Pharmacological Modulation of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparative Evaluation of Binding Affinities and Functional Activities of BK Analogs at Human B2R
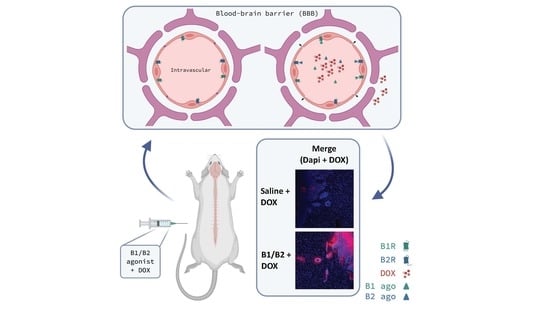
2.2. Effects of Kinin B1 and B2 Agonist Analogs on DOX Delivery to Tumor in F98 Glioma-Bearing Rats
2.3. Effects of Kinin B2R Agonist Analog NG291 on the BBB Permeability in Normal Condition
2.4. Effects of Acute Administration of the Kinin B2 Agonist Analog NG291 on Brain Metastases
2.5. Effects of Kinin B2 Agonist Analog NG291 on BBB Permeability in the Irradiated Mouse Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Kinin Peptide Analogs
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Generation of Stable Human Kinin B2R-HEK 293 Cell Line
4.4. Radioligand Binding Assays
4.5. IP-One Accumulation Assays
4.6. Animal Studies
4.6.1. F98 Syngeneic Rat Model of Glioblastoma
4.6.2. Doxorubicin Delivery in Rat Brain
4.6.3. Cranial Window Surgery
4.6.4. Intravital Fluorescence Microscopy
4.6.5. T1 Syngeneic Mouse Model of Brain Metastasis
4.6.6. Mouse Model of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury
Preparation of MPIOs
In Vivo MRI Acquisitions and Image Analysis
Histological Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: Bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, K.L.; Ningaraj, N.S. Modulation of brain tumor capillaries for enhanced drug delivery selectively to brain tumor. Cancer Control. 2004, 11, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuwelt, E.; Abbott, N.J.; Abrey, L.; Banks, W.A.; Blakley, B.; Davis, T.; Engelhardt, B.; Grammas, P.; Nedergaard, M.; Nutt, J. Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. The targeted delivery of cancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier: Chemical modifications of drugs or drug-nanoparticles? Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laquintana, V.; Trapani, A.; Denora, N.; Wang, F.; Gallo, J.M.; Trapani, G. New strategies to deliver anticancer drugs to brain tumors. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavance, M.A.; Blanchette, M.; Fortin, D. Recent advances in blood-brain barrier disruption as a CNS delivery strategy. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drapeau, A.; Fortin, D. Chemotherapy Delivery Strategies to the Central Nervous System: Neither Optional nor Superfluous. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, D. Drug Delivery Technology to the CNS in the Treatment of Brain Tumors: The Sherbrooke Experience. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muldoon, L.L.; Soussain, C.; Jahnke, K.; Johanson, C.; Siegal, T.; Smith, Q.R.; Hall, W.A.; Hynynen, K.; Senter, P.D.; Peereboom, D.M.; et al. Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: A reality check. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, H. Research spotlight: Emergence of EPR effect theory and development of clinical applications for cancer therapy. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.; Mane, S. EPR effect: Promising approach for tumor targeted drug delivery. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 2, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Islam, W.; Maeda, H. Exploiting the dynamics of the EPR effect and strategies to improve the therapeutic effects of nanomedicines by using EPR effect enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerich, D.F.; Dean, R.L.; Osborn, C.; Bartus, R.T. The development of the bradykinin agonist labradimil as a means to increase the permeability of the blood-brain barrier: From concept to clinical evaluation. Clin. Pharm. 2001, 40, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados, M.D.; Schold, S.C.; Fine, H.A.; Jaeckle, K.; Hochberg, F.; Mechtler, L.; Fetell, M.R.; Phuphanich, S.; Feun, L.; Janus, T.J.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of RMP-7 in combination with carboplatin administered intravenously for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro. Oncol. 2003, 5, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.; Jakacki, R.; Widemann, B.; Aikin, A.; Libucha, M.; Packer, R.; Vezina, G.; Reaman, G.; Shaw, D.; Krailo, M.; et al. Phase II trial of intravenous lobradimil and carboplatin in childhood brain tumors: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Black, K.L.; Gobin, Y.P.; Farahani, K.; Nelson, G.; Villablanca, P.; Kabbinavar, F.; Viñeula, F.; Wortel, C.H. Intra-arterial Cereport (RMP-7) and carboplatin: A dose escalation study for recurrent malignant gliomas. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 270–278; discussion 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Krailo, M.; Mehta, M.; Warren, K.; Allen, J.; Jakacki, R.; Villablanca, J.G.; Chiba, A.; Reaman, G. A Phase I study of concurrent RMP-7 and carboplatin with radiation therapy for children with newly diagnosed brainstem gliomas. Cancer 2005, 104, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Neugebauer, W.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood-brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Bovenzi, V.; Savard, M.; Dubuc, C.; Fortier, A.; Neugebauer, W.; Tremblay, L.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Tsanaclis, A.M.; Lepage, M.; et al. Induction of selective blood-tumor barrier permeability and macromolecular transport by a biostable kinin B1 receptor agonist in a glioma rat model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Dubuc, C.; Tremblay, L.; Tsanaclis, A.M.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Selective tumor blood-brain barrier opening with the kinin B2 receptor agonist [Phe(8)psi(CH(2)NH)Arg(9)]-BK in a F98 glioma rat model: An MRI study. Neuropeptides 2010, 44, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.I.; Kang, W.; Davy, P.M.; Shi, Y.; Sun, S.; Allsopp, R.C.; Lu, Y. Monocyte Trafficking, Engraftment, and Delivery of Nanoparticles and an Exogenous Gene into the Acutely Inflamed Brain Tissue—Evaluations on Monocyte-Based Delivery System for the Central Nervous System. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.W.Y.; Viswanathan, S. Recent progress on developing exogenous monocyte/macrophage-based therapies for inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, F.; Farooq, R.K.; Ahmed, N. Monocyte as an Emerging Tool for Targeted Drug Delivery: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 5296–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Luo, H.; Zeng, L.; Ye, L.; Lu, Y. Quantitative evaluation of monocyte transmigration into the brain following chemical opening of the blood-brain barrier in mice. Brain Res. 2006, 1098, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bélanger, S.; Bovenzi, V.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Amblard, M.; Martinez, J.; Lammek, B.; Savard, M.; Gobeil, F. Structure-activity relationships of novel peptide agonists of the human bradykinin B2 receptor. Peptides 2009, 30, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, M.; Labonté, J.; Dubuc, C.; Neugebauer, W.; D’Orléans-Juste, P.; Gobeil, F. Further pharmacological evaluation of a novel synthetic peptide bradykinin B2 receptor agonist. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, L.; Waeckel, L.; Vincent, M.P.; Chollet, C.; Gobeil, F.; Marre, M.; Bruneval, P.; Richer, C.; Roussel, R.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; et al. Selective kinin receptor agonists as cardioprotective agents in myocardial ischemia and diabetes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desposito, D.; Potier, L.; Chollet, C.; Gobeil, F.; Roussel, R.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Bouby, N.; Waeckel, L. Kinin receptor agonism restores hindlimb postischemic neovascularization capacity in diabetic mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marketou, M.; Kintsurashvili, E.; Papanicolaou, K.N.; Lucero, H.A.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Cardioprotective effects of a selective B(2) receptor agonist of bradykinin post-acute myocardial infarct. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawolak, M.T.; Gera, L.; Morissette, G.; Stewart, J.M.; Marceau, F. B-9972 (D-Arg-[Hyp3,Igl5,Oic7,Igl8]-bradykinin) is an inactivation-resistant agonist of the bradykinin B2 receptor derived from the peptide antagonist B-9430 (D-Arg-[Hyp3,Igl5,D-Igl7,Oic8]-bradykinin): Pharmacologic profile and effective induction of receptor degradation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, B.; Wang, R.; Xie, Z.; Ruan, H.; Li, J.; Xie, C.; Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, M. Effect of Retro-Inverso Isomer of Bradykinin on Size-Dependent Penetration of Blood-Brain Tumor Barrier. Small 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Shen, Q.; Xie, C.; Lu, W.; Peng, C.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Su, B.; Gao, C.; Liu, M. Retro-inverso bradykinin opens the door of blood-brain tumor barrier for nanocarriers in glioma treatment. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Zhang, Y.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Jolesz, F.A.; McDannold, N.J. The kinetics of blood brain barrier permeability and targeted doxorubicin delivery into brain induced by focused ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, K.K. A Critical Overview of Targeted Therapies for Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Fang, M.; Alroy, J.; Sahagian, G.G. Imagable 4T1 model for the study of late stage breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorger, M.; Felding-Habermann, B. Capturing changes in the brain microenvironment during initial steps of breast cancer brain metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2958–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, F.M.; Minafra, L.; Forte, G.I.; Cammarata, F.P.; Lio, D.; Messa, C.; Gilardi, M.C.; Bravatà, V. Portrait of inflammatory response to ionizing radiation treatment. J. Inflamm. 2015, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marceau, F.; Hess, J.F.; Bachvarov, D.R. The B1 receptors for kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1998, 50, 357–386. [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westphal, M.; Maire, C.L.; Lamszus, K. EGFR as a Target for Glioblastoma Treatment: An Unfulfilled Promise. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulason, K.O.; Schneider, J.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Filippi, C.G.; Pramanik, B.; Wong, T.; Fralin, S.; Tan, K.; Ray, A.; Alter, R.A.; et al. Superselective intraarterial cerebral infusion of cetuximab with blood brain barrier disruption combined with Stupp Protocol for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2018, 12, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hou, X.; Ye, L.; Lou, J. The effect of RMP-7 and its derivative on transporting Evans blue liposomes into the brain. Drug Deliv. 2004, 11, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, C.L. Methylmethacrylate-sulfopropylmethacrylate nanoparticles with surface RMP-7 for targeting delivery of antiretroviral drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Tsao, C.W. Neuroprotection against apoptosis of SK-N-MC cells using RMP-7- and lactoferrin-grafted liposomes carrying quercetin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2857–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanovich, E.; Bartus, R.T.; Friden, P.M.; Dean, R.L.; Le, H.Q.; Brightman, M.W. Pathway across blood-brain barrier opened by the bradykinin agonist, RMP-7. Brain Res. 1995, 705, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Xue, Y.X.; Liu, Y.H. Bradykinin increases the permeability of the blood-tumor barrier by the caveolae-mediated transcellular pathway. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningaraj, N.S.; Rao, M.; Hashizume, K.; Asotra, K.; Black, K.L. Regulation of blood-brain tumor barrier permeability by calcium-activated potassium channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raidoo, D.M.; Sawant, S.; Mahabeer, R.; Bhoola, K.D. Kinin receptors are expressed in human astrocytic tumour cells. Immunopharmacology 1999, 43, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, N.F.; Sénécal, J.; da Silva, V.D.; Roxo, M.R.; Ferreira, N.P.; de Morais, R.L.T.; Pesquero, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Couture, R.; Morrone, F.B. Primary Role for Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors in Glioma Proliferation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7869–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Leung, Y.M.; Huang, S.M.; Wong, K.L. Bradykinin-induced cell migration and COX-2 production mediated by the bradykinin B1 receptor in glioma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2010, 110, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, V.; Sontheimer, H. Bradykinin promotes the chemotactic invasion of primary brain tumors. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4858–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hsu, J.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Lai, S.W.; Huang, B.R.; Tsai, C.F.; Lu, D.Y. Bradykinin B1 receptor contributes to interleukin-8 production and glioblastoma migration through interaction of STAT3 and SP-1. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inda, M.M.; Bonavia, R.; Seoane, J. Glioblastoma multiforme: A look inside its heterogeneous nature. Cancers 2014, 6, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortin, D.; Desjardins, A.; Benko, A.; Niyonsega, T.; Boudrias, M. Enhanced chemotherapy delivery by intraarterial infusion and blood-brain barrier disruption in malignant brain tumors: The Sherbrooke experience. Cancer 2005, 103, 2606–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D.; Morin, P.A.; Belzile, F.; Mathieu, D.; Paré, F.M. Intra-arterial carboplatin as a salvage strategy in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 119, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, R.S.; Khatri, D.; Reichman, N.; Patel, N.V.; Wong, T.; Fralin, S.R.; Li, M.; Ellis, J.A.; Ortiz, R.; Langer, D.J.; et al. Super selective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of modern chemotherapeutics after blood-brain barrier disruption: Where are we now, and where we are going. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, S.; Briganti, G.; Mancuso, M.; Saran, A. Neurocognitive Decline Following Radiotherapy: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2020, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fike, J.R.; Gobbel, G.T.; Mesiwala, A.H.; Shin, H.J.; Nakagawa, M.; Lamborn, K.R.; Seilhan, T.M.; Elliott, P.J. Cerebrovascular effects of the bradykinin analog RMP-7 in normal and irradiated dog brain. J. Neurooncol. 1998, 37, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabold, R.; Erös, C.; Zweckberger, K.; Relton, J.; Beck, H.; Nussberger, J.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Bader, M.; Whalley, E.; Plesnila, N. The role of bradykinin B(1) and B(2) receptors for secondary brain damage after traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suh, J.H.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E.L. Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikpa, D.; Whittingstall, L.; Fouquet, J.P.; Radulska, A.; Tremblay, L.; Lebel, R.; Paquette, B.; Lepage, M. Cerebrovascular inflammation promotes the formation of brain metastases. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.; Benoit, P.; David, M. Applications of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Experimental Investigations in Small Animal Models. In Gamma Knife Radiosurgery; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karger, C.P.; Münter, M.W.; Heiland, S.; Peschke, P.; Debus, J.; Hartmann, G.H. Dose-response curves and tolerance doses for late functional changes in the normal rat brain after stereotactic radiosurgery evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging: Influence of end points and follow-up time. Radiat Res. 2002, 157, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAteer, M.A.; Sibson, N.R.; von Zur Muhlen, C.; Schneider, J.E.; Lowe, A.S.; Warrick, N.; Channon, K.M.; Anthony, D.C.; Choudhury, R.P. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of acute brain inflammation using microparticles of iron oxide. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girard, S.; Kadhim, H.; Larouche, A.; Roy, M.; Gobeil, F.; Sébire, G. Pro-inflammatory disequilibrium of the IL-1 beta/IL-1ra ratio in an experimental model of perinatal brain damages induced by lipopolysaccharide and hypoxia-ischemia. Cytokine 2008, 43, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, C.D.; Chacόn, C.; Corthorn, J.; Ehrenfeld, P.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Valdés, G. Temporospatial Changes of Kinin B2 Receptors During the Estrous Cycle and Pregnancy in the Rat Uterus1. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 64, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savard, M.; Barbaz, D.; Bélanger, S.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Bkaily, G.; D’orléans-Juste, P.; Coté, J.; Bovenzi, V.; Gobeil, F. Expression of endogenous nuclear bradykinin B2 receptors mediating signaling in immediate early gene activation. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 216, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, C.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Lessard, A.; Fortier, A.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Rizzolio, F.; Geha, S.; Giordano, A.; et al. Targeting intracellular B2 receptors using novel cell-penetrating antagonists to arrest growth and induce apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9885–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- abu Alla, S.; Quitterer, U.; Grigoriev, S.; Maidhof, A.; Haasemann, M.; Jarnagin, K.; Müller-Esterl, W. Extracellular domains of the bradykinin B2 receptor involved in ligand binding and agonist sensing defined by anti-peptide antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Sequence (Codename) | Theoretical m.w. | Observed m.w | Purity (%) | Binding (IC50; nM) | IP1 Assays (EC50; nM) | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-Arg1-Pro2-Pro3-Gly4-Phe5-Ser6-Pro7-Phe8-Arg9-OH (BK) | 1060.2 | 1060.4 | 99.0 | 4 | 0.3 | - |
| [Hyp3, Thi5, NChg7, Thi8]-BK (NG291) | 1130.4 | 1130.5 | 100 | 3 | 0.9 | [25] |
| [Hyp3, Thi5, (4Me)Tyr8(ΨCH2NH)Arg9]-BK (Labradimil) | 1098.3 | 1098.3 | 99.8 | 17 | 47 | [13] |
| dArg[Hyp3, Igl5, Oic7, Igl8]-BK (B9972) | 1338.6 | 1339.4 | 99.3 | 199 | 158 | [30] |
| d(retroinverso)-BK (RI-BK) | 1060.2 | 1061.8 | 95.2 | >10,000 | >10,000 | [31,32] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sikpa, D.; Whittingstall, L.; Savard, M.; Lebel, R.; Côté, J.; McManus, S.; Chemtob, S.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Pharmacological Modulation of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100279
Sikpa D, Whittingstall L, Savard M, Lebel R, Côté J, McManus S, Chemtob S, Fortin D, Lepage M, Gobeil F. Pharmacological Modulation of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(10):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100279
Chicago/Turabian StyleSikpa, Dina, Lisa Whittingstall, Martin Savard, Réjean Lebel, Jérôme Côté, Stephen McManus, Sylvain Chemtob, David Fortin, Martin Lepage, and Fernand Gobeil. 2020. "Pharmacological Modulation of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 10: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100279
APA StyleSikpa, D., Whittingstall, L., Savard, M., Lebel, R., Côté, J., McManus, S., Chemtob, S., Fortin, D., Lepage, M., & Gobeil, F. (2020). Pharmacological Modulation of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability by Kinin Analogs in Normal and Pathologic Conditions. Pharmaceuticals, 13(10), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100279