A Wearable Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Ammonia Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Buffers
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Gas Sensors Fabrication
2.4. Gas Sensing Setup and Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gas Sensor Design
3.2. Optimization of the Hydrogel Composition
3.3. NH3 Gas Sensor Response
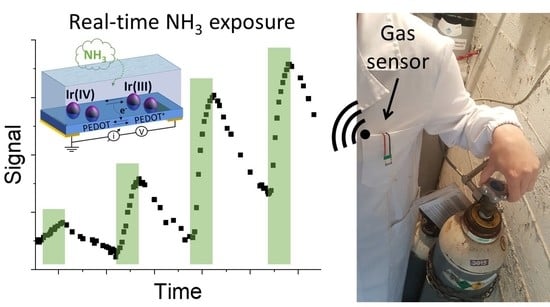
3.4. Development of a Flexible Gas Sensor for Wearable Applications
| Sensing Material | Substrate | Connectivity | Range (ppm) | Sensitivity (% ppm−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs/PANi/PU foam | PDMS | Wired | 5–200 | 0.65 | [42] |
| PEDOT: PSS NWs | PET | BT | 0.75–6 | 0.25 | [45] |
| PTS/PANi | PET | NFC | 5–200 | 45 | [46] |
| PANi/PAN | Textile | Wired | 10–2000 | N/A | [43] |
| C-PPy NPs | Plastic | Wired RFID tag | 0.1–25 | 0.2 | [23] |
| PEDOT: PSS/Ag NWs | PET | Wired | 0.5–25 | 1.40 | [47] |
| PANI/MoS2 | PDMS | Wired | 0.05–30 | N/A | [44] |
| PEDOT: PSS/IrOx Ps | PET | BT | 17–7899 | 0.8 | this work |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cawthon, D.; Hamlin, D.; Steward, A.; Davis, C.; Cavender, F.; Goad, P. Field studies on the ammonia odor threshold based on ambient air-sampling following accidental releases. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2009, 91, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammonia, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7664417.html (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Tanguy, N.R.; Thompson, M.; Yan, N. A review on advances in application of polyaniline for ammonia detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 1044–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanich, R. Chem/bio wearable sensors: Current and future direction. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesaard, T.; Lorwongtragool, P.; Kerdcharoen, T. Development of Fabric-Based Chemical Gas Sensors for Use as Wearable Electronic Noses. Sensors 2015, 15, 1885–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, W.; Jian, J. Wearable electronic nose for human skin odor identification: A preliminary study. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Sowade, E.; Watthanawisuth, N.; Baumann, R.R.; Kerdcharoen, T. A Novel Wearable Electronic Nose for Healthcare Based on Flexible Printed Chemical Sensor Array. Sensors 2014, 14, 19700–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Cho, M.; Li, Y.; Cho, I.; Suh, J.-H.; Del Orbe, D.; Jeong, Y.; Ren, T.-L.; Park, I. Biomimetic Turbinate-like Artificial Nose for Hydrogen Detection Based on 3D Porous Laser-Induced Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24386–24394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamsa-ard, T.; Seesaard, T.; Kerdcharoen, T. Wearable Sensor of Humanoid Robot-Based Textile Chemical Sensors for Odor Detection and Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences, and Technology (ICEAST), Phuket, Thailand, 4–7 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, M.; Sun, L. Characteristics of an organic semiconductor polyaniline film as a sensor for NH3 gas. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1994, 40, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, A.L.; Shirshov, Y.M.; Piletsky, S.A. Ammonia sensors based on sensitive polyaniline films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 37, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, G.; Yao, J. Flexible ZnO/PANI/nonwoven nanocomposite based high-sensitive NH3 gas sensor via vapor phase polymerization method. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Kumar, R.T.R. Polyaniline Anchored MWCNTs on Fabric for High Performance Wearable Ammonia Sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Fan, H.; Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yadav, A.K.; Dong, G.; Wang, W.; Dong, W.; Wang, S. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline on the ethylenediamine modified polyethylene terephthalate fibers for a flexible room temperature ammonia gas sensor with high responses. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Lu, H.; Tian, T.; Liu, F.; Sun, P.; et al. Room temperature high performance NH3 sensor based on GO-rambutan-like polyaniline hollow nanosphere hybrid assembled to flexible PET substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tai, H.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Z.; Du, X.; Xie, G.; Jiang, Y. A high-performance flexible gas sensor based on self-assembled PANI-CeO2 nanocomposite thin film for trace-level NH3 detection at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, K.; Sun, D. Wearable and flexible bacterial cellulose/polyaniline ammonia sensor based on a synergistic doping strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Park, E.; Kweon, O.Y.; Park, S.J.; Jang, J. Novel flexible chemical gas sensor based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanotube membrane. Talanta 2010, 82, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Chen, W.; Shen, W.; Peng, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Song, W.; Tan, R. Enhanced flexible room temperature ammonia sensor based on PEDOT: PSS thin film with FeCl3 additives prepared by inkjet printing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, C.; Choi, M.S.; Mirzaei, A.; Im, S.S.; Ahn, H.; Kim, H.W. Sonochemical synthesis of PEDOT:PSS intercalated ammonium vanadate nanofiber composite for room-temperature NH3 sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Yue, F.; Liu, S.; Jing, C.; Cheng, Y.; et al. A flexible polypyrrole/silk-fiber ammonia sensor assisted by silica nanosphere template. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 317, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Oh, J.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, W.; Jang, J. Wireless, Room Temperature Volatile Organic Compound Sensor Based on Polypyrrole Nanoparticle Immobilized Ultrahigh Frequency Radio Frequency Identification Tag. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33139–33147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, A.; Lee, N.-E. Recent Advancements in Development of Wearable Gas Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, I.; Tessarolo, M.; Mariani, F.; Cramer, T.; Tonelli, D.; Scavetta, E.; Fraboni, B. Nanoparticle gated semiconducting polymer for a new generation of electrochemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2018, 273, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, F.; Gualandi, I.; Tonelli, D.; Decataldo, F.; Possanzini, L.; Fraboni, B.; Scavetta, E. Design of an electrochemically gated organic semiconductor for pH sensing. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 116, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possanzini, L.; Decataldo, F.; Mariani, F.; Gualandi, I.; Tessarolo, M.; Scavetta, E.; Fraboni, B. Textile sensors platform for the selective and simultaneous detection of chloride ion and pH in sweat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, F.; Serafini, M.; Gualandi, I.; Arcangeli, D.; Decataldo, F.; Possanzini, L.; Tessarolo, M.; Tonelli, D.; Fraboni, B.; Scavetta, E. Advanced Wound Dressing for Real-Time pH Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majder-Łopatka, M.; Węsierski, T.; Dmochowska, A.; Salamonowicz, Z.; Polańczyk, A. The Influence of Hydrogen on the Indications of the Electrochemical Carbon Monoxide Sensors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decataldo, F.; Gualandi, I.; Tessarolo, M.; Scavetta, E.; Fraboni, B. Transient-doped organic electrochemical transistors working in current-enhancing mode as sensing devices for low concentration of oxygen dissolved in solution. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 91103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschner, A.; Kirchmeyer, S.; Lövenich, W.; Merker, U.; Reuter, K. PEDOT: Principles and Applications of an Intrinsically Conductive Polymer; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, G. Boric Acid in Kjeldahl Analysis. J. Chem. Educ. 2013, 90, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoni, E.; Tschon, M.; Palazzo, B.; Nitti, P.; Martini, L.; Rimondini, L. Agarose Gel as Biomaterial or Scaffold for Implantation Surgery: Characterization, Histological and Histomorphometric Study on Soft Tissue Response. Connect. Tissue Res. 2012, 53, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, A.; Borzacchiello, R.; Netti, P.A. Pore structure and swelling behavior of porous hydrogels prepared via a thermal reverse-casting technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.-R.; Gui, X.; Xie, X.; Tao, K.; Shen, Y.; et al. An intrinsically stretchable humidity sensor based on anti-drying, self-healing and transparent organohydrogels. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Han, S.; Yang, B.-R.; Gui, X.; Tao, K.; Liu, C.; Miao, J.; Norford, L.K. Extremely Deformable, Transparent, and High-Performance Gas Sensor Based on Ionic Conductive Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, K.; Gao, H.; Wu, H.; Cao, S.; Huang, L.; Ni, Y. Anti-freezing and moisturizing conductive hydrogels for strain sensing and moist-electric generation applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Corral, J.; Mitrani, H.; Dade-Robertson, M.; Zhang, M.; Maiello, P. Agarose gel as a soil analogue for development of advanced bio-mediated soil improvement methods. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.; Xiong, J.-Y.; Liu, X.-Y. Determination of agarose gel pore size: Absorbance measurements vis a vis other techniques. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 28, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuvikene, R.; Truus, K.; Kollist, A.; Volobujeva, O.; Mellikov, E.; Pehk, T. Gel-forming structures and stages of red algal galactans of different sulfation levels. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 20, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armisen, R.; Galatas, F. Production, properties and uses of agar. In Production and Utilization of Products from Commercial Seaweeds; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1987; Volume 288, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Park, H.; Yun, J.Y.; Jin, S.W.; Sun, L.; Zi, G.; Ha, J.S. Polyurethane foam coated with a multi-walled carbon nanotube/polyaniline nanocomposite for a skin-like stretchable array of multi-functional sensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Flexible and conductive nanofiber-structured single yarn sensor for smart wearable devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, M.; Lv, Z.; Wan, P. Stretchable Electronic Sensors of Nanocomposite Network Films for Ultrasensitive Chemical Vapor Sensing. Small 2017, 13, 1701697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhou, C.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, H.; Duan, X. A Fully Integrated Wireless Flexible Ammonia Sensor Fabricated by Soft Nano-Lithography. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, P.; Cheng, W.; Yan, K.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Highly Sensitive, Printable Nanostructured Conductive Polymer Wireless Sensor for Food Spoilage Detection. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4570–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Zhuo, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, X. Flexible Ammonia Sensor Based on PEDOT:PSS/Silver Nanowire Composite Film for Meat Freshness Monitoring. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serafini, M.; Mariani, F.; Gualandi, I.; Decataldo, F.; Possanzini, L.; Tessarolo, M.; Fraboni, B.; Tonelli, D.; Scavetta, E. A Wearable Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Ammonia Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21237905
Serafini M, Mariani F, Gualandi I, Decataldo F, Possanzini L, Tessarolo M, Fraboni B, Tonelli D, Scavetta E. A Wearable Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Ammonia Detection. Sensors. 2021; 21(23):7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21237905
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerafini, Martina, Federica Mariani, Isacco Gualandi, Francesco Decataldo, Luca Possanzini, Marta Tessarolo, Beatrice Fraboni, Domenica Tonelli, and Erika Scavetta. 2021. "A Wearable Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Ammonia Detection" Sensors 21, no. 23: 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21237905
APA StyleSerafini, M., Mariani, F., Gualandi, I., Decataldo, F., Possanzini, L., Tessarolo, M., Fraboni, B., Tonelli, D., & Scavetta, E. (2021). A Wearable Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Ammonia Detection. Sensors, 21(23), 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21237905