Electrochemical Oxidation of Monosaccharides at Nanoporous Gold with Controlled Atomic Surface Orientation and Non-Enzymatic Galactose Sensing
Abstract
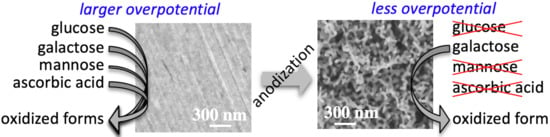
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of NPG with Different Facet Contributions
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Surface Crystallographic Orientation of NPG on Glucose Electrochemistry
3.2. Electrochemistry of Monosaccharides at the NPG Electrode
3.3. Effect of Cl– Ions on the Electrochemistry of Monosaccharides at the NPG Electrode
3.4. Non-Enzymatic Detection of Galactose With Ammperometry and Interference Effects
3.5. Recovery Test of Galactose in a Serum Sample
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toghill, K.E.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: A perspective and an evaluation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 1246–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.X.; Xu, C.X.; Pang, M.L.; Wang, S.L. Simultaneous determination of galactose, glucose, lactose and galactooligosaccharides in galactooligosaccharides raw materials by highperformance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.I.; Berry, G.T.; Rubio-Gozalbo, M.E. Galactose metabolism and health. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.; Elsas, L.J.; Wierenga, K.J. Galactose toxicity in animals. Iubmb Life 2009, 61, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; Singhal, R.; Malhotra, B.D.; Sehgal, N.; Kumar, A. Langmuir-Blodgett film based biosensor for estimation of galactose in milk. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Yang, J.; Ou, Y.N.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, C.Q.; Zheng, H.Z.; Long, Y.J. Peroxidase-like activity of 2 ′,7 ′--difluorofluorescein and its application for galactose detection. Talanta 2018, 182, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehit, E.; Altintas, Z. Significance of nanomaterials in electrochemical glucose sensors: An updated review (2016–2020). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picher, M.M.; Kupcu, S.; Huang, C.J.; Dostalek, J.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Ertl, P. Nanobiotechnology advanced antifouling surfaces for the continuous electrochemical monitoring of glucose in whole blood using a lab-on-a-chip. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.W.; Toi, P.T.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Lee, H.B.; Hanif, A.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, N.E. Fully stretchable capillary microfluidics-integrated nanoporous gold Electrochemical sensor for wearable continuous glucose monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14567–14575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyong, P.; Krampa, F.D.; Aniweh, Y.; Awandare, G.A. Enzyme-based amperometric galactose biosensors: A review. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3663–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.; Loew, N.; Tsugawa, W.; Lin, C.E.; Probst, D.; La Belle, J.T.; Sode, K. The electrochemical behavior of a FAD dependent glucose dehydrogenase with direct electron transfer subunit by immobilization on self-assembled monolayers. Bioelectrochem. 2018, 121, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremey, E.; Stines-Chaumeil, C.; Gounel, S.; Mano, N. Designing an O-2-Insensitive glucose oxidase for improved electrochemical applications. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 2520–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.H.; Prodanovic, R.; Guven, G.; Ostafe, R.; Schwaneberg, U. Electrochemical oxidation of glucose using mutant glucose oxidase from directed protein evolution for biosensor and biofuel cell applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridara, T.; Upan, J.; Saianand, G.; Tuantranont, A.; Karuwan, C.; Jakmunee, J. Non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on carbon nanodots and copper oxide nanocomposites electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, N.N.; Xu, H.J.; Zhao, W.C.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, X. Highly responsive and ultrasensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on au foam. Sensors 2019, 19, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arul, P.; Gowthaman, N.S.K.; Abraham John, S.; Tominaga, M. Tunable electrochemical synthesis of 3D nucleated microparticles like Cu-BTC MOF-carbon nanotubes composite: Enzyme free ultrasensitive determination of glucose in a complex biological fluid. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, L.B.; Hou, H.Q.; Niwa, O.; You, T.Y. Pd-Ni alloy nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber composites: Preparation, structure, and superior electrocatalytic properties for sugar analysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5898–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, K.; Mahapatra, D.R. Electrochemical nonenzymatic sensing of glucose using advanced nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.J.; Hu, M.; Tu, F.H.; Tang, X.Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.L.; Xia, Y. Ultra-rapid fabrication of highly surface-roughened nanoporous gold film from AuSn alloy with improved performance for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Xia, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.L. A rapid anodic fabrication of nanoporous gold in NH4Cl solution for nonenzymatic glucose detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, H802–H808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, B.K.; Raj, C.R. Enzyme-free amperometric sensing of glucose by using gold nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, P.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, T.H.; Ma, J.M. Nanomaterials for electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose biosensors. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3487–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, J.K.; Neupane, D.; Nepal, B.; Mikhaylov, V.; Demchenko, A.V.; Stine, K.J. Preparation, modification, characterization, and biosensing application of nanoporous gold using electrochemical techniques. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukeri, A.; Bertotti, M. Nanoporous gold surface: An efficient platform for hydrogen evolution reaction at very low overpotential. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zalm, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, A.C. Review-recent advances in the development of nanoporous Au for sensing applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Shin, H.; Kang, C. Catalytic glucose oxidation on a polycrystalline gold electrode with an amalgamation treatment (TM 05092). Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3781–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzavilla, S.; Horch, S.; Stephens, I.E.L.; Seger, B.; Chorkendorff, I. Structure sensitivity in the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 with gold catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3774–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, K.C.; Jia, C.G.; Cao, B.X.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.C.; Kim, K.; Wang, W.M. Comparison of catalytic activity between Au(110) and Au(111) for the electro-oxidation of methanol and formic acid: Experiment and density functional theory calculation. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 256, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, Y.; Takayama, H.; Hirano, Y. Facile control of surface crystallographic orientation of anodized nanoporous gold catalyst and its application for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Catal. 2020, 389, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.P.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.L. Facile fabrication of nanoporous gold film electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J. Effect of pH on Anodic formation of nanoporous gold films in chloride solutions: Optimization of anodization for ultrahigh porous structures. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4844–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaszewski, M.; Soszko, M.; Czerwinski, A. Electrochemical methods of real surface area determination of noble metal electrodes—an Overview. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 4442–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.W.; Adzic, R.R.; Yeager, E.B. Electrochemical oxidation of glucose on single crystal and polycrystalline gold surfaces in phosphate buffer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Ning, S.C.; Liu, P.; Ding, Y.; Hirata, A.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.W. Tuning surface structure of 3D nanoporous gold by surfactant-free electrochemical potential cycling. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 170361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Huang, W.; Zheng, J.F.; Niu, Z.J.; Li, Z.L. Nonenzymatic amperometric response of glucose on a nanoporous gold film electrode fabricated by a rapid and simple electrochemical method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.D. Premonolayer oxidation and its role in electrocatalysis. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.L. Electrochemical glucose sensor based on one-step construction of gold nanoparticle-chitosan composite film. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 138, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellette, R.J.; Rawn, J.D. Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 889–928. [Google Scholar]
- Manowitz, P.; Stoecker, P.W.; Yacynych, A.M. Galactose biosensors using composite polymers to prevent interferences. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkiran, B.; Erden, P.E.; Kilic, E. Electrochemical biosensing of galactose based on carbon materials: Graphene versus multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.J.; Bae, Y.H. Glucose oxidase, lactate oxidase, and galactose oxidase enzyme electrode based on polypyrrole with polyanion/PEG/enzyme conjugate dopant. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, M.; Bozgeyik, I.; Cevik, E.; Abasiyanik, M.F. A novel amperometric galactose biosensor based on galactose oxidase-poly(N-glycidylpyrrole-co-pyrrole). Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmantray, F.; Touisni, N.; Hecquet, L.; Mousty, C. Amperometric biosensor based on galactose oxidase immobilized in clay matrix. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, E.; Katakis, I.; Narvaez, A.; Dominguez, E. A multianalyte flow electrochemical cell: Application to the simultaneous determination of carbohydrates based on bioelectrocatalytic detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, M. Novel electrochemical sensing of galactose using GalOxNPs/CHIT modified pencil graphite electrode. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 483, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.N.; Lee, Y.; Son, Y. Enhanced sensitivity of a galactose biosensor fabricated with a bundle of conducting polymer microtubules. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, J.; Whittaker, J.W.; Ruzgas, T. The use of single walled carbon nanotubes dispersed in a chitosan matrix for preparation of a galactose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyabharathi, C.; Ahrens, P.; Hasse, U.; Scholz, F. Identification of low-index crystal planes of polycrystalline gold on the basis of electrochemical oxide layer formation. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Electrode | Enzyme | LOD (µM) | Linear Range (mM) | Sensitivity | Response Time (s) | Working Potential (V) a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,3-DAB|Res|Pt | GalOx | 50.0 | 0.05–6.0 | - | 18 | +0.7 | [40] |
| Co3O4|Graphene|GCE | GalOx | 3.0 | 0.009–0.6 | 6.6 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 15 | +0.7 | [41] |
| Co3O4|MWCNTs|GCE | GalOx | 0.9 | 0.009–1.0 | 10.4 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 15 | +0.7 | [41] |
| PEG|Polyanion|Pt | GalOx | - | 0.0–24.0 | 106 nA mM−1 cm−2 | <40 | +0.4 | [42] |
| PEP|Au | GalOx | 25.0 | 2.0–16.0 | 1.8 µA mM−1 | 5 | +0.7 | [43] |
| Laponite clay|Pt | GalOx | 1.0 | 0.001–1.6 | 85.0 mA mM−1 cm−2 | 5 | +0.6 | [44] |
| NADP+|Os|CPE | GADH | 200 | 1.0–3.0 | 1.7 µA mM−1 cm−2 | - | +0.15 | [45] |
| CHIT|PGE | GalOx | 50.0 | 0.05–25 | 7.0 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 2 | +1.1 | [46] |
| Microtubeles|ITO | GalOx | 10 | 0.1–1.0 | 6.37 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 30–40 | +0.60 | [47] |
| CHIT|SWCNT|GCE | GalOx | 25 | Up to 1.0 | 1126 nA mM−1 cm−2 | - | −0.4 | [48] |
| NPG | none | 5.0 | 0.01–1.8 | 1.0 µA mM−1 cm−2 | 10 | −0.1 | This work |
| Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 8.6 | 86 | 5.2 |
| 100 | 90 | 90 | 7.9 |
| 1000 | 1010 | 101 | 4.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mie, Y.; Katagai, S.; Ikegami, M. Electrochemical Oxidation of Monosaccharides at Nanoporous Gold with Controlled Atomic Surface Orientation and Non-Enzymatic Galactose Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 5632. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195632
Mie Y, Katagai S, Ikegami M. Electrochemical Oxidation of Monosaccharides at Nanoporous Gold with Controlled Atomic Surface Orientation and Non-Enzymatic Galactose Sensing. Sensors. 2020; 20(19):5632. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195632
Chicago/Turabian StyleMie, Yasuhiro, Shizuka Katagai, and Masiki Ikegami. 2020. "Electrochemical Oxidation of Monosaccharides at Nanoporous Gold with Controlled Atomic Surface Orientation and Non-Enzymatic Galactose Sensing" Sensors 20, no. 19: 5632. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195632
APA StyleMie, Y., Katagai, S., & Ikegami, M. (2020). Electrochemical Oxidation of Monosaccharides at Nanoporous Gold with Controlled Atomic Surface Orientation and Non-Enzymatic Galactose Sensing. Sensors, 20(19), 5632. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195632