Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-Adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
Abstract
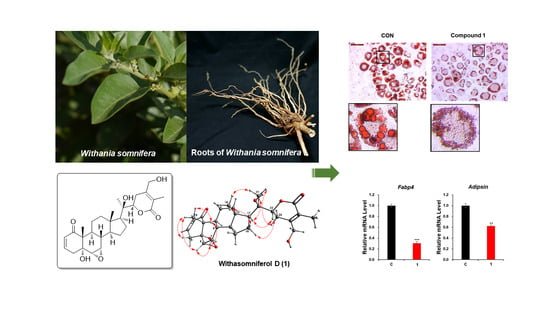
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of Compound 1
2.2. Structural Elucidation of Compound 1
2.3. Evaluation of the Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Compound 1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedure and Plant Material
3.2. Extraction and Separation/Isolation
3.3. Computational Analyses
3.4. Cell Culture and Differentiation
3.5. Cell Viability
3.6. Oil Red O Staining
3.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayaprakasam, B.; Zhang, Y.; Seeram, N.P.; Nair, M.G. Growth inhibition of human tumor cell lines by withanolides from Withania somnifera leaves. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, B.; Kumar, N.; Ahmad, A.H.; Rastogi, S.K. Influence of phytochemical composition on in vitro antioxidant and reducing activities of Indian ginseng [Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal] root extracts. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Yousuf, S.; Nawaz, S.A.; Ahmed, S.; Atta, R. Cholinesterase inhibiting withanolides from Withania somnifera. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mary, N.K.; Babu, B.H.; Padikkala, J. Antiatherogenic effect of Caps HT2, a herbal Ayurvedic medicine formulation. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-ur-Rahman, Y.M.; Gul, W.; Qureshi, S.; Choudhary, M.I.; Voelter, W.; Hoff, A.; Jens, F.; Naz, A. Cholinesterase inhibiting Withanolides from Withania somnifera. Heterocycles 1998, 48, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.K.; Satyan, K.S.; Chakrabarti, A. Effect of Trasina, an Ayurvedic herbal formulation, on pancreatic islet superoxide dismutase activity in hyperglycaemic rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 35, 297–299. [Google Scholar]
- Dhuley, J.N. Effect of ashwagandha on lipid peroxidation in stress-induced animals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 60, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Ramanathan, M.; Ghosal, S.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Effect of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides on iron-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzera, M.; Choudhary, M.I.; Khan, I.A. Quantitative HPLC analysis of withanolides in Withania somnifera. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsakka, M.; Grigorescu, E.; Stanescu, U.; Stanescu, U.; Dorneanu, V. New data referring to chemistry of Withania somnifera species. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 1990, 94, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Murakami, T.; Kishi, A.; Yoshikawa, M. Structures of withanosides I, II, III, IV, V, VI and VII new withanolide glycosides from the roots of Indian Withania somnifera D and inhibitory activity for tachyphylaxis to clonidine in isolated guineapig ileum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 96, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.B.; Gupta, M. Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Herz, W., Grisebach, H., Kirby, G.W., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Vienna, Austria, 1994; Volume 63, pp. 1–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, W.-N.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Lin, R.; Shan, S.-M.; Zhu, M.-D.; Luo, J.-G.; Kong, L.-Y. Cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulate var. villosa and the apoptosis-inducing effect via ROS generation and the activation of MAPK in human osteosarcoma cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53089–53100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Cytotoxicity and Immunosuppressive Activity of Withanoliedes from Discopodiumpenninervium. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhiraja, R.D.; Sudhir, S.; Garg, K.N. Antiinflmmatory Activity of 3 β-Hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-withanolide F. Planta Med. 1984, 50, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, S.K.; De Barun, K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Variations in the antitumor constituents of Withania somnifera dunal. Experientia 1974, 30, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareggiani, G.; Picollo, M.I.; Zerba, E.; Burton, G.; Tettamanzi, M.C.; Benedetti-Doctorovich, M.O.V.; Veleiro, A.S. Antifeedant Activity of Withanolides from Salpichroa origanifolia on Musca domestica. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, A.V.; Leiva Gonzalez, S.; Barboza, G.E.; Careaga, V.P.; Calvo, J.C.; Sacca, P.A.; Nicotra, V.E. Phytochemical Study of the Genus Salpichroa (Solanaceae), Chemotaxonomic Considerations, and Biological Evaluation in Prostate and Breast Cancer Cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, C.-M.; Gallagher, R.J.; Timmermann, B.N. Antiproliferative withanolides from several solanaceous spicies. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, L.; Kuttan, G. Immunomodulatory activity of Withania somnifera. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 71, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Yi, S.A.; Beemelmanns, C.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, K.H. Anti-Adipogenic Pregnane Steroid from a Hydractinia-Associated Fungus, Cladosporium sphaerospermum SW67. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Ryoo, R.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Trichothecene and tremulane sesquiterpenes from a hallucinogenic mushroom Gymnopilus junonius and their cytotoxicity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.A.; Park, E.J.; Lee, D.; Song, J.H.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S.; Yoo, J.E. Estrogenic Activity of Sanguiin H-6 through Activation of Estrogen Receptor α Coactivator-Binding Site. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Li, C.; Kwon, M.; Oh, T.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Ko, S.K.; Kim, C.S.; Cao, S.; et al. Herqueilenone A, a unique rearranged benzoquinone-chromanone from the hawaiian volcanic soil-associated fungal strain Penicillium herquei FT729. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H. Cytotoxic withanolides from the roots of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera). J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Jo, M.S.; Yu, J.S.; Ko, Y.J.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, K.H. Withaninsams A and B: Phenylpropanoid esters from the roots of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera). Plants 2019, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Shibata, K.; Umehara, K. Cell differentiation inducing steroids from Withania somnifera L.(Dun.). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1646–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.M.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Brooks, A.D.; Tewary, P.; Xuan, L.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Sayers, T.J.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Cytotoxic and other withanolides from aeroponically grown Physalis philadelphica. Phytochemistry 2018, 152, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, U.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose tissue regulates insulin sensitivity: Role of adipogenesis, de novo lipogenesis and novel lipids. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.; Seo, Y.J.; Song, J.H.; Chei, S.; Lee, B.Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes browning by inducing UCP1 expression and mito-chondrial activity in 3T3-L1 and subcutaneous white adipocytes. J. Ginseng. Res. 2019, 43, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Rayalam, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Ambati, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Baile, C.A. Withaferin A induces apoptosis and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biofactors 2008, 33, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.A.; Lee, J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Kim, S.; et al. Fermented ginseng extract, BST204, disturbs adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through inhibition of S6 kinase 1 signaling. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) (
) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) (  ) correlations for 1.
) correlations for 1.
 ) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) (
) and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) (  ) correlations for 1.
) correlations for 1.



| Position | 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | 203.3 s | |
| 2 | 5.85 dd (10.0, 2.0 | 128.8 d |
| 3 | 6.59 ddd (10.0, 5.0, 2.0) | 139.5 d |
| 4α | 2.53 dd (19.0, 5.0) | 36.5 t |
| 4β | 2.68 br d (19.0) | |
| 5 | 73.2 s | |
| 6 | 3.05 d (4.0) | 55.8 d |
| 7 | 3.32 m | 56.7 d |
| 8 | 1.78 m | 34.9 d |
| 9 | 1.56 m | 35.4 d |
| 10 | 50.8 s | |
| 11α | 2.74 m | 21.4 t |
| 11β | 1.35 m | |
| 12α | 1.37 m | 40.2 t |
| 12β | 2.08 m | |
| 13 | 43.7 s | |
| 14 | 1.43 m | 51.8 d |
| 15α | 1.85 m | 22.8 t |
| 15β | 1.37 m | |
| 16α | 1.58 m | 21.6 t |
| 16β | 2.03 m | |
| 17 | 1.54 m | 54.1 d |
| 18 | 0.96 s | 13.6 q |
| 19 | 1.18 s | 14.5 q |
| 20 | 75.1 s | |
| 21 | 1.34 s | 20.9 q |
| 22 | 4.22 dd (13.5, 4.0) | 81.8 d |
| 23α | 2.29 m | 25.7 t |
| 23β | 2.60 m | |
| 24 | 150.1 s | |
| 25 | 122.2 s | |
| 26 | 166.0 s | |
| 27 | 1.89 s | 11.8 q |
| 28a | 4.35 d (14.0) | 61.2 t |
| 28b | 4.48 d (14.0) | |
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | 5′-ACGGCCAGGTCATCACTATTG-3′ | 5′-TGGATGCCACAGGATTCCA-3′ |
| Adipsin | 5′-CATGCTCGGCCCTACATG-3′ | 5′-CACAGAGTCGTCATCCGTCAC-3′ |
| Fabp4 | 5′-AAGGTGAAGAGCATCATAACCCT-3′ | 5′-TCACGCCTTTCATAACACATTCC-3′ |
| SREBP1 | 5′-AACGTCACTTCCAGCTAGAC-3′ | 5′-CCACTAAGGTGCCTACAGAGC-3′ |
| ATGL | 5′-TTCACCATCCGCTTGTTGGAG-3′ | 5′-AGATGGTCACCCAATTTCCTC-3′ |
| HSL | 5′-CACAAAGGCTGCTTCTACGG-3′ | 5′-GGAGAGAGTCTGCAGGAACG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.; Yu, J.S.; Kim, J.-C.; Jang, T.S.; Pang, C.; Kim, K.H. Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-Adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101017
Lee BS, Yoo MJ, Kang H, Lee SR, Kim S, Yu JS, Kim J-C, Jang TS, Pang C, Kim KH. Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-Adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(10):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Bum Soo, Min Jeong Yoo, Heesun Kang, Seoung Rak Lee, Sil Kim, Jae Sik Yu, Jin-Chul Kim, Tae Su Jang, Changhyun Pang, and Ki Hyun Kim. 2021. "Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-Adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 10: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101017
APA StyleLee, B. S., Yoo, M. J., Kang, H., Lee, S. R., Kim, S., Yu, J. S., Kim, J. -C., Jang, T. S., Pang, C., & Kim, K. H. (2021). Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-Adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Pharmaceuticals, 14(10), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101017