakis, A.C.; Ketterings, Q.M. Proximal sensor-based algorithm for variable rate nitrogen application in maize in northeast U.S.A. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sarma, D.; Nath, P. Ground and river water quality monitoring using a smartphone-based pH sensor. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 57151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Blumenfeld, N.R.; Laksanasopin, T.; Sia, S.K. Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Recent Developments in a Connected Age. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bai, H.; Shi, G. Conducting polymer nanomaterials: Electrosynthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, A.; Loo, A.H.; Pumera, M. Graphene for impedimetric biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2014, 81, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, K.L. Electromechanical Transducers at the Nanoscale: Actuation and Sensing of Motion in Nanoelectromechanical Systems (NEMS). Small 2005, 1, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, B.E.; Anslyn, E.V. Pattern-based peptide recognition. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, H.; Joseph, A.; Park, J.; Emadi, A. Advanced Micro- and Nano-Gas Sensor Technology: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, M.R.; Vikesland, P.J. Nanomaterial enabled sensors for environmental contaminants. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Acha, N.; Elosúa, C.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J. Fluorescent sensors for the detection of heavy metal ions in aqueous media. Sensors 2019, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Kim, J.-S. MEMS based highly sensitive dual FET gas sensor using graphene decorated Pd-Ag alloy nanoparticles for H2 detection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozi, N.; Ahmad, A.; Heng, L.Y.; Shyuan, L.K.; Abu Hanifah, S. Electrochemical Sunset Yellow Biosensor Based on Photocured Polyacrylamide Membrane for Food Dye Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, J.A.; Rushworth, J.V.H.; Millner, P.A. Biosensor Regeneration: A Review of Common Techniques and Outcomes. Langmuir 2014, 36, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, G.J. New chromogenic and fluorogenic reagents and sensors for neutral and ionic analytes based on covalent bond formation–a review of recent developments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsman, N.; Goentoro, L. Allosteric proteins as logarithmic sensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4423–E4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinov, R.; Tsai, C.-J.; Ma, B. The underappreciated role of allostery in the cellular network. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, M.; Ptitsyn, A.; McLamore, E.S.; Claussen, J.C. Nanomaterial-mediated Biosensors for Monitoring Glucose. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, T.; Foster, R.; Hao, Y. Detecting vital signs with wearablewireless sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 10837–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.M. The Great Digital Homonym. In Digitally Deaf; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mosbah, A.; Campanacci, V.; Lartigue, A.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C.; Darbon, H. Solution structure of a chemosensory protein from the moth Mamestra brassicae. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, J. Small Molecule Immunosensing Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Sensors 2010, 10, 7323–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramgir, N.S.; Yang, Y.; Zacharias, M. Nanowire-based sensors. Small 2010, 6, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portney, N.G.; Ozkan, M. Nano-oncology: Drug delivery, imaging, and sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caygill, R.L.; Blair, G.E.; Millner, P.A. A review on viral biosensors to detect human pathogens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 681, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Koucianos, E. Biosensors: A tutorial review. IEEE Potentials 2006, 52, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, X.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, J. A review of impedance measurements of whole cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakare, V.; Khire, G. Role of Emerging Technology for Building Smart Hospital Information System. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 11, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Mobile phone-based biosensing: An emerging “diagnostic and communication” technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Luo, W.; Chiang, S.; Kappel, T.; Mejia, C.; Tseng, D.; Chan, R.Y.L.; Yan, E.; Qi, H.; Shabbir, F.; et al. Imaging and Sizing of Single DNA Molecules on a Mobile Phone. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12725–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guner, H.; Ozgur, E.; Kokturk, G.; Celik, M.; Esen, E.; Topal, A.E.; Ayas, S.; Uludag, Y.; Elbuken, C.; Dana, A. A smartphone based surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi) platform for on-site biodetection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, A.A.; Bonham, A.J.; White, R.J.; Zimmer, M.P.; Yadgar, R.J.; Hobza, T.M.; Honea, J.W.; Ben-Yaacov, I.; Plaxco, K.W. CheapStat: An Open-Source, “Do-It-Yourself” Potentiostat for Analytical and Educational Applications. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, D.M.; Lee, B.E.; Jun, S.; Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.; McLamore, E.S. ABE-Stat, a Fully Open-Source and Versatile Wireless Potentiostat Project Including Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B3056–B3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, A.; Pesko, M.; Porcius, M.; Fortuna, C.; Mladenić, D. Using Machine Learning on Sensor Data. J. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2010, 18, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghahramani, Z. Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence. Nature 2015, 521, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, S.; Lonini, L.; Jayaraman, A.; Mohr, D.C.; Kording, K.P. Voodoo Machine Learning for Clinical Predictions. Biorxiv 2016, 059774. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.; Padron, A.V.; Hagerty, K.J.; Nelson, N.; Chi, S.; Keyhani, N.O.; Katz, J.; Datta, S.P.A.; Gomes, C.; McLamore, E.S. Post hoc support vector machine learning for impedimetric biosensors based on weak protein–ligand interactions. Analyst 2018, 143, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vamos, T. Judea pearl: Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems. Decis. Support Syst. 1992, 8, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, D.; Poggio, T. A computational theory of human stereo vision. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Boil. Sci. 1979, 204, 301–328. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based sensing system using ZnO and graphene modified electrodes for VOCs detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, N.D.; Miluzzo, E.; Lu, H.; Peebles, D.; Choudhury, T.; Campbell, A.T. Adhoc And Sensor Networks: A Survey of Mobile Phone Sensing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2010, 48, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhusal, N.; Shrestha, S.; Pote, N.; Alocilja, E.C. Nanoparticle-based biosensing of tuberculosis, an affordable and practical alternative to current methods. Biosensors 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordillo-Marroquín, C.; Gómez-Velasco, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, H.J.; Pryg, K.; Shinners, J.; Murray, N.; Muñoz-Jiménez, S.G.; Bencomo-Alerm, A.; Gómez-Bustamante, A.; Jonapá-Gómez, L.; et al. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Biosensing Assay Quantitatively Enhances Acid-Fast Bacilli Count in Paucibacillary Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Biosensors 2018, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Qi, H.; Luo, W.; Tseng, D.; Ki, S.J.; Wan, Z.; Göröcs, Z.; Bentolila, L.A.; Wu, T.-T.; Sun, R.; et al. Fluorescent Imaging of Single Nanoparticles and Viruses on a Smart Phone. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9147–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Cai, G.; Wang, S.; Liao, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. A microfluidic colorimetric biosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticle aggregation and smart phone imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Martinez-Hurtado, J.; Garcia-Melendrez, A.; Vasconcellos, F.D.C.; Lowe, C.R. A smartphone algorithm with inter-phone repeatability for the analysis of colorimetric tests. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ruiz, N.; Curto, V.F.; Erenas, M.M.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Diamond, D.; Palma, A.J.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. Smartphone-Based Simultaneous pH and Nitrite Colorimetric Determination for Paper Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9554–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.E.; Larson, D.R.; Webb, W.W. Precise nanometer localization analysis for individual fluorescent probes. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunda, N.S.K.; Gautam, S.H.; Mitra, S.K. Artificial Intelligence Based Mobile Application for Water Quality Monitoring. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B3031–B3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, D.C.; Patiño, L.; Mendez, C.; De Oliveira, D.A.; Torres, A.M.; Gomes, C.L.; McLamore, E.S. Laser Scribed Graphene Biosensor for Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food Samples Using Locally Sourced Materials. Biosensors 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, A.P.; Hilmer, K.M.; Collyer, C.A.; Shepard, E.M.; Elmore, B.O.; Brown, D.E.; Dooley, D.M.; Guss, J.M. Structure and Inhibition of Human Diamine Oxidase. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 9810–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babiceanu, R.F.; Seker, R. Big Data and virtualization for manufacturing cyber-physical systems: A survey of the current status and future outlook. Comput. Ind. 2016, 81, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Buyya, R.; Ramamohanarao, K. Big Data Analytics = Machine Learning + Cloud Computing. in Big Data: Principles and Paradigms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.03115. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, K.; Khandelwal, Y.; Krishna, B.S.; Ravi, V. Analytics in/for cloud-an interdependence: A review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 102, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, J.; Perer, A. Orion: A system for modeling, transformation and visualization of multidimensional heterogeneous networks. Inf. Vis. 2014, 13, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Levy, E.; Ferbrache, A.; Stepanowsky, P.; Farcas, C.; Wang, S.; Brunner, S.; Bath, T.; Wu, Y.; Ohno-Machado, L. MAGI: A Node.js web service for fast microRNA-Seq analysis in a GPU infrastructure. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2826–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolte, H.; MacVicar, T.D.; Tellkamp, F.; Krüger, M. Instant Clue: A Software Suite for Interactive Data Visualization and Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, G.; Kim, P.-G.; Yoon, J.; Han, G.; Park, S.-J.; Song, W.; Lee, B. Closha: Bioinformatics workflow system for the analysis of massive sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Zgraggen, E.; Buratti, B.; Kossmann, F.; Eichmann, P.; Chung, Y.; Binnig, C.; Upfal, E.; Kraska, T. Democratizing Data Science through Interactive Curation of ML Pipelines. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Management of Data—SIGMOD ’19, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 30 June–5 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Binnig, C.; Buratti, B.; Chung, Y.; Cousins, C.; Kraska, T.; Shang, Z.; Upfal, E.; Zeleznik, R.; Zgraggen, E. Towards Interactive Curation & Automatic Tuning of ML Pipelines. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Computing within Limits—LIMITS ’16, Toronto, ON, Canada, 14–16 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.; Servan-Schreiber, S.; Zgraggen, E.; Kraska, T. Towards Quantifying Uncertainty in Data Analysis & Exploration. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2018, 41, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tou, J.T.; Gonzalez, R.C. Automatic recognition of handwritten characters via feature extraction and multi-level decision. Int. J. Parallel Program. 1972, 1, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Meng, X.; Yang, C.; Huang, L. Feature extraction for online handwritten characters using Delaunay triangulation. Comput. Graph. 2006, 30, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMSOL. Introduction to COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3; Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, P.R.W. Multiphysics Modeling Using COMSOL®: A First Principles Approach; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.; Sato, S. Lego NXT as a learning tool. 2010. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1822198&preflayout=flat (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Datta, S.P.A. Emergence of Digital Twins—Is this the march of reason? J. Innov. Manag. 2017, 5, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meystel, A. Intelligent control: A sketch of the theory. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 1989, 2, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanopoulos, G.; Han, C. Intelligent systems in process engineering: A review. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1996, 20, 743–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meystel, A. Architectures for intelligent control systems: The science of autonomous intelligence. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, Chicago, IL, USA, 25–27 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Antsaklis, P.; Passino, K.; Wang, S. An introduction to autonomous control systems. IEEE Control Syst. 1991, 11, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Albaladejo, C.; Soto, F.; Torres, R.; Sánchez, P.; Lopez, J.A. A Low-Cost Sensor Buoy System for Monitoring Shallow Marine Environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 9613–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardee, A.B.; Jacob, F.; Monod, J. The genetic control and cytoplasmic expression of “Inducibility” in the synthesis of β-galactosidase by E. coli. J. Mol. Boil. 1959, 1, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.K.; Dubes, R.C. Algorithms for Clustering Data; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Forstmann, B.U.; Dutilh, G.; Brown, S.; Neumann, J.; Von Cramon, D.Y.; Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. Striatum and pre-SMA facilitate decision-making under time pressure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17538–17542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gold, C.; Damböck, D.; Lorenz, L.; Bengler, K. Take over! How long does it take to get the driver back into the loop? Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2013, 57, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabri, G.; Zambonelli, F.; Leonardi, L. MARS: A programmable coordination architecture for mobile agents. IEEE Internet Comput. 2000, 4, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, E. Sensor Network Interoperability and Reconfiguration Through Mobile Agents. Ph.D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DeMaio, A.R.; Rockstrom, J. Human and planetary health: Towards a common language. Lancet 2015, 386, e36–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Lo, S. Planetary health: A new science for exceptional action. Lancet 2015, 386, 1921–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitmee, S.; Haines, A.; Beyrer, C.; Boltz, F.; Capon, A.G.; Dias, B.F.D.S.; Ezeh, A.; Frumkin, H.; Gong, P.; Head, P.; et al. Safeguarding human health in the Anthropocene epoch: Report of The Rockefeller Foundation–Lancet Commission on planetary health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1973–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Torres, I.; Vanegas, D.C.; McLamore, E.S.; Hurtado, D. Mercury Pollution and Artisanal Gold Mining in Alto Cauca, Colombia: Woman’s Perception of Health and Environmental Impacts. J. Environ. Dev. 2018, 27, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbasir, S.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Morgan, V.L.; Schmidt, H.; Casso-Hartmann, L.M.; Vanegas, D.C.; Velez-Torres, I.; McLamore, E.S.; Abdelbasir, S.; Morgan, V.M. Graphene-Anchored Cuprous Oxide Nanoparticles from Waste Electric Cables for Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12176–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, K.; Nagafuchi, O.; Kawakami, T.; Inoue, T.; Yokota, K.; Serikawa, Y.; Cyio, B.; Elvince, R. Human health risk assessment of mercury vapor around artisanal small-scale gold mining area, Palu city, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, M.H. Dissolved Concentrations, Sources, and Risk Evaluation of Selected Metals in Surface Water from Mangla Lake, Pakistan. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabe, Y.; Tsuno, H.; Nishimura, F.; Tanii, N.; Maruno, H.; Tsurukawa, M.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumura, C. Bioaccumulation and primary risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants with various bivalves. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U. S. E. P. a Oppt. Quantitative Risk Assessment Calculations. EPA Sustain. Futur. Framew. Man. 2012, EPA-748-B12-001, 2012. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-05/documents/13.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Hills, K.D.; Oliveira, D.A.; Cavallaro, N.D.; Gomes, C.L.; McLamore, E.S. Actuation of chitosan-aptamer nanobrush borders for pathogen sensing. Analyst 2018, 143, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castell-Perez, E.; Gomes, C.; Tahtouh, J.; Moreira, R.; McLamore, E.S.; Knowles, H.S. Food Processing and Waste Within the Nexus Framework. Curr. Sustain. Energy Rep. 2017, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, F.; Elliott, T. Regional and on-farm wireless sensor networks for agricultural systems in Eastern Washington. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 61, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, T.; Misra, S.; Raghuwanshi, N.S. Wireless sensor networks for agriculture: The state-of-the-art in practice and future challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 118, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, T.; Anandamurugan, S. Challenges and Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks in Smart Farming—A Survey. In Advances in Big Data and Cloud Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Shirude, S.B.; Kolhe, S.R. Agent-based architecture for developing recommender system in libraries. In Knowledge Computing and its Applications: Knowledge Computing in Specific Domains; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, R.B. THE TECHNOLOGICAL SOCIETY. By Jacques Ellul. Translated from the French by John Wilkinson. With an Introduction by Robert K. Merton. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1964. 449 pp. $10.95. Soc. Forces 1968, 46, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. ASTM F2761-09(2013) Medical Devices and Medical Systems—Essential Safety Requirements for Equipment Comprising the Patient-Centric Integrated Clinical Environment (ICE); Subcommittee: F29.21 (ASTM); ASTM: Montgomery County, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Makary, M.A.; Daniel, M. Medical error-the third leading cause of death in the US. BMJ 2016, 353, i2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, A.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J. Planetary Health Watch: Integrated monitoring in the Anthropocene epoch. Lancet Planet. Heal. 2018, 2, e141–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Challenge | Opportunities |
| Extraction of information from sensor data for real time decision support |
|
| Controlling or modulating sensor hysteresis in situ |
|
| Mobility and connectivity in agricultural and environmental systems |
|
| Integrating SNAPS into a standardized platform |
|
| Development of data informed decision as a service (DIDA’S) |
|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLamore, E.S.; Palit Austin Datta, S.; Morgan, V.; Cavallaro, N.; Kiker, G.; Jenkins, D.M.; Rong, Y.; Gomes, C.; Claussen, J.; Vanegas, D.; et al. SNAPS: Sensor Analytics Point Solutions for Detection and Decision Support Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224935
McLamore ES, Palit Austin Datta S, Morgan V, Cavallaro N, Kiker G, Jenkins DM, Rong Y, Gomes C, Claussen J, Vanegas D, et al. SNAPS: Sensor Analytics Point Solutions for Detection and Decision Support Systems. Sensors. 2019; 19(22):4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224935
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLamore, Eric S., Shoumen Palit Austin Datta, Victoria Morgan, Nicholas Cavallaro, Greg Kiker, Daniel M. Jenkins, Yue Rong, Carmen Gomes, Jonathan Claussen, Diana Vanegas, and et al. 2019. "SNAPS: Sensor Analytics Point Solutions for Detection and Decision Support Systems" Sensors 19, no. 22: 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224935
APA StyleMcLamore, E. S., Palit Austin Datta, S., Morgan, V., Cavallaro, N., Kiker, G., Jenkins, D. M., Rong, Y., Gomes, C., Claussen, J., Vanegas, D., & Alocilja, E. C. (2019). SNAPS: Sensor Analytics Point Solutions for Detection and Decision Support Systems. Sensors, 19(22), 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224935